728x90
우분투에서 Squid 및 Webmin을 설치하는 방법
테스트 환경
$ lsb_release -d
Description: Ubuntu 22.04.2 LTSSquid 설치
sudo apt-get updatesudo apt-get install -y squidvim /etc/squid/squid.confcat /etc/squid/squid.conf | egrep -v '^$|^#'$ cat /etc/squid/squid.conf | egrep -v '^$|^#'
acl localnet src 0.0.0.1-0.255.255.255 # RFC 1122 "this" network (LAN)
acl localnet src 10.0.0.0/8 # RFC 1918 local private network (LAN)
acl localnet src 100.64.0.0/10 # RFC 6598 shared address space (CGN)
acl localnet src 169.254.0.0/16 # RFC 3927 link-local (directly plugged) machines
acl localnet src 172.16.0.0/12 # RFC 1918 local private network (LAN)
acl localnet src 192.168.0.0/16 # RFC 1918 local private network (LAN)
acl localnet src fc00::/7 # RFC 4193 local private network range
acl localnet src fe80::/10 # RFC 4291 link-local (directly plugged) machines
acl SSL_ports port 443
acl Safe_ports port 80 # http
acl Safe_ports port 21 # ftp
acl Safe_ports port 443 # https
acl Safe_ports port 70 # gopher
acl Safe_ports port 210 # wais
acl Safe_ports port 1025-65535 # unregistered ports
acl Safe_ports port 280 # http-mgmt
acl Safe_ports port 488 # gss-http
acl Safe_ports port 591 # filemaker
acl Safe_ports port 777 # multiling http
http_access deny !Safe_ports
http_access deny CONNECT !SSL_ports
http_access allow localhost manager
http_access deny manager
include /etc/squid/conf.d/*.conf
http_access allow localhost
http_access deny all
http_port 3128
coredump_dir /var/spool/squid
refresh_pattern ^ftp: 1440 20% 10080
refresh_pattern ^gopher: 1440 0% 1440
refresh_pattern -i (/cgi-bin/|\?) 0 0% 0
refresh_pattern \/(Packages|Sources)(|\.bz2|\.gz|\.xz)$ 0 0% 0 refresh-ims
refresh_pattern \/Release(|\.gpg)$ 0 0% 0 refresh-ims
refresh_pattern \/InRelease$ 0 0% 0 refresh-ims
refresh_pattern \/(Translation-.*)(|\.bz2|\.gz|\.xz)$ 0 0% 0 refresh-ims
refresh_pattern . 0 20% 4320squid.conf
더보기
vim squid.conf# WELCOME TO SQUID 5.2
# ----------------------------
#
# This is the documentation for the Squid configuration file.
# This documentation can also be found online at:
# http://www.squid-cache.org/Doc/config/
#
# You may wish to look at the Squid home page and wiki for the
# FAQ and other documentation:
# http://www.squid-cache.org/
# http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq
# http://wiki.squid-cache.org/ConfigExamples
#
# This documentation shows what the defaults for various directives
# happen to be. If you don't need to change the default, you should
# leave the line out of your squid.conf in most cases.
#
# In some cases "none" refers to no default setting at all,
# while in other cases it refers to the value of the option
# - the comments for that keyword indicate if this is the case.
#
# Configuration options can be included using the "include" directive.
# Include takes a list of files to include. Quoting and wildcards are
# supported.
#
# For example,
#
# include /path/to/included/file/squid.acl.config
#
# Includes can be nested up to a hard-coded depth of 16 levels.
# This arbitrary restriction is to prevent recursive include references
# from causing Squid entering an infinite loop whilst trying to load
# configuration files.
#
# Values with byte units
#
# Squid accepts size units on some size related directives. All
# such directives are documented with a default value displaying
# a unit.
#
# Units accepted by Squid are:
# bytes - byte
# KB - Kilobyte (1024 bytes)
# MB - Megabyte
# GB - Gigabyte
#
# Values with time units
#
# Time-related directives marked with either "time-units" or
# "time-units-small" accept a time unit. The supported time units are:
#
# nanosecond (time-units-small only)
# microsecond (time-units-small only)
# millisecond
# second
# minute
# hour
# day
# week
# fortnight
# month - 30 days
# year - 31557790080 milliseconds (just over 365 days)
# decade
#
# Values with spaces, quotes, and other special characters
#
# Squid supports directive parameters with spaces, quotes, and other
# special characters. Surround such parameters with "double quotes". Use
# the configuration_includes_quoted_values directive to enable or
# disable that support.
#
# Squid supports reading configuration option parameters from external
# files using the syntax:
# parameters("/path/filename")
# For example:
# acl allowlist dstdomain parameters("/etc/squid/allowlist.txt")
#
# Conditional configuration
#
# If-statements can be used to make configuration directives
# depend on conditions:
#
# if <CONDITION>
# ... regular configuration directives ...
# [else
# ... regular configuration directives ...]
# endif
#
# The else part is optional. The keywords "if", "else", and "endif"
# must be typed on their own lines, as if they were regular
# configuration directives.
#
# NOTE: An else-if condition is not supported.
#
# These individual conditions types are supported:
#
# true
# Always evaluates to true.
# false
# Always evaluates to false.
# <integer> = <integer>
# Equality comparison of two integer numbers.
#
#
# SMP-Related Macros
#
# The following SMP-related preprocessor macros can be used.
#
# ${process_name} expands to the current Squid process "name"
# (e.g., squid1, squid2, or cache1).
#
# ${process_number} expands to the current Squid process
# identifier, which is an integer number (e.g., 1, 2, 3) unique
# across all Squid processes of the current service instance.
#
# ${service_name} expands into the current Squid service instance
# name identifier which is provided by -n on the command line.
#
# Logformat Macros
#
# Logformat macros can be used in many places outside of the logformat
# directive. In theory, all of the logformat codes can be used as %macros,
# where they are supported. In practice, a %macro expands as a dash (-) when
# the transaction does not yet have enough information and a value is needed.
#
# There is no definitive list of what tokens are available at the various
# stages of the transaction.
#
# And some information may already be available to Squid but not yet
# committed where the macro expansion code can access it (report
# such instances!). The macro will be expanded into a single dash
# ('-') in such cases. Not all macros have been tested.
#
# TAG: broken_vary_encoding
# This option is not yet supported by Squid-3.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: cache_vary
# This option is not yet supported by Squid-3.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: error_map
# This option is not yet supported by Squid-3.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: external_refresh_check
# This option is not yet supported by Squid-3.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: location_rewrite_program
# This option is not yet supported by Squid-3.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: refresh_stale_hit
# This option is not yet supported by Squid-3.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: dns_v4_first
# Remove this line. Squid no longer supports preferential treatment of DNS A records.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: cache_peer_domain
# Replace with dstdomain ACLs and cache_peer_access.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: ie_refresh
# Remove this line. The behaviour enabled by this is no longer needed.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: sslproxy_cafile
# Remove this line. Use tls_outgoing_options cafile= instead.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: sslproxy_capath
# Remove this line. Use tls_outgoing_options capath= instead.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: sslproxy_cipher
# Remove this line. Use tls_outgoing_options cipher= instead.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: sslproxy_client_certificate
# Remove this line. Use tls_outgoing_options cert= instead.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: sslproxy_client_key
# Remove this line. Use tls_outgoing_options key= instead.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: sslproxy_flags
# Remove this line. Use tls_outgoing_options flags= instead.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: sslproxy_options
# Remove this line. Use tls_outgoing_options options= instead.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: sslproxy_version
# Remove this line. Use tls_outgoing_options options= instead.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: hierarchy_stoplist
# Remove this line. Use always_direct or cache_peer_access ACLs instead if you need to prevent cache_peer use.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: log_access
# Remove this line. Use acls with access_log directives to control access logging
#Default:
# none
# TAG: log_icap
# Remove this line. Use acls with icap_log directives to control icap logging
#Default:
# none
# TAG: ignore_ims_on_miss
# Remove this line. The HTTP/1.1 feature is now configured by 'cache_miss_revalidate'.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: balance_on_multiple_ip
# Remove this line. Squid performs a 'Happy Eyeballs' algorithm, this multiple-IP algorithm is not longer relevant.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: chunked_request_body_max_size
# Remove this line. Squid is now HTTP/1.1 compliant.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: dns_v4_fallback
# Remove this line. Squid performs a 'Happy Eyeballs' algorithm, the 'fallback' algorithm is no longer relevant.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: emulate_httpd_log
# Replace this with an access_log directive using the format 'common' or 'combined'.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: forward_log
# Use a regular access.log with ACL limiting it to MISS events.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: ftp_list_width
# Remove this line. Configure FTP page display using the CSS controls in errorpages.css instead.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: ignore_expect_100
# Remove this line. The HTTP/1.1 feature is now fully supported by default.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: log_fqdn
# Remove this option from your config. To log FQDN use %>A in the log format.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: log_ip_on_direct
# Remove this option from your config. To log server or peer names use %<A in the log format.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: maximum_single_addr_tries
# Replaced by connect_retries. The behaviour has changed, please read the documentation before altering.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: referer_log
# Replace this with an access_log directive using the format 'referrer'.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: update_headers
# Remove this line. The feature is supported by default in storage types where update is implemented.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: url_rewrite_concurrency
# Remove this line. Set the 'concurrency=' option of url_rewrite_children instead.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: useragent_log
# Replace this with an access_log directive using the format 'useragent'.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: dns_testnames
# Remove this line. DNS is no longer tested on startup.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: extension_methods
# Remove this line. All valid methods for HTTP are accepted by default.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: zero_buffers
#Default:
# none
# TAG: incoming_rate
#Default:
# none
# TAG: server_http11
# Remove this line. HTTP/1.1 is supported by default.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: upgrade_http0.9
# Remove this line. ICY/1.0 streaming protocol is supported by default.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: zph_local
# Alter these entries. Use the qos_flows directive instead.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: header_access
# Since squid-3.0 replace with request_header_access or reply_header_access
# depending on whether you wish to match client requests or server replies.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: httpd_accel_no_pmtu_disc
# Since squid-3.0 use the 'disable-pmtu-discovery' flag on http_port instead.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: wais_relay_host
# Replace this line with 'cache_peer' configuration.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: wais_relay_port
# Replace this line with 'cache_peer' configuration.
#Default:
# none
# OPTIONS FOR SMP
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: workers
# Number of main Squid processes or "workers" to fork and maintain.
# 0: "no daemon" mode, like running "squid -N ..."
# 1: "no SMP" mode, start one main Squid process daemon (default)
# N: start N main Squid process daemons (i.e., SMP mode)
#
# In SMP mode, each worker does nearly all what a single Squid daemon
# does (e.g., listen on http_port and forward HTTP requests).
#Default:
# SMP support disabled.
# TAG: cpu_affinity_map
# Usage: cpu_affinity_map process_numbers=P1,P2,... cores=C1,C2,...
#
# Sets 1:1 mapping between Squid processes and CPU cores. For example,
#
# cpu_affinity_map process_numbers=1,2,3,4 cores=1,3,5,7
#
# affects processes 1 through 4 only and places them on the first
# four even cores, starting with core #1.
#
# CPU cores are numbered starting from 1. Requires support for
# sched_getaffinity(2) and sched_setaffinity(2) system calls.
#
# Multiple cpu_affinity_map options are merged.
#
# See also: workers
#Default:
# Let operating system decide.
# TAG: shared_memory_locking on|off
# Whether to ensure that all required shared memory is available by
# "locking" that shared memory into RAM when Squid starts. The
# alternative is faster startup time followed by slightly slower
# performance and, if not enough RAM is actually available during
# runtime, mysterious crashes.
#
# SMP Squid uses many shared memory segments. These segments are
# brought into Squid memory space using an mmap(2) system call. During
# Squid startup, the mmap() call often succeeds regardless of whether
# the system has enough RAM. In general, Squid cannot tell whether the
# kernel applies this "optimistic" memory allocation policy (but
# popular modern kernels usually use it).
#
# Later, if Squid attempts to actually access the mapped memory
# regions beyond what the kernel is willing to allocate, the
# "optimistic" kernel simply kills Squid kid with a SIGBUS signal.
# Some of the memory limits enforced by the kernel are currently
# poorly understood: We do not know how to detect and check them. This
# option ensures that the mapped memory will be available.
#
# This option may have a positive performance side-effect: Locking
# memory at start avoids runtime paging I/O. Paging slows Squid down.
#
# Locking memory may require a large enough RLIMIT_MEMLOCK OS limit,
# CAP_IPC_LOCK capability, or equivalent.
#Default:
# shared_memory_locking off
# TAG: hopeless_kid_revival_delay time-units
# Normally, when a kid process dies, Squid immediately restarts the
# kid. A kid experiencing frequent deaths is marked as "hopeless" for
# the duration specified by this directive. Hopeless kids are not
# automatically restarted.
#
# Currently, zero values are not supported because they result in
# misconfigured SMP Squid instances running forever, endlessly
# restarting each dying kid. To effectively disable hopeless kids
# revival, set the delay to a huge value (e.g., 1 year).
#
# Reconfiguration also clears all hopeless kids designations, allowing
# for manual revival of hopeless kids.
#Default:
# hopeless_kid_revival_delay 1 hour
# OPTIONS FOR AUTHENTICATION
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: auth_param
# This is used to define parameters for the various authentication
# schemes supported by Squid.
#
# format: auth_param scheme parameter [setting]
#
# The order in which authentication schemes are presented to the client is
# dependent on the order the scheme first appears in config file. IE
# has a bug (it's not RFC 2617 compliant) in that it will use the basic
# scheme if basic is the first entry presented, even if more secure
# schemes are presented. For now use the order in the recommended
# settings section below. If other browsers have difficulties (don't
# recognize the schemes offered even if you are using basic) either
# put basic first, or disable the other schemes (by commenting out their
# program entry).
#
# Once an authentication scheme is fully configured, it can only be
# shutdown by shutting squid down and restarting. Changes can be made on
# the fly and activated with a reconfigure. I.E. You can change to a
# different helper, but not unconfigure the helper completely.
#
# Please note that while this directive defines how Squid processes
# authentication it does not automatically activate authentication.
# To use authentication you must in addition make use of ACLs based
# on login name in http_access (proxy_auth, proxy_auth_regex or
# external with %LOGIN used in the format tag). The browser will be
# challenged for authentication on the first such acl encountered
# in http_access processing and will also be re-challenged for new
# login credentials if the request is being denied by a proxy_auth
# type acl.
#
# WARNING: authentication can't be used in a transparently intercepting
# proxy as the client then thinks it is talking to an origin server and
# not the proxy. This is a limitation of bending the TCP/IP protocol to
# transparently intercepting port 80, not a limitation in Squid.
# Ports flagged 'transparent', 'intercept', or 'tproxy' have
# authentication disabled.
#
# === Parameters common to all schemes. ===
#
# "program" cmdline
# Specifies the command for the external authenticator.
#
# By default, each authentication scheme is not used unless a
# program is specified.
#
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/Features/AddonHelpers for
# more details on helper operations and creating your own.
#
# "key_extras" format
# Specifies a string to be append to request line format for
# the authentication helper. "Quoted" format values may contain
# spaces and logformat %macros. In theory, any logformat %macro
# can be used. In practice, a %macro expands as a dash (-) if
# the helper request is sent before the required macro
# information is available to Squid.
#
# By default, Squid uses request formats provided in
# scheme-specific examples below (search for %credentials).
#
# The expanded key_extras value is added to the Squid credentials
# cache and, hence, will affect authentication. It can be used to
# autenticate different users with identical user names (e.g.,
# when user authentication depends on http_port).
#
# Avoid adding frequently changing information to key_extras. For
# example, if you add user source IP, and it changes frequently
# in your environment, then max_user_ip ACL is going to treat
# every user+IP combination as a unique "user", breaking the ACL
# and wasting a lot of memory on those user records. It will also
# force users to authenticate from scratch whenever their IP
# changes.
#
# "realm" string
# Specifies the protection scope (aka realm name) which is to be
# reported to the client for the authentication scheme. It is
# commonly part of the text the user will see when prompted for
# their username and password.
#
# For Basic the default is "Squid proxy-caching web server".
# For Digest there is no default, this parameter is mandatory.
# For NTLM and Negotiate this parameter is ignored.
#
# "children" numberofchildren [startup=N] [idle=N] [concurrency=N]
# [queue-size=N] [on-persistent-overload=action]
# [reservation-timeout=seconds]
#
# The maximum number of authenticator processes to spawn. If
# you start too few Squid will have to wait for them to process
# a backlog of credential verifications, slowing it down. When
# password verifications are done via a (slow) network you are
# likely to need lots of authenticator processes.
#
# The startup= and idle= options permit some skew in the exact
# amount run. A minimum of startup=N will begin during startup
# and reconfigure. Squid will start more in groups of up to
# idle=N in an attempt to meet traffic needs and to keep idle=N
# free above those traffic needs up to the maximum.
#
# The concurrency= option sets the number of concurrent requests
# the helper can process. The default of 0 is used for helpers
# who only supports one request at a time. Setting this to a
# number greater than 0 changes the protocol used to include a
# channel ID field first on the request/response line, allowing
# multiple requests to be sent to the same helper in parallel
# without waiting for the response.
#
# Concurrency must not be set unless it's known the helper
# supports the input format with channel-ID fields.
#
# The queue-size option sets the maximum number of queued
# requests. A request is queued when no existing child can
# accept it due to concurrency limit and no new child can be
# started due to numberofchildren limit. The default maximum is
# 2*numberofchildren. Squid is allowed to temporarily exceed the
# configured maximum, marking the affected helper as
# "overloaded". If the helper overload lasts more than 3
# minutes, the action prescribed by the on-persistent-overload
# option applies.
#
# The on-persistent-overload=action option specifies Squid
# reaction to a new helper request arriving when the helper
# has been overloaded for more that 3 minutes already. The number
# of queued requests determines whether the helper is overloaded
# (see the queue-size option).
#
# Two actions are supported:
#
# die Squid worker quits. This is the default behavior.
#
# ERR Squid treats the helper request as if it was
# immediately submitted, and the helper immediately
# replied with an ERR response. This action has no effect
# on the already queued and in-progress helper requests.
#
# NOTE: NTLM and Negotiate schemes do not support concurrency
# in the Squid code module even though some helpers can.
#
# The reservation-timeout=seconds option allows NTLM and Negotiate
# helpers to forget about clients that abandon their in-progress
# connection authentication without closing the connection. The
# timeout is measured since the last helper response received by
# Squid for the client. Fractional seconds are not supported.
#
# After the timeout, the helper will be used for other clients if
# there are no unreserved helpers available. In the latter case,
# the old client attempt to resume authentication will not be
# forwarded to the helper (and the client should open a new HTTP
# connection and retry authentication from scratch).
#
# By default, reservations do not expire and clients that keep
# their connections open without completing authentication may
# exhaust all NTLM and Negotiate helpers.
#
# "keep_alive" on|off
# If you experience problems with PUT/POST requests when using
# the NTLM or Negotiate schemes then you can try setting this
# to off. This will cause Squid to forcibly close the connection
# on the initial request where the browser asks which schemes
# are supported by the proxy.
#
# For Basic and Digest this parameter is ignored.
#
# "utf8" on|off
# Useful for sending credentials to authentication backends that
# expect UTF-8 encoding (e.g., LDAP).
#
# When this option is enabled, Squid uses HTTP Accept-Language
# request header to guess the received credentials encoding
# (ISO-Latin-1, CP1251, or UTF-8) and then converts the first
# two encodings into UTF-8.
#
# When this option is disabled and by default, Squid sends
# credentials in their original (i.e. received) encoding.
#
# This parameter is only honored for Basic and Digest schemes.
# For Basic, the entire username:password credentials are
# checked and, if necessary, re-encoded. For Digest -- just the
# username component. For NTLM and Negotiate schemes, this
# parameter is ignored.
#
#
# === Example Configuration ===
#
# This configuration displays the recommended authentication scheme
# order from most to least secure with recommended minimum configuration
# settings for each scheme:
#
##auth_param negotiate program <uncomment and complete this line to activate>
##auth_param negotiate children 20 startup=0 idle=1
##
##auth_param digest program <uncomment and complete this line to activate>
##auth_param digest children 20 startup=0 idle=1
##auth_param digest realm Squid proxy-caching web server
##auth_param digest nonce_garbage_interval 5 minutes
##auth_param digest nonce_max_duration 30 minutes
##auth_param digest nonce_max_count 50
##
##auth_param ntlm program <uncomment and complete this line to activate>
##auth_param ntlm children 20 startup=0 idle=1
##
##auth_param basic program <uncomment and complete this line>
##auth_param basic children 5 startup=5 idle=1
##auth_param basic credentialsttl 2 hours
#Default:
# none
# TAG: authenticate_cache_garbage_interval
# The time period between garbage collection across the username cache.
# This is a trade-off between memory utilization (long intervals - say
# 2 days) and CPU (short intervals - say 1 minute). Only change if you
# have good reason to.
#Default:
# authenticate_cache_garbage_interval 1 hour
# TAG: authenticate_ttl
# The time a user & their credentials stay in the logged in
# user cache since their last request. When the garbage
# interval passes, all user credentials that have passed their
# TTL are removed from memory.
#Default:
# authenticate_ttl 1 hour
# TAG: authenticate_ip_ttl
# If you use proxy authentication and the 'max_user_ip' ACL,
# this directive controls how long Squid remembers the IP
# addresses associated with each user. Use a small value
# (e.g., 60 seconds) if your users might change addresses
# quickly, as is the case with dialup. You might be safe
# using a larger value (e.g., 2 hours) in a corporate LAN
# environment with relatively static address assignments.
#Default:
# authenticate_ip_ttl 1 second
# ACCESS CONTROLS
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: external_acl_type
# This option defines external acl classes using a helper program
# to look up the status
#
# external_acl_type name [options] FORMAT /path/to/helper [helper arguments]
#
# Options:
#
# ttl=n TTL in seconds for cached results (defaults to 3600
# for 1 hour)
#
# negative_ttl=n
# TTL for cached negative lookups (default same
# as ttl)
#
# grace=n Percentage remaining of TTL where a refresh of a
# cached entry should be initiated without needing to
# wait for a new reply. (default is for no grace period)
#
# cache=n The maximum number of entries in the result cache. The
# default limit is 262144 entries. Each cache entry usually
# consumes at least 256 bytes. Squid currently does not remove
# expired cache entries until the limit is reached, so a proxy
# will sooner or later reach the limit. The expanded FORMAT
# value is used as the cache key, so if the details in FORMAT
# are highly variable, a larger cache may be needed to produce
# reduction in helper load.
#
# children-max=n
# Maximum number of acl helper processes spawned to service
# external acl lookups of this type. (default 5)
#
# children-startup=n
# Minimum number of acl helper processes to spawn during
# startup and reconfigure to service external acl lookups
# of this type. (default 0)
#
# children-idle=n
# Number of acl helper processes to keep ahead of traffic
# loads. Squid will spawn this many at once whenever load
# rises above the capabilities of existing processes.
# Up to the value of children-max. (default 1)
#
# concurrency=n concurrency level per process. Only used with helpers
# capable of processing more than one query at a time.
#
# queue-size=N The queue-size option sets the maximum number of
# queued requests. A request is queued when no existing
# helper can accept it due to concurrency limit and no
# new helper can be started due to children-max limit.
# If the queued requests exceed queue size, the acl is
# ignored. The default value is set to 2*children-max.
#
# protocol=2.5 Compatibility mode for Squid-2.5 external acl helpers.
#
# ipv4 / ipv6 IP protocol used to communicate with this helper.
# The default is to auto-detect IPv6 and use it when available.
#
#
# FORMAT is a series of %macro codes. See logformat directive for a full list
# of the accepted codes. Although note that at the time of any external ACL
# being tested data may not be available and thus some %macro expand to '-'.
#
# In addition to the logformat codes; when processing external ACLs these
# additional macros are made available:
#
# %ACL The name of the ACL being tested.
#
# %DATA The ACL arguments specified in the referencing config
# 'acl ... external' line, separated by spaces (an
# "argument string"). see acl external.
#
# If there are no ACL arguments %DATA expands to '-'.
#
# If you do not specify a DATA macro inside FORMAT,
# Squid automatically appends %DATA to your FORMAT.
# Note that Squid-3.x may expand %DATA to whitespace
# or nothing in this case.
#
# By default, Squid applies URL-encoding to each ACL
# argument inside the argument string. If an explicit
# encoding modifier is used (e.g., %#DATA), then Squid
# encodes the whole argument string as a single token
# (e.g., with %#DATA, spaces between arguments become
# %20).
#
# If SSL is enabled, the following formating codes become available:
#
# %USER_CERT SSL User certificate in PEM format
# %USER_CERTCHAIN SSL User certificate chain in PEM format
# %USER_CERT_xx SSL User certificate subject attribute xx
# %USER_CA_CERT_xx SSL User certificate issuer attribute xx
#
#
# NOTE: all other format codes accepted by older Squid versions
# are deprecated.
#
#
# General request syntax:
#
# [channel-ID] FORMAT-values
#
#
# FORMAT-values consists of transaction details expanded with
# whitespace separation per the config file FORMAT specification
# using the FORMAT macros listed above.
#
# Request values sent to the helper are URL escaped to protect
# each value in requests against whitespaces.
#
# If using protocol=2.5 then the request sent to the helper is not
# URL escaped to protect against whitespace.
#
# NOTE: protocol=3.0 is deprecated as no longer necessary.
#
# When using the concurrency= option the protocol is changed by
# introducing a query channel tag in front of the request/response.
# The query channel tag is a number between 0 and concurrency-1.
# This value must be echoed back unchanged to Squid as the first part
# of the response relating to its request.
#
#
# The helper receives lines expanded per the above format specification
# and for each input line returns 1 line starting with OK/ERR/BH result
# code and optionally followed by additional keywords with more details.
#
#
# General result syntax:
#
# [channel-ID] result keyword=value ...
#
# Result consists of one of the codes:
#
# OK
# the ACL test produced a match.
#
# ERR
# the ACL test does not produce a match.
#
# BH
# An internal error occurred in the helper, preventing
# a result being identified.
#
# The meaning of 'a match' is determined by your squid.conf
# access control configuration. See the Squid wiki for details.
#
# Defined keywords:
#
# user= The users name (login)
#
# password= The users password (for login= cache_peer option)
#
# message= Message describing the reason for this response.
# Available as %o in error pages.
# Useful on (ERR and BH results).
#
# tag= Apply a tag to a request. Only sets a tag once,
# does not alter existing tags.
#
# log= String to be logged in access.log. Available as
# %ea in logformat specifications.
#
# clt_conn_tag= Associates a TAG with the client TCP connection.
# Please see url_rewrite_program related documentation
# for this kv-pair.
#
# Any keywords may be sent on any response whether OK, ERR or BH.
#
# All response keyword values need to be a single token with URL
# escaping, or enclosed in double quotes (") and escaped using \ on
# any double quotes or \ characters within the value. The wrapping
# double quotes are removed before the value is interpreted by Squid.
# \r and \n are also replace by CR and LF.
#
# Some example key values:
#
# user=John%20Smith
# user="John Smith"
# user="J. \"Bob\" Smith"
#Default:
# none
# TAG: acl
# Defining an Access List
#
# Every access list definition must begin with an aclname and acltype,
# followed by either type-specific arguments or a quoted filename that
# they are read from.
#
# acl aclname acltype argument ...
# acl aclname acltype "file" ...
#
# When using "file", the file should contain one item per line.
#
#
# ACL Options
#
# Some acl types supports options which changes their default behaviour:
#
# -i,+i By default, regular expressions are CASE-SENSITIVE. To make them
# case-insensitive, use the -i option. To return case-sensitive
# use the +i option between patterns, or make a new ACL line
# without -i.
#
# -n Disable lookups and address type conversions. If lookup or
# conversion is required because the parameter type (IP or
# domain name) does not match the message address type (domain
# name or IP), then the ACL would immediately declare a mismatch
# without any warnings or lookups.
#
# -m[=delimiters]
# Perform a list membership test, interpreting values as
# comma-separated token lists and matching against individual
# tokens instead of whole values.
# The optional "delimiters" parameter specifies one or more
# alternative non-alphanumeric delimiter characters.
# non-alphanumeric delimiter characters.
#
# -- Used to stop processing all options, in the case the first acl
# value has '-' character as first character (for example the '-'
# is a valid domain name)
#
# Some acl types require suspending the current request in order
# to access some external data source.
# Those which do are marked with the tag [slow], those which
# don't are marked as [fast].
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl
# for further information
#
# ***** ACL TYPES AVAILABLE *****
#
# acl aclname src ip-address/mask ... # clients IP address [fast]
# acl aclname src addr1-addr2/mask ... # range of addresses [fast]
# acl aclname dst [-n] ip-address/mask ... # URL host's IP address [slow]
# acl aclname localip ip-address/mask ... # IP address the client connected to [fast]
#
#if USE_SQUID_EUI
# acl aclname arp mac-address ...
# acl aclname eui64 eui64-address ...
# # [fast]
# # MAC (EUI-48) and EUI-64 addresses use xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx notation.
# #
# # The 'arp' ACL code is not portable to all operating systems.
# # It works on Linux, Solaris, Windows, FreeBSD, and some other
# # BSD variants.
# #
# # The eui_lookup directive is required to be 'on' (the default)
# # and Squid built with --enable-eui for MAC/EUI addresses to be
# # available for this ACL.
# #
# # Squid can only determine the MAC/EUI address for IPv4
# # clients that are on the same subnet. If the client is on a
# # different subnet, then Squid cannot find out its address.
# #
# # IPv6 protocol does not contain ARP. MAC/EUI is either
# # encoded directly in the IPv6 address or not available.
#endif
# acl aclname clientside_mark mark[/mask] ...
# # matches CONNMARK of an accepted connection [fast]
# # DEPRECATED. Use the 'client_connection_mark' instead.
#
# acl aclname client_connection_mark mark[/mask] ...
# # matches CONNMARK of an accepted connection [fast]
# #
# # mark and mask are unsigned integers (hex, octal, or decimal).
# # If multiple marks are given, then the ACL matches if at least
# # one mark matches.
# #
# # Uses netfilter-conntrack library.
# # Requires building Squid with --enable-linux-netfilter.
# #
# # The client, various intermediaries, and Squid itself may set
# # CONNMARK at various times. The last CONNMARK set wins. This ACL
# # checks the mark present on an accepted connection or set by
# # Squid afterwards, depending on the ACL check timing. This ACL
# # effectively ignores any mark set by other agents after Squid has
# # accepted the connection.
#
# acl aclname srcdomain .foo.com ...
# # reverse lookup, from client IP [slow]
# acl aclname dstdomain [-n] .foo.com ...
# # Destination server from URL [fast]
# acl aclname srcdom_regex [-i] \.foo\.com ...
# # regex matching client name [slow]
# acl aclname dstdom_regex [-n] [-i] \.foo\.com ...
# # regex matching server [fast]
# #
# # For dstdomain and dstdom_regex a reverse lookup is tried if a IP
# # based URL is used and no match is found. The name "none" is used
# # if the reverse lookup fails.
#
# acl aclname src_as number ...
# acl aclname dst_as number ...
# # [fast]
# # Except for access control, AS numbers can be used for
# # routing of requests to specific caches. Here's an
# # example for routing all requests for AS#1241 and only
# # those to mycache.mydomain.net:
# # acl asexample dst_as 1241
# # cache_peer_access mycache.mydomain.net allow asexample
# # cache_peer_access mycache_mydomain.net deny all
#
# acl aclname peername myPeer ...
# acl aclname peername_regex [-i] regex-pattern ...
# # [fast]
# # match against a named cache_peer entry
# # set unique name= on cache_peer lines for reliable use.
#
# acl aclname time [day-abbrevs] [h1:m1-h2:m2]
# # [fast]
# # day-abbrevs:
# # S - Sunday
# # M - Monday
# # T - Tuesday
# # W - Wednesday
# # H - Thursday
# # F - Friday
# # A - Saturday
# # h1:m1 must be less than h2:m2
#
# acl aclname url_regex [-i] ^http:// ...
# # regex matching on whole URL [fast]
# acl aclname urllogin [-i] [^a-zA-Z0-9] ...
# # regex matching on URL login field
# acl aclname urlpath_regex [-i] \.gif$ ...
# # regex matching on URL path [fast]
#
# acl aclname port 80 70 21 0-1024... # destination TCP port [fast]
# # ranges are alloed
# acl aclname localport 3128 ... # TCP port the client connected to [fast]
# # NP: for interception mode this is usually '80'
#
# acl aclname myportname 3128 ... # *_port name [fast]
#
# acl aclname proto HTTP FTP ... # request protocol [fast]
#
# acl aclname method GET POST ... # HTTP request method [fast]
#
# acl aclname http_status 200 301 500- 400-403 ...
# # status code in reply [fast]
#
# acl aclname browser [-i] regexp ...
# # pattern match on User-Agent header (see also req_header below) [fast]
#
# acl aclname referer_regex [-i] regexp ...
# # pattern match on Referer header [fast]
# # Referer is highly unreliable, so use with care
#
# acl aclname ident [-i] username ...
# acl aclname ident_regex [-i] pattern ...
# # string match on ident output [slow]
# # use REQUIRED to accept any non-null ident.
#
# acl aclname proxy_auth [-i] username ...
# acl aclname proxy_auth_regex [-i] pattern ...
# # perform http authentication challenge to the client and match against
# # supplied credentials [slow]
# #
# # takes a list of allowed usernames.
# # use REQUIRED to accept any valid username.
# #
# # Will use proxy authentication in forward-proxy scenarios, and plain
# # http authenticaiton in reverse-proxy scenarios
# #
# # NOTE: when a Proxy-Authentication header is sent but it is not
# # needed during ACL checking the username is NOT logged
# # in access.log.
# #
# # NOTE: proxy_auth requires a EXTERNAL authentication program
# # to check username/password combinations (see
# # auth_param directive).
# #
# # NOTE: proxy_auth can't be used in a transparent/intercepting proxy
# # as the browser needs to be configured for using a proxy in order
# # to respond to proxy authentication.
#
# acl aclname snmp_community string ...
# # A community string to limit access to your SNMP Agent [fast]
# # Example:
# #
# # acl snmppublic snmp_community public
#
# acl aclname maxconn number
# # This will be matched when the client's IP address has
# # more than <number> TCP connections established. [fast]
# # NOTE: This only measures direct TCP links so X-Forwarded-For
# # indirect clients are not counted.
#
# acl aclname max_user_ip [-s] number
# # This will be matched when the user attempts to log in from more
# # than <number> different ip addresses. The authenticate_ip_ttl
# # parameter controls the timeout on the ip entries. [fast]
# # If -s is specified the limit is strict, denying browsing
# # from any further IP addresses until the ttl has expired. Without
# # -s Squid will just annoy the user by "randomly" denying requests.
# # (the counter is reset each time the limit is reached and a
# # request is denied)
# # NOTE: in acceleration mode or where there is mesh of child proxies,
# # clients may appear to come from multiple addresses if they are
# # going through proxy farms, so a limit of 1 may cause user problems.
#
# acl aclname random probability
# # Pseudo-randomly match requests. Based on the probability given.
# # Probability may be written as a decimal (0.333), fraction (1/3)
# # or ratio of matches:non-matches (3:5).
#
# acl aclname req_mime_type [-i] mime-type ...
# # regex match against the mime type of the request generated
# # by the client. Can be used to detect file upload or some
# # types HTTP tunneling requests [fast]
# # NOTE: This does NOT match the reply. You cannot use this
# # to match the returned file type.
#
# acl aclname req_header header-name [-i] any\.regex\.here
# # regex match against any of the known request headers. May be
# # thought of as a superset of "browser", "referer" and "mime-type"
# # ACL [fast]
#
# acl aclname rep_mime_type [-i] mime-type ...
# # regex match against the mime type of the reply received by
# # squid. Can be used to detect file download or some
# # types HTTP tunneling requests. [fast]
# # NOTE: This has no effect in http_access rules. It only has
# # effect in rules that affect the reply data stream such as
# # http_reply_access.
#
# acl aclname rep_header header-name [-i] any\.regex\.here
# # regex match against any of the known reply headers. May be
# # thought of as a superset of "browser", "referer" and "mime-type"
# # ACLs [fast]
#
# acl aclname external class_name [arguments...]
# # external ACL lookup via a helper class defined by the
# # external_acl_type directive [slow]
#
# acl aclname user_cert attribute values...
# # match against attributes in a user SSL certificate
# # attribute is one of DN/C/O/CN/L/ST or a numerical OID [fast]
#
# acl aclname ca_cert attribute values...
# # match against attributes a users issuing CA SSL certificate
# # attribute is one of DN/C/O/CN/L/ST or a numerical OID [fast]
#
# acl aclname ext_user [-i] username ...
# acl aclname ext_user_regex [-i] pattern ...
# # string match on username returned by external acl helper [slow]
# # use REQUIRED to accept any non-null user name.
#
# acl aclname tag tagvalue ...
# # string match on tag returned by external acl helper [fast]
# # DEPRECATED. Only the first tag will match with this ACL.
# # Use the 'note' ACL instead for handling multiple tag values.
#
# acl aclname hier_code codename ...
# # string match against squid hierarchy code(s); [fast]
# # e.g., DIRECT, PARENT_HIT, NONE, etc.
# #
# # NOTE: This has no effect in http_access rules. It only has
# # effect in rules that affect the reply data stream such as
# # http_reply_access.
#
# acl aclname note [-m[=delimiters]] name [value ...]
# # match transaction annotation [fast]
# # Without values, matches any annotation with a given name.
# # With value(s), matches any annotation with a given name that
# # also has one of the given values.
# # If the -m flag is used, then the value of the named
# # annotation is interpreted as a list of tokens, and the ACL
# # matches individual name=token pairs rather than whole
# # name=value pairs. See "ACL Options" above for more info.
# # Annotation sources include note and adaptation_meta directives
# # as well as helper and eCAP responses.
#
# acl aclname annotate_transaction [-m[=delimiters]] key=value ...
# acl aclname annotate_transaction [-m[=delimiters]] key+=value ...
# # Always matches. [fast]
# # Used for its side effect: This ACL immediately adds a
# # key=value annotation to the current master transaction.
# # The added annotation can then be tested using note ACL and
# # logged (or sent to helpers) using %note format code.
# #
# # Annotations can be specified using replacement and addition
# # formats. The key=value form replaces old same-key annotation
# # value(s). The key+=value form appends a new value to the old
# # same-key annotation. Both forms create a new key=value
# # annotation if no same-key annotation exists already. If
# # -m flag is used, then the value is interpreted as a list
# # and the annotation will contain key=token pair(s) instead of the
# # whole key=value pair.
# #
# # This ACL is especially useful for recording complex multi-step
# # ACL-driven decisions. For example, the following configuration
# # avoids logging transactions accepted after aclX matched:
# #
# # # First, mark transactions accepted after aclX matched
# # acl markSpecial annotate_transaction special=true
# # http_access allow acl001
# # ...
# # http_access deny acl100
# # http_access allow aclX markSpecial
# #
# # # Second, do not log marked transactions:
# # acl markedSpecial note special true
# # access_log ... deny markedSpecial
# #
# # # Note that the following would not have worked because aclX
# # # alone does not determine whether the transaction was allowed:
# # access_log ... deny aclX # Wrong!
# #
# # Warning: This ACL annotates the transaction even when negated
# # and even if subsequent ACLs fail to match. For example, the
# # following three rules will have exactly the same effect as far
# # as annotations set by the "mark" ACL are concerned:
# #
# # some_directive acl1 ... mark # rule matches if mark is reached
# # some_directive acl1 ... !mark # rule never matches
# # some_directive acl1 ... mark !all # rule never matches
#
# acl aclname annotate_client [-m[=delimiters]] key=value ...
# acl aclname annotate_client [-m[=delimiters]] key+=value ...
# #
# # Always matches. [fast]
# # Used for its side effect: This ACL immediately adds a
# # key=value annotation to the current client-to-Squid
# # connection. Connection annotations are propagated to the current
# # and all future master transactions on the annotated connection.
# # See the annotate_transaction ACL for details.
# #
# # For example, the following configuration avoids rewriting URLs
# # of transactions bumped by SslBump:
# #
# # # First, mark bumped connections:
# # acl markBumped annotate_client bumped=true
# # ssl_bump peek acl1
# # ssl_bump stare acl2
# # ssl_bump bump acl3 markBumped
# # ssl_bump splice all
# #
# # # Second, do not send marked transactions to the redirector:
# # acl markedBumped note bumped true
# # url_rewrite_access deny markedBumped
# #
# # # Note that the following would not have worked because acl3 alone
# # # does not determine whether the connection is going to be bumped:
# # url_rewrite_access deny acl3 # Wrong!
#
# acl aclname adaptation_service service ...
# # Matches the name of any icap_service, ecap_service,
# # adaptation_service_set, or adaptation_service_chain that Squid
# # has used (or attempted to use) for the master transaction.
# # This ACL must be defined after the corresponding adaptation
# # service is named in squid.conf. This ACL is usable with
# # adaptation_meta because it starts matching immediately after
# # the service has been selected for adaptation.
#
# acl aclname transaction_initiator initiator ...
# # Matches transaction's initiator [fast]
# #
# # Supported initiators are:
# # esi: matches transactions fetching ESI resources
# # certificate-fetching: matches transactions fetching
# # a missing intermediate TLS certificate
# # cache-digest: matches transactions fetching Cache Digests
# # from a cache_peer
# # htcp: matches HTCP requests from peers
# # icp: matches ICP requests to peers
# # icmp: matches ICMP RTT database (NetDB) requests to peers
# # asn: matches asns db requests
# # internal: matches any of the above
# # client: matches transactions containing an HTTP or FTP
# # client request received at a Squid *_port
# # all: matches any transaction, including internal transactions
# # without a configurable initiator and hopefully rare
# # transactions without a known-to-Squid initiator
# #
# # Multiple initiators are ORed.
#
# acl aclname has component
# # matches a transaction "component" [fast]
# #
# # Supported transaction components are:
# # request: transaction has a request header (at least)
# # response: transaction has a response header (at least)
# # ALE: transaction has an internally-generated Access Log Entry
# # structure; bugs notwithstanding, all transaction have it
# #
# # For example, the following configuration helps when dealing with HTTP
# # clients that close connections without sending a request header:
# #
# # acl hasRequest has request
# # acl logMe note important_transaction
# # # avoid "logMe ACL is used in context without an HTTP request" warnings
# # access_log ... logformat=detailed hasRequest logMe
# # # log request-less transactions, instead of ignoring them
# # access_log ... logformat=brief !hasRequest
# #
# # Multiple components are not supported for one "acl" rule, but
# # can be specified (and are ORed) using multiple same-name rules:
# #
# # # OK, this strange logging daemon needs request or response,
# # # but can work without either a request or a response:
# # acl hasWhatMyLoggingDaemonNeeds has request
# # acl hasWhatMyLoggingDaemonNeeds has response
#
#acl aclname at_step step
# # match against the current request processing step [fast]
# # Valid steps are:
# # GeneratingCONNECT: Generating HTTP CONNECT request headers
#
# acl aclname any-of acl1 acl2 ...
# # match any one of the acls [fast or slow]
# # The first matching ACL stops further ACL evaluation.
# #
# # ACLs from multiple any-of lines with the same name are ORed.
# # For example, A = (a1 or a2) or (a3 or a4) can be written as
# # acl A any-of a1 a2
# # acl A any-of a3 a4
# #
# # This group ACL is fast if all evaluated ACLs in the group are fast
# # and slow otherwise.
#
# acl aclname all-of acl1 acl2 ...
# # match all of the acls [fast or slow]
# # The first mismatching ACL stops further ACL evaluation.
# #
# # ACLs from multiple all-of lines with the same name are ORed.
# # For example, B = (b1 and b2) or (b3 and b4) can be written as
# # acl B all-of b1 b2
# # acl B all-of b3 b4
# #
# # This group ACL is fast if all evaluated ACLs in the group are fast
# # and slow otherwise.
#
# Examples:
# acl macaddress arp 09:00:2b:23:45:67
# acl myexample dst_as 1241
# acl password proxy_auth REQUIRED
# acl fileupload req_mime_type -i ^multipart/form-data$
# acl javascript rep_mime_type -i ^application/x-javascript$
#
#Default:
# ACLs all, manager, localhost, to_localhost, and CONNECT are predefined.
#
#
# Recommended minimum configuration:
#
# Example rule allowing access from your local networks.
# Adapt to list your (internal) IP networks from where browsing
# should be allowed
acl localnet src 0.0.0.1-0.255.255.255 # RFC 1122 "this" network (LAN)
acl localnet src 10.0.0.0/8 # RFC 1918 local private network (LAN)
acl localnet src 100.64.0.0/10 # RFC 6598 shared address space (CGN)
acl localnet src 169.254.0.0/16 # RFC 3927 link-local (directly plugged) machines
acl localnet src 172.16.0.0/12 # RFC 1918 local private network (LAN)
acl localnet src 192.168.0.0/16 # RFC 1918 local private network (LAN)
acl localnet src fc00::/7 # RFC 4193 local private network range
acl localnet src fe80::/10 # RFC 4291 link-local (directly plugged) machines
acl SSL_ports port 443
acl Safe_ports port 80 # http
acl Safe_ports port 21 # ftp
acl Safe_ports port 443 # https
acl Safe_ports port 70 # gopher
acl Safe_ports port 210 # wais
acl Safe_ports port 1025-65535 # unregistered ports
acl Safe_ports port 280 # http-mgmt
acl Safe_ports port 488 # gss-http
acl Safe_ports port 591 # filemaker
acl Safe_ports port 777 # multiling http
# TAG: proxy_protocol_access
# Determine which client proxies can be trusted to provide correct
# information regarding real client IP address using PROXY protocol.
#
# Requests may pass through a chain of several other proxies
# before reaching us. The original source details may by sent in:
# * HTTP message Forwarded header, or
# * HTTP message X-Forwarded-For header, or
# * PROXY protocol connection header.
#
# This directive is solely for validating new PROXY protocol
# connections received from a port flagged with require-proxy-header.
# It is checked only once after TCP connection setup.
#
# A deny match results in TCP connection closure.
#
# An allow match is required for Squid to permit the corresponding
# TCP connection, before Squid even looks for HTTP request headers.
# If there is an allow match, Squid starts using PROXY header information
# to determine the source address of the connection for all future ACL
# checks, logging, etc.
#
# SECURITY CONSIDERATIONS:
#
# Any host from which we accept client IP details can place
# incorrect information in the relevant header, and Squid
# will use the incorrect information as if it were the
# source address of the request. This may enable remote
# hosts to bypass any access control restrictions that are
# based on the client's source addresses.
#
# This clause only supports fast acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#Default:
# all TCP connections to ports with require-proxy-header will be denied
# TAG: follow_x_forwarded_for
# Determine which client proxies can be trusted to provide correct
# information regarding real client IP address.
#
# Requests may pass through a chain of several other proxies
# before reaching us. The original source details may by sent in:
# * HTTP message Forwarded header, or
# * HTTP message X-Forwarded-For header, or
# * PROXY protocol connection header.
#
# PROXY protocol connections are controlled by the proxy_protocol_access
# directive which is checked before this.
#
# If a request reaches us from a source that is allowed by this
# directive, then we trust the information it provides regarding
# the IP of the client it received from (if any).
#
# For the purpose of ACLs used in this directive the src ACL type always
# matches the address we are testing and srcdomain matches its rDNS.
#
# On each HTTP request Squid checks for X-Forwarded-For header fields.
# If found the header values are iterated in reverse order and an allow
# match is required for Squid to continue on to the next value.
# The verification ends when a value receives a deny match, cannot be
# tested, or there are no more values to test.
# NOTE: Squid does not yet follow the Forwarded HTTP header.
#
# The end result of this process is an IP address that we will
# refer to as the indirect client address. This address may
# be treated as the client address for access control, ICAP, delay
# pools and logging, depending on the acl_uses_indirect_client,
# icap_uses_indirect_client, delay_pool_uses_indirect_client,
# log_uses_indirect_client and tproxy_uses_indirect_client options.
#
# This clause only supports fast acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#
# SECURITY CONSIDERATIONS:
#
# Any host from which we accept client IP details can place
# incorrect information in the relevant header, and Squid
# will use the incorrect information as if it were the
# source address of the request. This may enable remote
# hosts to bypass any access control restrictions that are
# based on the client's source addresses.
#
# For example:
#
# acl localhost src 127.0.0.1
# acl my_other_proxy srcdomain .proxy.example.com
# follow_x_forwarded_for allow localhost
# follow_x_forwarded_for allow my_other_proxy
#Default:
# X-Forwarded-For header will be ignored.
# TAG: acl_uses_indirect_client on|off
# Controls whether the indirect client address
# (see follow_x_forwarded_for) is used instead of the
# direct client address in acl matching.
#
# NOTE: maxconn ACL considers direct TCP links and indirect
# clients will always have zero. So no match.
#Default:
# acl_uses_indirect_client on
# TAG: delay_pool_uses_indirect_client on|off
# Controls whether the indirect client address
# (see follow_x_forwarded_for) is used instead of the
# direct client address in delay pools.
#Default:
# delay_pool_uses_indirect_client on
# TAG: log_uses_indirect_client on|off
# Controls whether the indirect client address
# (see follow_x_forwarded_for) is used instead of the
# direct client address in the access log.
#Default:
# log_uses_indirect_client on
# TAG: tproxy_uses_indirect_client on|off
# Controls whether the indirect client address
# (see follow_x_forwarded_for) is used instead of the
# direct client address when spoofing the outgoing client.
#
# This has no effect on requests arriving in non-tproxy
# mode ports.
#
# SECURITY WARNING: Usage of this option is dangerous
# and should not be used trivially. Correct configuration
# of follow_x_forwarded_for with a limited set of trusted
# sources is required to prevent abuse of your proxy.
#Default:
# tproxy_uses_indirect_client off
# TAG: spoof_client_ip
# Control client IP address spoofing of TPROXY traffic based on
# defined access lists.
#
# spoof_client_ip allow|deny [!]aclname ...
#
# If there are no "spoof_client_ip" lines present, the default
# is to "allow" spoofing of any suitable request.
#
# Note that the cache_peer "no-tproxy" option overrides this ACL.
#
# This clause supports fast acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#Default:
# Allow spoofing on all TPROXY traffic.
# TAG: http_access
# Allowing or Denying access based on defined access lists
#
# To allow or deny a message received on an HTTP, HTTPS, or FTP port:
# http_access allow|deny [!]aclname ...
#
# NOTE on default values:
#
# If there are no "access" lines present, the default is to deny
# the request.
#
# If none of the "access" lines cause a match, the default is the
# opposite of the last line in the list. If the last line was
# deny, the default is allow. Conversely, if the last line
# is allow, the default will be deny. For these reasons, it is a
# good idea to have an "deny all" entry at the end of your access
# lists to avoid potential confusion.
#
# This clause supports both fast and slow acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#
#Default:
# Deny, unless rules exist in squid.conf.
#
#
# Recommended minimum Access Permission configuration:
#
# Deny requests to certain unsafe ports
http_access deny !Safe_ports
# Deny CONNECT to other than secure SSL ports
http_access deny CONNECT !SSL_ports
# Only allow cachemgr access from localhost
http_access allow localhost manager
http_access deny manager
# We strongly recommend the following be uncommented to protect innocent
# web applications running on the proxy server who think the only
# one who can access services on "localhost" is a local user
#http_access deny to_localhost
#
# INSERT YOUR OWN RULE(S) HERE TO ALLOW ACCESS FROM YOUR CLIENTS
#
include /etc/squid/conf.d/*.conf
# Example rule allowing access from your local networks.
# Adapt localnet in the ACL section to list your (internal) IP networks
# from where browsing should be allowed
#http_access allow localnet
http_access allow localhost
# And finally deny all other access to this proxy
http_access deny all
# TAG: adapted_http_access
# Allowing or Denying access based on defined access lists
#
# Essentially identical to http_access, but runs after redirectors
# and ICAP/eCAP adaptation. Allowing access control based on their
# output.
#
# If not set then only http_access is used.
#Default:
# Allow, unless rules exist in squid.conf.
# TAG: http_reply_access
# Allow replies to client requests. This is complementary to http_access.
#
# http_reply_access allow|deny [!] aclname ...
#
# NOTE: if there are no access lines present, the default is to allow
# all replies.
#
# If none of the access lines cause a match the opposite of the
# last line will apply. Thus it is good practice to end the rules
# with an "allow all" or "deny all" entry.
#
# This clause supports both fast and slow acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#Default:
# Allow, unless rules exist in squid.conf.
# TAG: icp_access
# Allowing or Denying access to the ICP port based on defined
# access lists
#
# icp_access allow|deny [!]aclname ...
#
# NOTE: The default if no icp_access lines are present is to
# deny all traffic. This default may cause problems with peers
# using ICP.
#
# This clause only supports fast acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#
## Allow ICP queries from local networks only
##icp_access allow localnet
##icp_access deny all
#Default:
# Deny, unless rules exist in squid.conf.
# TAG: htcp_access
# Allowing or Denying access to the HTCP port based on defined
# access lists
#
# htcp_access allow|deny [!]aclname ...
#
# See also htcp_clr_access for details on access control for
# cache purge (CLR) HTCP messages.
#
# NOTE: The default if no htcp_access lines are present is to
# deny all traffic. This default may cause problems with peers
# using the htcp option.
#
# This clause only supports fast acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#
## Allow HTCP queries from local networks only
##htcp_access allow localnet
##htcp_access deny all
#Default:
# Deny, unless rules exist in squid.conf.
# TAG: htcp_clr_access
# Allowing or Denying access to purge content using HTCP based
# on defined access lists.
# See htcp_access for details on general HTCP access control.
#
# htcp_clr_access allow|deny [!]aclname ...
#
# This clause only supports fast acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#
## Allow HTCP CLR requests from trusted peers
#acl htcp_clr_peer src 192.0.2.2 2001:DB8::2
#htcp_clr_access allow htcp_clr_peer
#htcp_clr_access deny all
#Default:
# Deny, unless rules exist in squid.conf.
# TAG: miss_access
# Determines whether network access is permitted when satisfying a request.
#
# For example;
# to force your neighbors to use you as a sibling instead of
# a parent.
#
# acl localclients src 192.0.2.0/24 2001:DB8::a:0/64
# miss_access deny !localclients
# miss_access allow all
#
# This means only your local clients are allowed to fetch relayed/MISS
# replies from the network and all other clients can only fetch cached
# objects (HITs).
#
# The default for this setting allows all clients who passed the
# http_access rules to relay via this proxy.
#
# This clause only supports fast acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#Default:
# Allow, unless rules exist in squid.conf.
# TAG: ident_lookup_access
# A list of ACL elements which, if matched, cause an ident
# (RFC 931) lookup to be performed for this request. For
# example, you might choose to always perform ident lookups
# for your main multi-user Unix boxes, but not for your Macs
# and PCs. By default, ident lookups are not performed for
# any requests.
#
# To enable ident lookups for specific client addresses, you
# can follow this example:
#
# acl ident_aware_hosts src 198.168.1.0/24
# ident_lookup_access allow ident_aware_hosts
# ident_lookup_access deny all
#
# Only src type ACL checks are fully supported. A srcdomain
# ACL might work at times, but it will not always provide
# the correct result.
#
# This clause only supports fast acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#Default:
# Unless rules exist in squid.conf, IDENT is not fetched.
# TAG: reply_body_max_size size [acl acl...]
# This option specifies the maximum size of a reply body. It can be
# used to prevent users from downloading very large files, such as
# MP3's and movies. When the reply headers are received, the
# reply_body_max_size lines are processed, and the first line where
# all (if any) listed ACLs are true is used as the maximum body size
# for this reply.
#
# This size is checked twice. First when we get the reply headers,
# we check the content-length value. If the content length value exists
# and is larger than the allowed size, the request is denied and the
# user receives an error message that says "the request or reply
# is too large." If there is no content-length, and the reply
# size exceeds this limit, the client's connection is just closed
# and they will receive a partial reply.
#
# WARNING: downstream caches probably can not detect a partial reply
# if there is no content-length header, so they will cache
# partial responses and give them out as hits. You should NOT
# use this option if you have downstream caches.
#
# WARNING: A maximum size smaller than the size of squid's error messages
# will cause an infinite loop and crash squid. Ensure that the smallest
# non-zero value you use is greater that the maximum header size plus
# the size of your largest error page.
#
# If you set this parameter none (the default), there will be
# no limit imposed.
#
# Configuration Format is:
# reply_body_max_size SIZE UNITS [acl ...]
# ie.
# reply_body_max_size 10 MB
#
#Default:
# No limit is applied.
# TAG: on_unsupported_protocol
# Determines Squid behavior when encountering strange requests at the
# beginning of an accepted TCP connection or the beginning of a bumped
# CONNECT tunnel. Controlling Squid reaction to unexpected traffic is
# especially useful in interception environments where Squid is likely
# to see connections for unsupported protocols that Squid should either
# terminate or tunnel at TCP level.
#
# on_unsupported_protocol <action> [!]acl ...
#
# The first matching action wins. Only fast ACLs are supported.
#
# Supported actions are:
#
# tunnel: Establish a TCP connection with the intended server and
# blindly shovel TCP packets between the client and server.
#
# respond: Respond with an error message, using the transfer protocol
# for the Squid port that received the request (e.g., HTTP
# for connections intercepted at the http_port). This is the
# default.
#
# Squid expects the following traffic patterns:
#
# http_port: a plain HTTP request
# https_port: SSL/TLS handshake followed by an [encrypted] HTTP request
# ftp_port: a plain FTP command (no on_unsupported_protocol support yet!)
# CONNECT tunnel on http_port: same as https_port
# CONNECT tunnel on https_port: same as https_port
#
# Currently, this directive has effect on intercepted connections and
# bumped tunnels only. Other cases are not supported because Squid
# cannot know the intended destination of other traffic.
#
# For example:
# # define what Squid errors indicate receiving non-HTTP traffic:
# acl foreignProtocol squid_error ERR_PROTOCOL_UNKNOWN ERR_TOO_BIG
# # define what Squid errors indicate receiving nothing:
# acl serverTalksFirstProtocol squid_error ERR_REQUEST_START_TIMEOUT
# # tunnel everything that does not look like HTTP:
# on_unsupported_protocol tunnel foreignProtocol
# # tunnel if we think the client waits for the server to talk first:
# on_unsupported_protocol tunnel serverTalksFirstProtocol
# # in all other error cases, just send an HTTP "error page" response:
# on_unsupported_protocol respond all
#
# See also: squid_error ACL
#Default:
# Respond with an error message to unidentifiable traffic
# TAG: auth_schemes
# Use this directive to customize authentication schemes presence and
# order in Squid's Unauthorized and Authentication Required responses.
#
# auth_schemes scheme1,scheme2,... [!]aclname ...
#
# where schemeN is the name of one of the authentication schemes
# configured using auth_param directives. At least one scheme name is
# required. Multiple scheme names are separated by commas. Either
# avoid whitespace or quote the entire schemes list.
#
# A special "ALL" scheme name expands to all auth_param-configured
# schemes in their configuration order. This directive cannot be used
# to configure Squid to offer no authentication schemes at all.
#
# The first matching auth_schemes rule determines the schemes order
# for the current Authentication Required transaction. Note that the
# future response is not yet available during auth_schemes evaluation.
#
# If this directive is not used or none of its rules match, then Squid
# responds with all configured authentication schemes in the order of
# auth_param directives in the configuration file.
#
# This directive does not determine when authentication is used or
# how each authentication scheme authenticates clients.
#
# The following example sends basic and negotiate authentication
# schemes, in that order, when requesting authentication of HTTP
# requests matching the isIE ACL (not shown) while sending all
# auth_param schemes in their configuration order to other clients:
#
# auth_schemes basic,negotiate isIE
# auth_schemes ALL all # explicit default
#
# This directive supports fast ACLs only.
#
# See also: auth_param.
#Default:
# use all auth_param schemes in their configuration order
# NETWORK OPTIONS
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: http_port
# Usage: port [mode] [options]
# hostname:port [mode] [options]
# 1.2.3.4:port [mode] [options]
#
# The socket addresses where Squid will listen for HTTP client
# requests. You may specify multiple socket addresses.
# There are three forms: port alone, hostname with port, and
# IP address with port. If you specify a hostname or IP
# address, Squid binds the socket to that specific
# address. Most likely, you do not need to bind to a specific
# address, so you can use the port number alone.
#
# If you are running Squid in accelerator mode, you
# probably want to listen on port 80 also, or instead.
#
# The -a command line option may be used to specify additional
# port(s) where Squid listens for proxy request. Such ports will
# be plain proxy ports with no options.
#
# You may specify multiple socket addresses on multiple lines.
#
# Modes:
#
# intercept Support for IP-Layer NAT interception delivering
# traffic to this Squid port.
# NP: disables authentication on the port.
#
# tproxy Support Linux TPROXY (or BSD divert-to) with spoofing
# of outgoing connections using the client IP address.
# NP: disables authentication on the port.
#
# accel Accelerator / reverse proxy mode
#
# ssl-bump For each CONNECT request allowed by ssl_bump ACLs,
# establish secure connection with the client and with
# the server, decrypt HTTPS messages as they pass through
# Squid, and treat them as unencrypted HTTP messages,
# becoming the man-in-the-middle.
#
# The ssl_bump option is required to fully enable
# bumping of CONNECT requests.
#
# Omitting the mode flag causes default forward proxy mode to be used.
#
#
# Accelerator Mode Options:
#
# defaultsite=domainname
# What to use for the Host: header if it is not present
# in a request. Determines what site (not origin server)
# accelerators should consider the default.
#
# no-vhost Disable using HTTP/1.1 Host header for virtual domain support.
#
# protocol= Protocol to reconstruct accelerated and intercepted
# requests with. Defaults to HTTP/1.1 for http_port and
# HTTPS/1.1 for https_port.
# When an unsupported value is configured Squid will
# produce a FATAL error.
# Values: HTTP or HTTP/1.1, HTTPS or HTTPS/1.1
#
# vport Virtual host port support. Using the http_port number
# instead of the port passed on Host: headers.
#
# vport=NN Virtual host port support. Using the specified port
# number instead of the port passed on Host: headers.
#
# act-as-origin
# Act as if this Squid is the origin server.
# This currently means generate new Date: and Expires:
# headers on HIT instead of adding Age:.
#
# ignore-cc Ignore request Cache-Control headers.
#
# WARNING: This option violates HTTP specifications if
# used in non-accelerator setups.
#
# allow-direct Allow direct forwarding in accelerator mode. Normally
# accelerated requests are denied direct forwarding as if
# never_direct was used.
#
# WARNING: this option opens accelerator mode to security
# vulnerabilities usually only affecting in interception
# mode. Make sure to protect forwarding with suitable
# http_access rules when using this.
#
#
# SSL Bump Mode Options:
# In addition to these options ssl-bump requires TLS/SSL options.
#
# generate-host-certificates[=<on|off>]
# Dynamically create SSL server certificates for the
# destination hosts of bumped CONNECT requests.When
# enabled, the cert and key options are used to sign
# generated certificates. Otherwise generated
# certificate will be selfsigned.
# If there is a CA certificate lifetime of the generated
# certificate equals lifetime of the CA certificate. If
# generated certificate is selfsigned lifetime is three
# years.
# This option is enabled by default when ssl-bump is used.
# See the ssl-bump option above for more information.
#
# dynamic_cert_mem_cache_size=SIZE
# Approximate total RAM size spent on cached generated
# certificates. If set to zero, caching is disabled. The
# default value is 4MB.
#
# TLS / SSL Options:
#
# tls-cert= Path to file containing an X.509 certificate (PEM format)
# to be used in the TLS handshake ServerHello.
#
# If this certificate is constrained by KeyUsage TLS
# feature it must allow HTTP server usage, along with
# any additional restrictions imposed by your choice
# of options= settings.
#
# When OpenSSL is used this file may also contain a
# chain of intermediate CA certificates to send in the
# TLS handshake.
#
# When GnuTLS is used this option (and any paired
# tls-key= option) may be repeated to load multiple
# certificates for different domains.
#
# Also, when generate-host-certificates=on is configured
# the first tls-cert= option must be a CA certificate
# capable of signing the automatically generated
# certificates.
#
# tls-key= Path to a file containing private key file (PEM format)
# for the previous tls-cert= option.
#
# If tls-key= is not specified tls-cert= is assumed to
# reference a PEM file containing both the certificate
# and private key.
#
# cipher= Colon separated list of supported ciphers.
# NOTE: some ciphers such as EDH ciphers depend on
# additional settings. If those settings are
# omitted the ciphers may be silently ignored
# by the OpenSSL library.
#
# options= Various SSL implementation options. The most important
# being:
#
# NO_SSLv3 Disallow the use of SSLv3
#
# NO_TLSv1 Disallow the use of TLSv1.0
#
# NO_TLSv1_1 Disallow the use of TLSv1.1
#
# NO_TLSv1_2 Disallow the use of TLSv1.2
#
# SINGLE_DH_USE
# Always create a new key when using
# temporary/ephemeral DH key exchanges
#
# SINGLE_ECDH_USE
# Enable ephemeral ECDH key exchange.
# The adopted curve should be specified
# using the tls-dh option.
#
# NO_TICKET
# Disable use of RFC5077 session tickets.
# Some servers may have problems
# understanding the TLS extension due
# to ambiguous specification in RFC4507.
#
# ALL Enable various bug workarounds
# suggested as "harmless" by OpenSSL
# Be warned that this reduces SSL/TLS
# strength to some attacks.
#
# See the OpenSSL SSL_CTX_set_options documentation for a
# more complete list.
#
# clientca= File containing the list of CAs to use when
# requesting a client certificate.
#
# tls-cafile= PEM file containing CA certificates to use when verifying
# client certificates. If not configured clientca will be
# used. May be repeated to load multiple files.
#
# capath= Directory containing additional CA certificates
# and CRL lists to use when verifying client certificates.
# Requires OpenSSL or LibreSSL.
#
# crlfile= File of additional CRL lists to use when verifying
# the client certificate, in addition to CRLs stored in
# the capath. Implies VERIFY_CRL flag below.
#
# tls-dh=[curve:]file
# File containing DH parameters for temporary/ephemeral DH key
# exchanges, optionally prefixed by a curve for ephemeral ECDH
# key exchanges.
# See OpenSSL documentation for details on how to create the
# DH parameter file. Supported curves for ECDH can be listed
# using the "openssl ecparam -list_curves" command.
# WARNING: EDH and EECDH ciphers will be silently disabled if
# this option is not set.
#
# sslflags= Various flags modifying the use of SSL:
# DELAYED_AUTH
# Don't request client certificates
# immediately, but wait until acl processing
# requires a certificate (not yet implemented).
# CONDITIONAL_AUTH
# Request a client certificate during the TLS
# handshake, but ignore certificate absence in
# the TLS client Hello. If the client does
# supply a certificate, it is validated.
# NO_SESSION_REUSE
# Don't allow for session reuse. Each connection
# will result in a new SSL session.
# VERIFY_CRL
# Verify CRL lists when accepting client
# certificates.
# VERIFY_CRL_ALL
# Verify CRL lists for all certificates in the
# client certificate chain.
#
# tls-default-ca[=off]
# Whether to use the system Trusted CAs. Default is OFF.
#
# tls-no-npn Do not use the TLS NPN extension to advertise HTTP/1.1.
#
# sslcontext= SSL session ID context identifier.
#
# Other Options:
#
# connection-auth[=on|off]
# use connection-auth=off to tell Squid to prevent
# forwarding Microsoft connection oriented authentication
# (NTLM, Negotiate and Kerberos)
#
# disable-pmtu-discovery=
# Control Path-MTU discovery usage:
# off lets OS decide on what to do (default).
# transparent disable PMTU discovery when transparent
# support is enabled.
# always disable always PMTU discovery.
#
# In many setups of transparently intercepting proxies
# Path-MTU discovery can not work on traffic towards the
# clients. This is the case when the intercepting device
# does not fully track connections and fails to forward
# ICMP must fragment messages to the cache server. If you
# have such setup and experience that certain clients
# sporadically hang or never complete requests set
# disable-pmtu-discovery option to 'transparent'.
#
# name= Specifies a internal name for the port. Defaults to
# the port specification (port or addr:port)
#
# tcpkeepalive[=idle,interval,timeout]
# Enable TCP keepalive probes of idle connections.
# In seconds; idle is the initial time before TCP starts
# probing the connection, interval how often to probe, and
# timeout the time before giving up.
#
# require-proxy-header
# Require PROXY protocol version 1 or 2 connections.
# The proxy_protocol_access is required to permit
# downstream proxies which can be trusted.
#
# worker-queues
# Ask TCP stack to maintain a dedicated listening queue
# for each worker accepting requests at this port.
# Requires TCP stack that supports the SO_REUSEPORT socket
# option.
#
# SECURITY WARNING: Enabling worker-specific queues
# allows any process running as Squid's effective user to
# easily accept requests destined to this port.
#
# If you run Squid on a dual-homed machine with an internal
# and an external interface we recommend you to specify the
# internal address:port in http_port. This way Squid will only be
# visible on the internal address.
#
#
# Squid normally listens to port 3128
http_port 3128
# TAG: https_port
# Usage: [ip:]port [mode] tls-cert=certificate.pem [options]
#
# The socket address where Squid will listen for client requests made
# over TLS or SSL connections. Commonly referred to as HTTPS.
#
# This is most useful for situations where you are running squid in
# accelerator mode and you want to do the TLS work at the accelerator
# level.
#
# You may specify multiple socket addresses on multiple lines,
# each with their own certificate and/or options.
#
# The tls-cert= option is mandatory on HTTPS ports.
#
# See http_port for a list of modes and options.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: ftp_port
# Enables Native FTP proxy by specifying the socket address where Squid
# listens for FTP client requests. See http_port directive for various
# ways to specify the listening address and mode.
#
# Usage: ftp_port address [mode] [options]
#
# WARNING: This is a new, experimental, complex feature that has seen
# limited production exposure. Some Squid modules (e.g., caching) do not
# currently work with native FTP proxying, and many features have not
# even been tested for compatibility. Test well before deploying!
#
# Native FTP proxying differs substantially from proxying HTTP requests
# with ftp:// URIs because Squid works as an FTP server and receives
# actual FTP commands (rather than HTTP requests with FTP URLs).
#
# Native FTP commands accepted at ftp_port are internally converted or
# wrapped into HTTP-like messages. The same happens to Native FTP
# responses received from FTP origin servers. Those HTTP-like messages
# are shoveled through regular access control and adaptation layers
# between the FTP client and the FTP origin server. This allows Squid to
# examine, adapt, block, and log FTP exchanges. Squid reuses most HTTP
# mechanisms when shoveling wrapped FTP messages. For example,
# http_access and adaptation_access directives are used.
#
# Modes:
#
# intercept Same as http_port intercept. The FTP origin address is
# determined based on the intended destination of the
# intercepted connection.
#
# tproxy Support Linux TPROXY for spoofing outgoing
# connections using the client IP address.
# NP: disables authentication and maybe IPv6 on the port.
#
# By default (i.e., without an explicit mode option), Squid extracts the
# FTP origin address from the login@origin parameter of the FTP USER
# command. Many popular FTP clients support such native FTP proxying.
#
# Options:
#
# name=token Specifies an internal name for the port. Defaults to
# the port address. Usable with myportname ACL.
#
# ftp-track-dirs
# Enables tracking of FTP directories by injecting extra
# PWD commands and adjusting Request-URI (in wrapping
# HTTP requests) to reflect the current FTP server
# directory. Tracking is disabled by default.
#
# protocol=FTP Protocol to reconstruct accelerated and intercepted
# requests with. Defaults to FTP. No other accepted
# values have been tested with. An unsupported value
# results in a FATAL error. Accepted values are FTP,
# HTTP (or HTTP/1.1), and HTTPS (or HTTPS/1.1).
#
# Other http_port modes and options that are not specific to HTTP and
# HTTPS may also work.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: tcp_outgoing_tos
# Allows you to select a TOS/Diffserv value for packets outgoing
# on the server side, based on an ACL.
#
# tcp_outgoing_tos ds-field [!]aclname ...
#
# Example where normal_service_net uses the TOS value 0x00
# and good_service_net uses 0x20
#
# acl normal_service_net src 10.0.0.0/24
# acl good_service_net src 10.0.1.0/24
# tcp_outgoing_tos 0x00 normal_service_net
# tcp_outgoing_tos 0x20 good_service_net
#
# TOS/DSCP values really only have local significance - so you should
# know what you're specifying. For more information, see RFC2474,
# RFC2475, and RFC3260.
#
# The TOS/DSCP byte must be exactly that - a octet value 0 - 255, or
# "default" to use whatever default your host has.
# Note that only multiples of 4 are usable as the two rightmost bits have
# been redefined for use by ECN (RFC 3168 section 23.1).
# The squid parser will enforce this by masking away the ECN bits.
#
# Processing proceeds in the order specified, and stops at first fully
# matching line.
#
# Only fast ACLs are supported.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: clientside_tos
# Allows you to select a TOS/DSCP value for packets being transmitted
# on the client-side, based on an ACL.
#
# clientside_tos ds-field [!]aclname ...
#
# Example where normal_service_net uses the TOS value 0x00
# and good_service_net uses 0x20
#
# acl normal_service_net src 10.0.0.0/24
# acl good_service_net src 10.0.1.0/24
# clientside_tos 0x00 normal_service_net
# clientside_tos 0x20 good_service_net
#
# Note: This feature is incompatible with qos_flows. Any TOS values set here
# will be overwritten by TOS values in qos_flows.
#
# The TOS/DSCP byte must be exactly that - a octet value 0 - 255, or
# "default" to use whatever default your host has.
# Note that only multiples of 4 are usable as the two rightmost bits have
# been redefined for use by ECN (RFC 3168 section 23.1).
# The squid parser will enforce this by masking away the ECN bits.
#
# This clause only supports fast acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: tcp_outgoing_mark
# Note: This option is only available if Squid is rebuilt with the
# Packet MARK (Linux)
#
# Allows you to apply a Netfilter mark value to outgoing packets
# on the server side, based on an ACL.
#
# tcp_outgoing_mark mark-value [!]aclname ...
#
# Example where normal_service_net uses the mark value 0x00
# and good_service_net uses 0x20
#
# acl normal_service_net src 10.0.0.0/24
# acl good_service_net src 10.0.1.0/24
# tcp_outgoing_mark 0x00 normal_service_net
# tcp_outgoing_mark 0x20 good_service_net
#
# Only fast ACLs are supported.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: mark_client_packet
# Note: This option is only available if Squid is rebuilt with the
# Packet MARK (Linux)
#
# Allows you to apply a Netfilter MARK value to packets being transmitted
# on the client-side, based on an ACL.
#
# mark_client_packet mark-value [!]aclname ...
#
# Example where normal_service_net uses the MARK value 0x00
# and good_service_net uses 0x20
#
# acl normal_service_net src 10.0.0.0/24
# acl good_service_net src 10.0.1.0/24
# mark_client_packet 0x00 normal_service_net
# mark_client_packet 0x20 good_service_net
#
# Note: This feature is incompatible with qos_flows. Any mark values set here
# will be overwritten by mark values in qos_flows.
#
# This clause only supports fast acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: mark_client_connection
# Note: This option is only available if Squid is rebuilt with the
# Packet MARK (Linux)
#
# Allows you to apply a Netfilter CONNMARK value to a connection
# on the client-side, based on an ACL.
#
# mark_client_connection mark-value[/mask] [!]aclname ...
#
# The mark-value and mask are unsigned integers (hex, octal, or decimal).
# The mask may be used to preserve marking previously set by other agents
# (e.g., iptables).
#
# A matching rule replaces the CONNMARK value. If a mask is also
# specified, then the masked bits of the original value are zeroed, and
# the configured mark-value is ORed with that adjusted value.
# For example, applying a mark-value 0xAB/0xF to 0x5F CONNMARK, results
# in a 0xFB marking (rather than a 0xAB or 0x5B).
#
# This directive semantics is similar to iptables --set-mark rather than
# --set-xmark functionality.
#
# The directive does not interfere with qos_flows (which uses packet MARKs,
# not CONNMARKs).
#
# Example where squid marks intercepted FTP connections:
#
# acl proto_ftp proto FTP
# mark_client_connection 0x200/0xff00 proto_ftp
#
# This clause only supports fast acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: qos_flows
# Allows you to select a TOS/DSCP value to mark outgoing
# connections to the client, based on where the reply was sourced.
# For platforms using netfilter, allows you to set a netfilter mark
# value instead of, or in addition to, a TOS value.
#
# By default this functionality is disabled. To enable it with the default
# settings simply use "qos_flows mark" or "qos_flows tos". Default
# settings will result in the netfilter mark or TOS value being copied
# from the upstream connection to the client. Note that it is the connection
# CONNMARK value not the packet MARK value that is copied.
#
# It is not currently possible to copy the mark or TOS value from the
# client to the upstream connection request.
#
# TOS values really only have local significance - so you should
# know what you're specifying. For more information, see RFC2474,
# RFC2475, and RFC3260.
#
# The TOS/DSCP byte must be exactly that - a octet value 0 - 255.
# Note that only multiples of 4 are usable as the two rightmost bits have
# been redefined for use by ECN (RFC 3168 section 23.1).
# The squid parser will enforce this by masking away the ECN bits.
#
# Mark values can be any unsigned 32-bit integer value.
#
# This setting is configured by setting the following values:
#
# tos|mark Whether to set TOS or netfilter mark values
#
# local-hit=0xFF Value to mark local cache hits.
#
# sibling-hit=0xFF Value to mark hits from sibling peers.
#
# parent-hit=0xFF Value to mark hits from parent peers.
#
# miss=0xFF[/mask] Value to mark cache misses. Takes precedence
# over the preserve-miss feature (see below), unless
# mask is specified, in which case only the bits
# specified in the mask are written.
#
# The TOS variant of the following features are only possible on Linux
# and require your kernel to be patched with the TOS preserving ZPH
# patch, available from http://zph.bratcheda.org
# No patch is needed to preserve the netfilter mark, which will work
# with all variants of netfilter.
#
# disable-preserve-miss
# This option disables the preservation of the TOS or netfilter
# mark. By default, the existing TOS or netfilter mark value of
# the response coming from the remote server will be retained
# and masked with miss-mark.
# NOTE: in the case of a netfilter mark, the mark must be set on
# the connection (using the CONNMARK target) not on the packet
# (MARK target).
#
# miss-mask=0xFF
# Allows you to mask certain bits in the TOS or mark value
# received from the remote server, before copying the value to
# the TOS sent towards clients.
# Default for tos: 0xFF (TOS from server is not changed).
# Default for mark: 0xFFFFFFFF (mark from server is not changed).
#
# All of these features require the --enable-zph-qos compilation flag
# (enabled by default). Netfilter marking also requires the
# libnetfilter_conntrack libraries (--with-netfilter-conntrack) and
# libcap 2.09+ (--with-libcap).
#
#Default:
# none
# TAG: tcp_outgoing_address
# Allows you to map requests to different outgoing IP addresses
# based on the username or source address of the user making
# the request.
#
# tcp_outgoing_address ipaddr [[!]aclname] ...
#
# For example;
# Forwarding clients with dedicated IPs for certain subnets.
#
# acl normal_service_net src 10.0.0.0/24
# acl good_service_net src 10.0.2.0/24
#
# tcp_outgoing_address 2001:db8::c001 good_service_net
# tcp_outgoing_address 10.1.0.2 good_service_net
#
# tcp_outgoing_address 2001:db8::beef normal_service_net
# tcp_outgoing_address 10.1.0.1 normal_service_net
#
# tcp_outgoing_address 2001:db8::1
# tcp_outgoing_address 10.1.0.3
#
# Processing proceeds in the order specified, and stops at first fully
# matching line.
#
# Squid will add an implicit IP version test to each line.
# Requests going to IPv4 websites will use the outgoing 10.1.0.* addresses.
# Requests going to IPv6 websites will use the outgoing 2001:db8:* addresses.
#
#
# NOTE: The use of this directive using client dependent ACLs is
# incompatible with the use of server side persistent connections. To
# ensure correct results it is best to set server_persistent_connections
# to off when using this directive in such configurations.
#
# NOTE: The use of this directive to set a local IP on outgoing TCP links
# is incompatible with using TPROXY to set client IP out outbound TCP links.
# When needing to contact peers use the no-tproxy cache_peer option and the
# client_dst_passthru directive re-enable normal forwarding such as this.
#
# This clause only supports fast acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#Default:
# Address selection is performed by the operating system.
# TAG: host_verify_strict
# Regardless of this option setting, when dealing with intercepted
# traffic, Squid always verifies that the destination IP address matches
# the Host header domain or IP (called 'authority form URL').
#
# This enforcement is performed to satisfy a MUST-level requirement in
# RFC 2616 section 14.23: "The Host field value MUST represent the naming
# authority of the origin server or gateway given by the original URL".
#
# When set to ON:
# Squid always responds with an HTTP 409 (Conflict) error
# page and logs a security warning if there is no match.
#
# Squid verifies that the destination IP address matches
# the Host header for forward-proxy and reverse-proxy traffic
# as well. For those traffic types, Squid also enables the
# following checks, comparing the corresponding Host header
# and Request-URI components:
#
# * The host names (domain or IP) must be identical,
# but valueless or missing Host header disables all checks.
# For the two host names to match, both must be either IP
# or FQDN.
#
# * Port numbers must be identical, but if a port is missing
# the scheme-default port is assumed.
#
#
# When set to OFF (the default):
# Squid allows suspicious requests to continue but logs a
# security warning and blocks caching of the response.
#
# * Forward-proxy traffic is not checked at all.
#
# * Reverse-proxy traffic is not checked at all.
#
# * Intercepted traffic which passes verification is handled
# according to client_dst_passthru.
#
# * Intercepted requests which fail verification are sent
# to the client original destination instead of DIRECT.
# This overrides 'client_dst_passthru off'.
#
# For now suspicious intercepted CONNECT requests are always
# responded to with an HTTP 409 (Conflict) error page.
#
#
# SECURITY NOTE:
#
# As described in CVE-2009-0801 when the Host: header alone is used
# to determine the destination of a request it becomes trivial for
# malicious scripts on remote websites to bypass browser same-origin
# security policy and sandboxing protections.
#
# The cause of this is that such applets are allowed to perform their
# own HTTP stack, in which case the same-origin policy of the browser
# sandbox only verifies that the applet tries to contact the same IP
# as from where it was loaded at the IP level. The Host: header may
# be different from the connected IP and approved origin.
#
#Default:
# host_verify_strict off
# TAG: client_dst_passthru
# With NAT or TPROXY intercepted traffic Squid may pass the request
# directly to the original client destination IP or seek a faster
# source using the HTTP Host header.
#
# Using Host to locate alternative servers can provide faster
# connectivity with a range of failure recovery options.
# But can also lead to connectivity trouble when the client and
# server are attempting stateful interactions unaware of the proxy.
#
# This option (on by default) prevents alternative DNS entries being
# located to send intercepted traffic DIRECT to an origin server.
# The clients original destination IP and port will be used instead.
#
# Regardless of this option setting, when dealing with intercepted
# traffic Squid will verify the Host: header and any traffic which
# fails Host verification will be treated as if this option were ON.
#
# see host_verify_strict for details on the verification process.
#Default:
# client_dst_passthru on
# TLS OPTIONS
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: tls_outgoing_options
# disable Do not support https:// URLs.
#
# cert=/path/to/client/certificate
# A client X.509 certificate to use when connecting.
#
# key=/path/to/client/private_key
# The private key corresponding to the cert= above.
#
# If key= is not specified cert= is assumed to
# reference a PEM file containing both the certificate
# and private key.
#
# cipher=... The list of valid TLS ciphers to use.
#
# min-version=1.N
# The minimum TLS protocol version to permit.
# To control SSLv3 use the options= parameter.
# Supported Values: 1.0 (default), 1.1, 1.2, 1.3
#
# options=... Specify various TLS/SSL implementation options.
#
# OpenSSL options most important are:
#
# NO_SSLv3 Disallow the use of SSLv3
#
# SINGLE_DH_USE
# Always create a new key when using
# temporary/ephemeral DH key exchanges
#
# NO_TICKET
# Disable use of RFC5077 session tickets.
# Some servers may have problems
# understanding the TLS extension due
# to ambiguous specification in RFC4507.
#
# ALL Enable various bug workarounds
# suggested as "harmless" by OpenSSL
# Be warned that this reduces SSL/TLS
# strength to some attacks.
#
# See the OpenSSL SSL_CTX_set_options documentation
# for a more complete list.
#
# GnuTLS options most important are:
#
# %NO_TICKETS
# Disable use of RFC5077 session tickets.
# Some servers may have problems
# understanding the TLS extension due
# to ambiguous specification in RFC4507.
#
# See the GnuTLS Priority Strings documentation
# for a more complete list.
# http://www.gnutls.org/manual/gnutls.html#Priority-Strings
#
#
# cafile= PEM file containing CA certificates to use when verifying
# the peer certificate. May be repeated to load multiple files.
#
# capath= A directory containing additional CA certificates to
# use when verifying the peer certificate.
# Requires OpenSSL or LibreSSL.
#
# crlfile=... A certificate revocation list file to use when
# verifying the peer certificate.
#
# flags=... Specify various flags modifying the TLS implementation:
#
# DONT_VERIFY_PEER
# Accept certificates even if they fail to
# verify.
# DONT_VERIFY_DOMAIN
# Don't verify the peer certificate
# matches the server name
#
# default-ca[=off]
# Whether to use the system Trusted CAs. Default is ON.
#
# domain= The peer name as advertised in its certificate.
# Used for verifying the correctness of the received peer
# certificate. If not specified the peer hostname will be
# used.
#Default:
# tls_outgoing_options min-version=1.0
# SSL OPTIONS
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: ssl_unclean_shutdown
# Note: This option is only available if Squid is rebuilt with the
# --with-openssl
#
# Some browsers (especially MSIE) bugs out on SSL shutdown
# messages.
#Default:
# ssl_unclean_shutdown off
# TAG: ssl_engine
# Note: This option is only available if Squid is rebuilt with the
# --with-openssl
#
# The OpenSSL engine to use. You will need to set this if you
# would like to use hardware SSL acceleration for example.
#
# Note: OpenSSL 3.0 and newer do not provide Engine support.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: sslproxy_session_ttl
# Note: This option is only available if Squid is rebuilt with the
# --with-openssl
#
# Sets the timeout value for SSL sessions
#Default:
# sslproxy_session_ttl 300
# TAG: sslproxy_session_cache_size
# Note: This option is only available if Squid is rebuilt with the
# --with-openssl
#
# Sets the cache size to use for ssl session
#Default:
# sslproxy_session_cache_size 2 MB
# TAG: sslproxy_foreign_intermediate_certs
# Note: This option is only available if Squid is rebuilt with the
# --with-openssl
#
# Many origin servers fail to send their full server certificate
# chain for verification, assuming the client already has or can
# easily locate any missing intermediate certificates.
#
# Squid uses the certificates from the specified file to fill in
# these missing chains when trying to validate origin server
# certificate chains.
#
# The file is expected to contain zero or more PEM-encoded
# intermediate certificates. These certificates are not treated
# as trusted root certificates, and any self-signed certificate in
# this file will be ignored.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: sslproxy_cert_sign_hash
# Note: This option is only available if Squid is rebuilt with the
# --with-openssl
#
# Sets the hashing algorithm to use when signing generated certificates.
# Valid algorithm names depend on the OpenSSL library used. The following
# names are usually available: sha1, sha256, sha512, and md5. Please see
# your OpenSSL library manual for the available hashes. By default, Squids
# that support this option use sha256 hashes.
#
# Squid does not forcefully purge cached certificates that were generated
# with an algorithm other than the currently configured one. They remain
# in the cache, subject to the regular cache eviction policy, and become
# useful if the algorithm changes again.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: ssl_bump
# Note: This option is only available if Squid is rebuilt with the
# --with-openssl
#
# This option is consulted when a CONNECT request is received on
# an http_port (or a new connection is intercepted at an
# https_port), provided that port was configured with an ssl-bump
# flag. The subsequent data on the connection is either treated as
# HTTPS and decrypted OR tunneled at TCP level without decryption,
# depending on the first matching bumping "action".
#
# ssl_bump <action> [!]acl ...
#
# The following bumping actions are currently supported:
#
# splice
# Become a TCP tunnel without decrypting proxied traffic.
# This is the default action.
#
# bump
# When used on step SslBump1, establishes a secure connection
# with the client first, then connect to the server.
# When used on step SslBump2 or SslBump3, establishes a secure
# connection with the server and, using a mimicked server
# certificate, with the client.
#
# peek
# Receive client (step SslBump1) or server (step SslBump2)
# certificate while preserving the possibility of splicing the
# connection. Peeking at the server certificate (during step 2)
# usually precludes bumping of the connection at step 3.
#
# stare
# Receive client (step SslBump1) or server (step SslBump2)
# certificate while preserving the possibility of bumping the
# connection. Staring at the server certificate (during step 2)
# usually precludes splicing of the connection at step 3.
#
# terminate
# Close client and server connections.
#
# Backward compatibility actions available at step SslBump1:
#
# client-first
# Bump the connection. Establish a secure connection with the
# client first, then connect to the server. This old mode does
# not allow Squid to mimic server SSL certificate and does not
# work with intercepted SSL connections.
#
# server-first
# Bump the connection. Establish a secure connection with the
# server first, then establish a secure connection with the
# client, using a mimicked server certificate. Works with both
# CONNECT requests and intercepted SSL connections, but does
# not allow to make decisions based on SSL handshake info.
#
# peek-and-splice
# Decide whether to bump or splice the connection based on
# client-to-squid and server-to-squid SSL hello messages.
# XXX: Remove.
#
# none
# Same as the "splice" action.
#
# All ssl_bump rules are evaluated at each of the supported bumping
# steps. Rules with actions that are impossible at the current step are
# ignored. The first matching ssl_bump action wins and is applied at the
# end of the current step. If no rules match, the splice action is used.
# See the at_step ACL for a list of the supported SslBump steps.
#
# This clause supports both fast and slow acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#
# See also: http_port ssl-bump, https_port ssl-bump, and acl at_step.
#
#
# # Example: Bump all TLS connections except those originating from
# # localhost or those going to example.com.
#
# acl broken_sites ssl::server_name .example.com
# ssl_bump splice localhost
# ssl_bump splice broken_sites
# ssl_bump bump all
#Default:
# Become a TCP tunnel without decrypting proxied traffic.
# TAG: sslproxy_cert_error
# Note: This option is only available if Squid is rebuilt with the
# --with-openssl
#
# Use this ACL to bypass server certificate validation errors.
#
# For example, the following lines will bypass all validation errors
# when talking to servers for example.com. All other
# validation errors will result in ERR_SECURE_CONNECT_FAIL error.
#
# acl BrokenButTrustedServers dstdomain example.com
# sslproxy_cert_error allow BrokenButTrustedServers
# sslproxy_cert_error deny all
#
# This clause only supports fast acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
# Using slow acl types may result in server crashes
#
# Without this option, all server certificate validation errors
# terminate the transaction to protect Squid and the client.
#
# SQUID_X509_V_ERR_INFINITE_VALIDATION error cannot be bypassed
# but should not happen unless your OpenSSL library is buggy.
#
# SECURITY WARNING:
# Bypassing validation errors is dangerous because an
# error usually implies that the server cannot be trusted
# and the connection may be insecure.
#
# See also: sslproxy_flags and DONT_VERIFY_PEER.
#Default:
# Server certificate errors terminate the transaction.
# TAG: sslproxy_cert_sign
# Note: This option is only available if Squid is rebuilt with the
# --with-openssl
#
#
# sslproxy_cert_sign <signing algorithm> acl ...
#
# The following certificate signing algorithms are supported:
#
# signTrusted
# Sign using the configured CA certificate which is usually
# placed in and trusted by end-user browsers. This is the
# default for trusted origin server certificates.
#
# signUntrusted
# Sign to guarantee an X509_V_ERR_CERT_UNTRUSTED browser error.
# This is the default for untrusted origin server certificates
# that are not self-signed (see ssl::certUntrusted).
#
# signSelf
# Sign using a self-signed certificate with the right CN to
# generate a X509_V_ERR_DEPTH_ZERO_SELF_SIGNED_CERT error in the
# browser. This is the default for self-signed origin server
# certificates (see ssl::certSelfSigned).
#
# This clause only supports fast acl types.
#
# When sslproxy_cert_sign acl(s) match, Squid uses the corresponding
# signing algorithm to generate the certificate and ignores all
# subsequent sslproxy_cert_sign options (the first match wins). If no
# acl(s) match, the default signing algorithm is determined by errors
# detected when obtaining and validating the origin server certificate.
#
# WARNING: SQUID_X509_V_ERR_DOMAIN_MISMATCH and ssl:certDomainMismatch can
# be used with sslproxy_cert_adapt, but if and only if Squid is bumping a
# CONNECT request that carries a domain name. In all other cases (CONNECT
# to an IP address or an intercepted SSL connection), Squid cannot detect
# the domain mismatch at certificate generation time when
# bump-server-first is used.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: sslproxy_cert_adapt
# Note: This option is only available if Squid is rebuilt with the
# --with-openssl
#
#
# sslproxy_cert_adapt <adaptation algorithm> acl ...
#
# The following certificate adaptation algorithms are supported:
#
# setValidAfter
# Sets the "Not After" property to the "Not After" property of
# the CA certificate used to sign generated certificates.
#
# setValidBefore
# Sets the "Not Before" property to the "Not Before" property of
# the CA certificate used to sign generated certificates.
#
# setCommonName or setCommonName{CN}
# Sets Subject.CN property to the host name specified as a
# CN parameter or, if no explicit CN parameter was specified,
# extracted from the CONNECT request. It is a misconfiguration
# to use setCommonName without an explicit parameter for
# intercepted or tproxied SSL connections.
#
# This clause only supports fast acl types.
#
# Squid first groups sslproxy_cert_adapt options by adaptation algorithm.
# Within a group, when sslproxy_cert_adapt acl(s) match, Squid uses the
# corresponding adaptation algorithm to generate the certificate and
# ignores all subsequent sslproxy_cert_adapt options in that algorithm's
# group (i.e., the first match wins within each algorithm group). If no
# acl(s) match, the default mimicking action takes place.
#
# WARNING: SQUID_X509_V_ERR_DOMAIN_MISMATCH and ssl:certDomainMismatch can
# be used with sslproxy_cert_adapt, but if and only if Squid is bumping a
# CONNECT request that carries a domain name. In all other cases (CONNECT
# to an IP address or an intercepted SSL connection), Squid cannot detect
# the domain mismatch at certificate generation time when
# bump-server-first is used.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: sslpassword_program
# Note: This option is only available if Squid is rebuilt with the
# --with-openssl
#
# Specify a program used for entering SSL key passphrases
# when using encrypted SSL certificate keys. If not specified
# keys must either be unencrypted, or Squid started with the -N
# option to allow it to query interactively for the passphrase.
#
# The key file name is given as argument to the program allowing
# selection of the right password if you have multiple encrypted
# keys.
#Default:
# none
# OPTIONS RELATING TO EXTERNAL SSL_CRTD
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: sslcrtd_program
# Note: This option is only available if Squid is rebuilt with the
# --enable-ssl-crtd
#
# Specify the location and options of the executable for certificate
# generator.
#
# /usr/lib/squid/security_file_certgen program can use a disk cache to improve response
# times on repeated requests. To enable caching, specify -s and -M
# parameters. If those parameters are not given, the program generates
# a new certificate on every request.
#
# For more information use:
# /usr/lib/squid/security_file_certgen -h
#Default:
# sslcrtd_program /usr/lib/squid/security_file_certgen -s /var/spool/squid/ssl_db -M 4MB
# TAG: sslcrtd_children
# Note: This option is only available if Squid is rebuilt with the
# --enable-ssl-crtd
#
# Specifies the maximum number of certificate generation processes that
# Squid may spawn (numberofchildren) and several related options. Using
# too few of these helper processes (a.k.a. "helpers") creates request
# queues. Using too many helpers wastes your system resources. Squid
# does not support spawning more than 32 helpers.
#
# Usage: numberofchildren [option]...
#
# The startup= and idle= options allow some measure of skew in your
# tuning.
#
# startup=N
#
# Sets the minimum number of processes to spawn when Squid
# starts or reconfigures. When set to zero the first request will
# cause spawning of the first child process to handle it.
#
# Starting too few children temporary slows Squid under load while it
# tries to spawn enough additional processes to cope with traffic.
#
# idle=N
#
# Sets a minimum of how many processes Squid is to try and keep available
# at all times. When traffic begins to rise above what the existing
# processes can handle this many more will be spawned up to the maximum
# configured. A minimum setting of 1 is required.
#
# queue-size=N
#
# Sets the maximum number of queued requests. A request is queued when
# no existing child is idle and no new child can be started due to
# numberofchildren limit. If the queued requests exceed queue size for
# more than 3 minutes squid aborts its operation. The default value is
# set to 2*numberofchildren.
#
# You must have at least one ssl_crtd process.
#Default:
# sslcrtd_children 32 startup=5 idle=1
# TAG: sslcrtvalidator_program
# Note: This option is only available if Squid is rebuilt with the
# --with-openssl
#
# Specify the location and options of the executable for ssl_crt_validator
# process.
#
# Usage: sslcrtvalidator_program [ttl=n] [cache=n] path ...
#
# Options:
# ttl=n TTL in seconds for cached results. The default is 60 secs
# cache=n limit the result cache size. The default value is 2048
#Default:
# none
# TAG: sslcrtvalidator_children
# Note: This option is only available if Squid is rebuilt with the
# --with-openssl
#
# Specifies the maximum number of certificate validation processes that
# Squid may spawn (numberofchildren) and several related options. Using
# too few of these helper processes (a.k.a. "helpers") creates request
# queues. Using too many helpers wastes your system resources. Squid
# does not support spawning more than 32 helpers.
#
# Usage: numberofchildren [option]...
#
# The startup= and idle= options allow some measure of skew in your
# tuning.
#
# startup=N
#
# Sets the minimum number of processes to spawn when Squid
# starts or reconfigures. When set to zero the first request will
# cause spawning of the first child process to handle it.
#
# Starting too few children temporary slows Squid under load while it
# tries to spawn enough additional processes to cope with traffic.
#
# idle=N
#
# Sets a minimum of how many processes Squid is to try and keep available
# at all times. When traffic begins to rise above what the existing
# processes can handle this many more will be spawned up to the maximum
# configured. A minimum setting of 1 is required.
#
# concurrency=
#
# The number of requests each certificate validator helper can handle in
# parallel. A value of 0 indicates the certficate validator does not
# support concurrency. Defaults to 1.
#
# When this directive is set to a value >= 1 then the protocol
# used to communicate with the helper is modified to include
# a request ID in front of the request/response. The request
# ID from the request must be echoed back with the response
# to that request.
#
# queue-size=N
#
# Sets the maximum number of queued requests. A request is queued when
# no existing child can accept it due to concurrency limit and no new
# child can be started due to numberofchildren limit. If the queued
# requests exceed queue size for more than 3 minutes squid aborts its
# operation. The default value is set to 2*numberofchildren.
#
# You must have at least one ssl_crt_validator process.
#Default:
# sslcrtvalidator_children 32 startup=5 idle=1 concurrency=1
# OPTIONS WHICH AFFECT THE NEIGHBOR SELECTION ALGORITHM
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: cache_peer
# To specify other caches in a hierarchy, use the format:
#
# cache_peer hostname type http-port icp-port [options]
#
# For example,
#
# # proxy icp
# # hostname type port port options
# # -------------------- -------- ----- ----- -----------
# cache_peer parent.foo.net parent 3128 3130 default
# cache_peer sib1.foo.net sibling 3128 3130 proxy-only
# cache_peer sib2.foo.net sibling 3128 3130 proxy-only
# cache_peer example.com parent 80 0 default
# cache_peer cdn.example.com sibling 3128 0
#
# type: either 'parent', 'sibling', or 'multicast'.
#
# proxy-port: The port number where the peer accept HTTP requests.
# For other Squid proxies this is usually 3128
# For web servers this is usually 80
#
# icp-port: Used for querying neighbor caches about objects.
# Set to 0 if the peer does not support ICP or HTCP.
# See ICP and HTCP options below for additional details.
#
#
# ==== ICP OPTIONS ====
#
# You MUST also set icp_port and icp_access explicitly when using these options.
# The defaults will prevent peer traffic using ICP.
#
#
# no-query Disable ICP queries to this neighbor.
#
# multicast-responder
# Indicates the named peer is a member of a multicast group.
# ICP queries will not be sent directly to the peer, but ICP
# replies will be accepted from it.
#
# closest-only Indicates that, for ICP_OP_MISS replies, we'll only forward
# CLOSEST_PARENT_MISSes and never FIRST_PARENT_MISSes.
#
# background-ping
# To only send ICP queries to this neighbor infrequently.
# This is used to keep the neighbor round trip time updated
# and is usually used in conjunction with weighted-round-robin.
#
#
# ==== HTCP OPTIONS ====
#
# You MUST also set htcp_port and htcp_access explicitly when using these options.
# The defaults will prevent peer traffic using HTCP.
#
#
# htcp Send HTCP, instead of ICP, queries to the neighbor.
# You probably also want to set the "icp-port" to 4827
# instead of 3130. This directive accepts a comma separated
# list of options described below.
#
# htcp=oldsquid Send HTCP to old Squid versions (2.5 or earlier).
#
# htcp=no-clr Send HTCP to the neighbor but without
# sending any CLR requests. This cannot be used with
# only-clr.
#
# htcp=only-clr Send HTCP to the neighbor but ONLY CLR requests.
# This cannot be used with no-clr.
#
# htcp=no-purge-clr
# Send HTCP to the neighbor including CLRs but only when
# they do not result from PURGE requests.
#
# htcp=forward-clr
# Forward any HTCP CLR requests this proxy receives to the peer.
#
#
# ==== PEER SELECTION METHODS ====
#
# The default peer selection method is ICP, with the first responding peer
# being used as source. These options can be used for better load balancing.
#
#
# default This is a parent cache which can be used as a "last-resort"
# if a peer cannot be located by any of the peer-selection methods.
# If specified more than once, only the first is used.
#
# round-robin Load-Balance parents which should be used in a round-robin
# fashion in the absence of any ICP queries.
# weight=N can be used to add bias.
#
# weighted-round-robin
# Load-Balance parents which should be used in a round-robin
# fashion with the frequency of each parent being based on the
# round trip time. Closer parents are used more often.
# Usually used for background-ping parents.
# weight=N can be used to add bias.
#
# carp Load-Balance parents which should be used as a CARP array.
# The requests will be distributed among the parents based on the
# CARP load balancing hash function based on their weight.
#
# userhash Load-balance parents based on the client proxy_auth or ident username.
#
# sourcehash Load-balance parents based on the client source IP.
#
# multicast-siblings
# To be used only for cache peers of type "multicast".
# ALL members of this multicast group have "sibling"
# relationship with it, not "parent". This is to a multicast
# group when the requested object would be fetched only from
# a "parent" cache, anyway. It's useful, e.g., when
# configuring a pool of redundant Squid proxies, being
# members of the same multicast group.
#
#
# ==== PEER SELECTION OPTIONS ====
#
# weight=N use to affect the selection of a peer during any weighted
# peer-selection mechanisms.
# The weight must be an integer; default is 1,
# larger weights are favored more.
# This option does not affect parent selection if a peering
# protocol is not in use.
#
# basetime=N Specify a base amount to be subtracted from round trip
# times of parents.
# It is subtracted before division by weight in calculating
# which parent to fectch from. If the rtt is less than the
# base time the rtt is set to a minimal value.
#
# ttl=N Specify a TTL to use when sending multicast ICP queries
# to this address.
# Only useful when sending to a multicast group.
# Because we don't accept ICP replies from random
# hosts, you must configure other group members as
# peers with the 'multicast-responder' option.
#
# no-delay To prevent access to this neighbor from influencing the
# delay pools.
#
# digest-url=URL Tell Squid to fetch the cache digest (if digests are
# enabled) for this host from the specified URL rather
# than the Squid default location.
#
#
# ==== CARP OPTIONS ====
#
# carp-key=key-specification
# use a different key than the full URL to hash against the peer.
# the key-specification is a comma-separated list of the keywords
# scheme, host, port, path, params
# Order is not important.
#
# ==== ACCELERATOR / REVERSE-PROXY OPTIONS ====
#
# originserver Causes this parent to be contacted as an origin server.
# Meant to be used in accelerator setups when the peer
# is a web server.
#
# forceddomain=name
# Set the Host header of requests forwarded to this peer.
# Useful in accelerator setups where the server (peer)
# expects a certain domain name but clients may request
# others. ie example.com or www.example.com
#
# no-digest Disable request of cache digests.
#
# no-netdb-exchange
# Disables requesting ICMP RTT database (NetDB).
#
#
# ==== AUTHENTICATION OPTIONS ====
#
# login=user:password
# If this is a personal/workgroup proxy and your parent
# requires proxy authentication.
#
# Note: The string can include URL escapes (i.e. %20 for
# spaces). This also means % must be written as %%.
#
# login=PASSTHRU
# Send login details received from client to this peer.
# Both Proxy- and WWW-Authorization headers are passed
# without alteration to the peer.
# Authentication is not required by Squid for this to work.
#
# Note: This will pass any form of authentication but
# only Basic auth will work through a proxy unless the
# connection-auth options are also used.
#
# login=PASS Send login details received from client to this peer.
# Authentication is not required by this option.
#
# If there are no client-provided authentication headers
# to pass on, but username and password are available
# from an external ACL user= and password= result tags
# they may be sent instead.
#
# Note: To combine this with proxy_auth both proxies must
# share the same user database as HTTP only allows for
# a single login (one for proxy, one for origin server).
# Also be warned this will expose your users proxy
# password to the peer. USE WITH CAUTION
#
# login=*:password
# Send the username to the upstream cache, but with a
# fixed password. This is meant to be used when the peer
# is in another administrative domain, but it is still
# needed to identify each user.
# The star can optionally be followed by some extra
# information which is added to the username. This can
# be used to identify this proxy to the peer, similar to
# the login=username:password option above.
#
# login=NEGOTIATE
# If this is a personal/workgroup proxy and your parent
# requires a secure proxy authentication.
# The first principal from the default keytab or defined by
# the environment variable KRB5_KTNAME will be used.
#
# WARNING: The connection may transmit requests from multiple
# clients. Negotiate often assumes end-to-end authentication
# and a single-client. Which is not strictly true here.
#
# login=NEGOTIATE:principal_name
# If this is a personal/workgroup proxy and your parent
# requires a secure proxy authentication.
# The principal principal_name from the default keytab or
# defined by the environment variable KRB5_KTNAME will be
# used.
#
# WARNING: The connection may transmit requests from multiple
# clients. Negotiate often assumes end-to-end authentication
# and a single-client. Which is not strictly true here.
#
# connection-auth=on|off
# Tell Squid that this peer does or not support Microsoft
# connection oriented authentication, and any such
# challenges received from there should be ignored.
# Default is auto to automatically determine the status
# of the peer.
#
# auth-no-keytab
# Do not use a keytab to authenticate to a peer when
# login=NEGOTIATE is specified. Let the GSSAPI
# implementation determine which already existing
# credentials cache to use instead.
#
#
# ==== SSL / HTTPS / TLS OPTIONS ====
#
# tls Encrypt connections to this peer with TLS.
#
# sslcert=/path/to/ssl/certificate
# A client X.509 certificate to use when connecting to
# this peer.
#
# sslkey=/path/to/ssl/key
# The private key corresponding to sslcert above.
#
# If sslkey= is not specified sslcert= is assumed to
# reference a PEM file containing both the certificate
# and private key.
#
# Notes:
#
# On Debian/Ubuntu systems a default snakeoil certificate is
# available in /etc/ssl and users can set:
#
# sslcert=/etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem
#
# and
#
# sslkey=/etc/ssl/private/ssl-cert-snakeoil.key
#
# for testing.
#
# sslcipher=... The list of valid SSL ciphers to use when connecting
# to this peer.
#
# tls-min-version=1.N
# The minimum TLS protocol version to permit. To control
# SSLv3 use the tls-options= parameter.
# Supported Values: 1.0 (default), 1.1, 1.2
#
# tls-options=... Specify various TLS implementation options.
#
# OpenSSL options most important are:
#
# NO_SSLv3 Disallow the use of SSLv3
#
# SINGLE_DH_USE
# Always create a new key when using
# temporary/ephemeral DH key exchanges
#
# NO_TICKET
# Disable use of RFC5077 session tickets.
# Some servers may have problems
# understanding the TLS extension due
# to ambiguous specification in RFC4507.
#
# ALL Enable various bug workarounds
# suggested as "harmless" by OpenSSL
# Be warned that this reduces SSL/TLS
# strength to some attacks.
#
# See the OpenSSL SSL_CTX_set_options documentation for a
# more complete list.
#
# GnuTLS options most important are:
#
# %NO_TICKETS
# Disable use of RFC5077 session tickets.
# Some servers may have problems
# understanding the TLS extension due
# to ambiguous specification in RFC4507.
#
# See the GnuTLS Priority Strings documentation
# for a more complete list.
# http://www.gnutls.org/manual/gnutls.html#Priority-Strings
#
# tls-cafile= PEM file containing CA certificates to use when verifying
# the peer certificate. May be repeated to load multiple files.
#
# sslcapath=... A directory containing additional CA certificates to
# use when verifying the peer certificate.
# Requires OpenSSL or LibreSSL.
#
# sslcrlfile=... A certificate revocation list file to use when
# verifying the peer certificate.
#
# sslflags=... Specify various flags modifying the SSL implementation:
#
# DONT_VERIFY_PEER
# Accept certificates even if they fail to
# verify.
#
# DONT_VERIFY_DOMAIN
# Don't verify the peer certificate
# matches the server name
#
# ssldomain= The peer name as advertised in it's certificate.
# Used for verifying the correctness of the received peer
# certificate. If not specified the peer hostname will be
# used.
#
# front-end-https[=off|on|auto]
# Enable the "Front-End-Https: On" header needed when
# using Squid as a SSL frontend in front of Microsoft OWA.
# See MS KB document Q307347 for details on this header.
# If set to auto the header will only be added if the
# request is forwarded as a https:// URL.
#
# tls-default-ca[=off]
# Whether to use the system Trusted CAs. Default is ON.
#
# tls-no-npn Do not use the TLS NPN extension to advertise HTTP/1.1.
#
# ==== GENERAL OPTIONS ====
#
# connect-timeout=N
# A peer-specific connect timeout.
# Also see the peer_connect_timeout directive.
#
# connect-fail-limit=N
# How many times connecting to a peer must fail before
# it is marked as down. Standby connection failures
# count towards this limit. Default is 10.
#
# allow-miss Disable Squid's use of only-if-cached when forwarding
# requests to siblings. This is primarily useful when
# icp_hit_stale is used by the sibling. Excessive use
# of this option may result in forwarding loops. One way
# to prevent peering loops when using this option, is to
# deny cache peer usage on requests from a peer:
# acl fromPeer ...
# cache_peer_access peerName deny fromPeer
#
# max-conn=N Limit the number of concurrent connections the Squid
# may open to this peer, including already opened idle
# and standby connections. There is no peer-specific
# connection limit by default.
#
# A peer exceeding the limit is not used for new
# requests unless a standby connection is available.
#
# max-conn currently works poorly with idle persistent
# connections: When a peer reaches its max-conn limit,
# and there are idle persistent connections to the peer,
# the peer may not be selected because the limiting code
# does not know whether Squid can reuse those idle
# connections.
#
# standby=N Maintain a pool of N "hot standby" connections to an
# UP peer, available for requests when no idle
# persistent connection is available (or safe) to use.
# By default and with zero N, no such pool is maintained.
# N must not exceed the max-conn limit (if any).
#
# At start or after reconfiguration, Squid opens new TCP
# standby connections until there are N connections
# available and then replenishes the standby pool as
# opened connections are used up for requests. A used
# connection never goes back to the standby pool, but
# may go to the regular idle persistent connection pool
# shared by all peers and origin servers.
#
# Squid never opens multiple new standby connections
# concurrently. This one-at-a-time approach minimizes
# flooding-like effect on peers. Furthermore, just a few
# standby connections should be sufficient in most cases
# to supply most new requests with a ready-to-use
# connection.
#
# Standby connections obey server_idle_pconn_timeout.
# For the feature to work as intended, the peer must be
# configured to accept and keep them open longer than
# the idle timeout at the connecting Squid, to minimize
# race conditions typical to idle used persistent
# connections. Default request_timeout and
# server_idle_pconn_timeout values ensure such a
# configuration.
#
# name=xxx Unique name for the peer.
# Required if you have multiple peers on the same host
# but different ports.
# This name can be used in cache_peer_access and similar
# directives to identify the peer.
# Can be used by outgoing access controls through the
# peername ACL type.
#
# no-tproxy Do not use the client-spoof TPROXY support when forwarding
# requests to this peer. Use normal address selection instead.
# This overrides the spoof_client_ip ACL.
#
# proxy-only objects fetched from the peer will not be stored locally.
#
#Default:
# none
# TAG: cache_peer_access
# Restricts usage of cache_peer proxies.
#
# Usage:
# cache_peer_access peer-name allow|deny [!]aclname ...
#
# For the required peer-name parameter, use either the value of the
# cache_peer name=value parameter or, if name=value is missing, the
# cache_peer hostname parameter.
#
# This directive narrows down the selection of peering candidates, but
# does not determine the order in which the selected candidates are
# contacted. That order is determined by the peer selection algorithms
# (see PEER SELECTION sections in the cache_peer documentation).
#
# If a deny rule matches, the corresponding peer will not be contacted
# for the current transaction -- Squid will not send ICP queries and
# will not forward HTTP requests to that peer. An allow match leaves
# the corresponding peer in the selection. The first match for a given
# peer wins for that peer.
#
# The relative order of cache_peer_access directives for the same peer
# matters. The relative order of any two cache_peer_access directives
# for different peers does not matter. To ease interpretation, it is a
# good idea to group cache_peer_access directives for the same peer
# together.
#
# A single cache_peer_access directive may be evaluated multiple times
# for a given transaction because individual peer selection algorithms
# may check it independently from each other. These redundant checks
# may be optimized away in future Squid versions.
#
# This clause only supports fast acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#
#Default:
# No peer usage restrictions.
# TAG: neighbor_type_domain
# Modify the cache_peer neighbor type when passing requests
# about specific domains to the peer.
#
# Usage:
# neighbor_type_domain neighbor parent|sibling domain domain ...
#
# For example:
# cache_peer foo.example.com parent 3128 3130
# neighbor_type_domain foo.example.com sibling .au .de
#
# The above configuration treats all requests to foo.example.com as a
# parent proxy unless the request is for a .au or .de ccTLD domain name.
#Default:
# The peer type from cache_peer directive is used for all requests to that peer.
# TAG: dead_peer_timeout (seconds)
# This controls how long Squid waits to declare a peer cache
# as "dead." If there are no ICP replies received in this
# amount of time, Squid will declare the peer dead and not
# expect to receive any further ICP replies. However, it
# continues to send ICP queries, and will mark the peer as
# alive upon receipt of the first subsequent ICP reply.
#
# This timeout also affects when Squid expects to receive ICP
# replies from peers. If more than 'dead_peer' seconds have
# passed since the last ICP reply was received, Squid will not
# expect to receive an ICP reply on the next query. Thus, if
# your time between requests is greater than this timeout, you
# will see a lot of requests sent DIRECT to origin servers
# instead of to your parents.
#Default:
# dead_peer_timeout 10 seconds
# TAG: forward_max_tries
# Limits the number of attempts to forward the request.
#
# For the purpose of this limit, Squid counts all high-level request
# forwarding attempts, including any same-destination retries after
# certain persistent connection failures and any attempts to use a
# different peer. However, low-level connection reopening attempts
# (enabled using connect_retries) are not counted.
#
# See also: forward_timeout and connect_retries.
#Default:
# forward_max_tries 25
# MEMORY CACHE OPTIONS
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: cache_mem (bytes)
# NOTE: THIS PARAMETER DOES NOT SPECIFY THE MAXIMUM PROCESS SIZE.
# IT ONLY PLACES A LIMIT ON HOW MUCH ADDITIONAL MEMORY SQUID WILL
# USE AS A MEMORY CACHE OF OBJECTS. SQUID USES MEMORY FOR OTHER
# THINGS AS WELL. SEE THE SQUID FAQ SECTION 8 FOR DETAILS.
#
# 'cache_mem' specifies the ideal amount of memory to be used
# for:
# * In-Transit objects
# * Hot Objects
# * Negative-Cached objects
#
# Data for these objects are stored in 4 KB blocks. This
# parameter specifies the ideal upper limit on the total size of
# 4 KB blocks allocated. In-Transit objects take the highest
# priority.
#
# In-transit objects have priority over the others. When
# additional space is needed for incoming data, negative-cached
# and hot objects will be released. In other words, the
# negative-cached and hot objects will fill up any unused space
# not needed for in-transit objects.
#
# If circumstances require, this limit will be exceeded.
# Specifically, if your incoming request rate requires more than
# 'cache_mem' of memory to hold in-transit objects, Squid will
# exceed this limit to satisfy the new requests. When the load
# decreases, blocks will be freed until the high-water mark is
# reached. Thereafter, blocks will be used to store hot
# objects.
#
# If shared memory caching is enabled, Squid does not use the shared
# cache space for in-transit objects, but they still consume as much
# local memory as they need. For more details about the shared memory
# cache, see memory_cache_shared.
#Default:
# cache_mem 256 MB
# TAG: maximum_object_size_in_memory (bytes)
# Objects greater than this size will not be attempted to kept in
# the memory cache. This should be set high enough to keep objects
# accessed frequently in memory to improve performance whilst low
# enough to keep larger objects from hoarding cache_mem.
#Default:
# maximum_object_size_in_memory 512 KB
# TAG: memory_cache_shared on|off
# Controls whether the memory cache is shared among SMP workers.
#
# The shared memory cache is meant to occupy cache_mem bytes and replace
# the non-shared memory cache, although some entities may still be
# cached locally by workers for now (e.g., internal and in-transit
# objects may be served from a local memory cache even if shared memory
# caching is enabled).
#
# By default, the memory cache is shared if and only if all of the
# following conditions are satisfied: Squid runs in SMP mode with
# multiple workers, cache_mem is positive, and Squid environment
# supports required IPC primitives (e.g., POSIX shared memory segments
# and GCC-style atomic operations).
#
# To avoid blocking locks, shared memory uses opportunistic algorithms
# that do not guarantee that every cachable entity that could have been
# shared among SMP workers will actually be shared.
#Default:
# "on" where supported if doing memory caching with multiple SMP workers.
# TAG: memory_cache_mode
# Controls which objects to keep in the memory cache (cache_mem)
#
# always Keep most recently fetched objects in memory (default)
#
# disk Only disk cache hits are kept in memory, which means
# an object must first be cached on disk and then hit
# a second time before cached in memory.
#
# network Only objects fetched from network is kept in memory
#Default:
# Keep the most recently fetched objects in memory
# TAG: memory_replacement_policy
# The memory replacement policy parameter determines which
# objects are purged from memory when memory space is needed.
#
# See cache_replacement_policy for details on algorithms.
#Default:
# memory_replacement_policy lru
# DISK CACHE OPTIONS
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: cache_replacement_policy
# The cache replacement policy parameter determines which
# objects are evicted (replaced) when disk space is needed.
#
# lru : Squid's original list based LRU policy
# heap GDSF : Greedy-Dual Size Frequency
# heap LFUDA: Least Frequently Used with Dynamic Aging
# heap LRU : LRU policy implemented using a heap
#
# Applies to any cache_dir lines listed below this directive.
#
# The LRU policies keeps recently referenced objects.
#
# The heap GDSF policy optimizes object hit rate by keeping smaller
# popular objects in cache so it has a better chance of getting a
# hit. It achieves a lower byte hit rate than LFUDA though since
# it evicts larger (possibly popular) objects.
#
# The heap LFUDA policy keeps popular objects in cache regardless of
# their size and thus optimizes byte hit rate at the expense of
# hit rate since one large, popular object will prevent many
# smaller, slightly less popular objects from being cached.
#
# Both policies utilize a dynamic aging mechanism that prevents
# cache pollution that can otherwise occur with frequency-based
# replacement policies.
#
# NOTE: if using the LFUDA replacement policy you should increase
# the value of maximum_object_size above its default of 4 MB to
# to maximize the potential byte hit rate improvement of LFUDA.
#
# For more information about the GDSF and LFUDA cache replacement
# policies see http://www.hpl.hp.com/techreports/1999/HPL-1999-69.html
# and http://fog.hpl.external.hp.com/techreports/98/HPL-98-173.html.
#Default:
# cache_replacement_policy lru
# TAG: minimum_object_size (bytes)
# Objects smaller than this size will NOT be saved on disk. The
# value is specified in bytes, and the default is 0 KB, which
# means all responses can be stored.
#Default:
# no limit
# TAG: maximum_object_size (bytes)
# Set the default value for max-size parameter on any cache_dir.
# The value is specified in bytes, and the default is 4 MB.
#
# If you wish to get a high BYTES hit ratio, you should probably
# increase this (one 32 MB object hit counts for 3200 10KB
# hits).
#
# If you wish to increase hit ratio more than you want to
# save bandwidth you should leave this low.
#
# NOTE: if using the LFUDA replacement policy you should increase
# this value to maximize the byte hit rate improvement of LFUDA!
# See cache_replacement_policy for a discussion of this policy.
#Default:
# maximum_object_size 4 MB
# TAG: cache_dir
# Format:
# cache_dir Type Directory-Name Fs-specific-data [options]
#
# You can specify multiple cache_dir lines to spread the
# cache among different disk partitions.
#
# Type specifies the kind of storage system to use. Only "ufs"
# is built by default. To enable any of the other storage systems
# see the --enable-storeio configure option.
#
# 'Directory' is a top-level directory where cache swap
# files will be stored. If you want to use an entire disk
# for caching, this can be the mount-point directory.
# The directory must exist and be writable by the Squid
# process. Squid will NOT create this directory for you.
#
# In SMP configurations, cache_dir must not precede the workers option
# and should use configuration macros or conditionals to give each
# worker interested in disk caching a dedicated cache directory.
#
#
# ==== The ufs store type ====
#
# "ufs" is the old well-known Squid storage format that has always
# been there.
#
# Usage:
# cache_dir ufs Directory-Name Mbytes L1 L2 [options]
#
# 'Mbytes' is the amount of disk space (MB) to use under this
# directory. The default is 100 MB. Change this to suit your
# configuration. Do NOT put the size of your disk drive here.
# Instead, if you want Squid to use the entire disk drive,
# subtract 20% and use that value.
#
# 'L1' is the number of first-level subdirectories which
# will be created under the 'Directory'. The default is 16.
#
# 'L2' is the number of second-level subdirectories which
# will be created under each first-level directory. The default
# is 256.
#
#
# ==== The aufs store type ====
#
# "aufs" uses the same storage format as "ufs", utilizing
# POSIX-threads to avoid blocking the main Squid process on
# disk-I/O. This was formerly known in Squid as async-io.
#
# Usage:
# cache_dir aufs Directory-Name Mbytes L1 L2 [options]
#
# see argument descriptions under ufs above
#
#
# ==== The diskd store type ====
#
# "diskd" uses the same storage format as "ufs", utilizing a
# separate process to avoid blocking the main Squid process on
# disk-I/O.
#
# Usage:
# cache_dir diskd Directory-Name Mbytes L1 L2 [options] [Q1=n] [Q2=n]
#
# see argument descriptions under ufs above
#
# Q1 specifies the number of unacknowledged I/O requests when Squid
# stops opening new files. If this many messages are in the queues,
# Squid won't open new files. Default is 64
#
# Q2 specifies the number of unacknowledged messages when Squid
# starts blocking. If this many messages are in the queues,
# Squid blocks until it receives some replies. Default is 72
#
# When Q1 < Q2 (the default), the cache directory is optimized
# for lower response time at the expense of a decrease in hit
# ratio. If Q1 > Q2, the cache directory is optimized for
# higher hit ratio at the expense of an increase in response
# time.
#
#
# ==== The rock store type ====
#
# Usage:
# cache_dir rock Directory-Name Mbytes [options]
#
# The Rock Store type is a database-style storage. All cached
# entries are stored in a "database" file, using fixed-size slots.
# A single entry occupies one or more slots.
#
# If possible, Squid using Rock Store creates a dedicated kid
# process called "disker" to avoid blocking Squid worker(s) on disk
# I/O. One disker kid is created for each rock cache_dir. Diskers
# are created only when Squid, running in daemon mode, has support
# for the IpcIo disk I/O module.
#
# swap-timeout=msec: Squid will not start writing a miss to or
# reading a hit from disk if it estimates that the swap operation
# will take more than the specified number of milliseconds. By
# default and when set to zero, disables the disk I/O time limit
# enforcement. Ignored when using blocking I/O module because
# blocking synchronous I/O does not allow Squid to estimate the
# expected swap wait time.
#
# max-swap-rate=swaps/sec: Artificially limits disk access using
# the specified I/O rate limit. Swap out requests that
# would cause the average I/O rate to exceed the limit are
# delayed. Individual swap in requests (i.e., hits or reads) are
# not delayed, but they do contribute to measured swap rate and
# since they are placed in the same FIFO queue as swap out
# requests, they may wait longer if max-swap-rate is smaller.
# This is necessary on file systems that buffer "too
# many" writes and then start blocking Squid and other processes
# while committing those writes to disk. Usually used together
# with swap-timeout to avoid excessive delays and queue overflows
# when disk demand exceeds available disk "bandwidth". By default
# and when set to zero, disables the disk I/O rate limit
# enforcement. Currently supported by IpcIo module only.
#
# slot-size=bytes: The size of a database "record" used for
# storing cached responses. A cached response occupies at least
# one slot and all database I/O is done using individual slots so
# increasing this parameter leads to more disk space waste while
# decreasing it leads to more disk I/O overheads. Should be a
# multiple of your operating system I/O page size. Defaults to
# 16KBytes. A housekeeping header is stored with each slot and
# smaller slot-sizes will be rejected. The header is smaller than
# 100 bytes.
#
#
# ==== COMMON OPTIONS ====
#
# no-store no new objects should be stored to this cache_dir.
#
# min-size=n the minimum object size in bytes this cache_dir
# will accept. It's used to restrict a cache_dir
# to only store large objects (e.g. AUFS) while
# other stores are optimized for smaller objects
# (e.g. Rock).
# Defaults to 0.
#
# max-size=n the maximum object size in bytes this cache_dir
# supports.
# The value in maximum_object_size directive sets
# the default unless more specific details are
# available (ie a small store capacity).
#
# Note: To make optimal use of the max-size limits you should order
# the cache_dir lines with the smallest max-size value first.
#
#Default:
# No disk cache. Store cache ojects only in memory.
#
# Uncomment and adjust the following to add a disk cache directory.
#cache_dir ufs /var/spool/squid 100 16 256
# TAG: store_dir_select_algorithm
# How Squid selects which cache_dir to use when the response
# object will fit into more than one.
#
# Regardless of which algorithm is used the cache_dir min-size
# and max-size parameters are obeyed. As such they can affect
# the selection algorithm by limiting the set of considered
# cache_dir.
#
# Algorithms:
#
# least-load
#
# This algorithm is suited to caches with similar cache_dir
# sizes and disk speeds.
#
# The disk with the least I/O pending is selected.
# When there are multiple disks with the same I/O load ranking
# the cache_dir with most available capacity is selected.
#
# When a mix of cache_dir sizes are configured the faster disks
# have a naturally lower I/O loading and larger disks have more
# capacity. So space used to store objects and data throughput
# may be very unbalanced towards larger disks.
#
#
# round-robin
#
# This algorithm is suited to caches with unequal cache_dir
# disk sizes.
#
# Each cache_dir is selected in a rotation. The next suitable
# cache_dir is used.
#
# Available cache_dir capacity is only considered in relation
# to whether the object will fit and meets the min-size and
# max-size parameters.
#
# Disk I/O loading is only considered to prevent overload on slow
# disks. This algorithm does not spread objects by size, so any
# I/O loading per-disk may appear very unbalanced and volatile.
#
# If several cache_dirs use similar min-size, max-size, or other
# limits to to reject certain responses, then do not group such
# cache_dir lines together, to avoid round-robin selection bias
# towards the first cache_dir after the group. Instead, interleave
# cache_dir lines from different groups. For example:
#
# store_dir_select_algorithm round-robin
# cache_dir rock /hdd1 ... min-size=100000
# cache_dir rock /ssd1 ... max-size=99999
# cache_dir rock /hdd2 ... min-size=100000
# cache_dir rock /ssd2 ... max-size=99999
# cache_dir rock /hdd3 ... min-size=100000
# cache_dir rock /ssd3 ... max-size=99999
#Default:
# store_dir_select_algorithm least-load
# TAG: max_open_disk_fds
# To avoid having disk as the I/O bottleneck Squid can optionally
# bypass the on-disk cache if more than this amount of disk file
# descriptors are open.
#
# A value of 0 indicates no limit.
#Default:
# no limit
# TAG: cache_swap_low (percent, 0-100)
# The low-water mark for AUFS/UFS/diskd cache object eviction by
# the cache_replacement_policy algorithm.
#
# Removal begins when the swap (disk) usage of a cache_dir is
# above this low-water mark and attempts to maintain utilization
# near the low-water mark.
#
# As swap utilization increases towards the high-water mark set
# by cache_swap_high object eviction becomes more agressive.
#
# The value difference in percentages between low- and high-water
# marks represent an eviction rate of 300 objects per second and
# the rate continues to scale in agressiveness by multiples of
# this above the high-water mark.
#
# Defaults are 90% and 95%. If you have a large cache, 5% could be
# hundreds of MB. If this is the case you may wish to set these
# numbers closer together.
#
# See also cache_swap_high and cache_replacement_policy
#Default:
# cache_swap_low 90
# TAG: cache_swap_high (percent, 0-100)
# The high-water mark for AUFS/UFS/diskd cache object eviction by
# the cache_replacement_policy algorithm.
#
# Removal begins when the swap (disk) usage of a cache_dir is
# above the low-water mark set by cache_swap_low and attempts to
# maintain utilization near the low-water mark.
#
# As swap utilization increases towards this high-water mark object
# eviction becomes more agressive.
#
# The value difference in percentages between low- and high-water
# marks represent an eviction rate of 300 objects per second and
# the rate continues to scale in agressiveness by multiples of
# this above the high-water mark.
#
# Defaults are 90% and 95%. If you have a large cache, 5% could be
# hundreds of MB. If this is the case you may wish to set these
# numbers closer together.
#
# See also cache_swap_low and cache_replacement_policy
#Default:
# cache_swap_high 95
# LOGFILE OPTIONS
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: logformat
# Usage:
#
# logformat <name> <format specification>
#
# Defines an access log format.
#
# The <format specification> is a string with embedded % format codes
#
# % format codes all follow the same basic structure where all
# components but the formatcode are optional and usually unnecessary,
# especially when dealing with common codes.
#
# % [encoding] [-] [[0]width] [{arg}] formatcode [{arg}]
#
# encoding escapes or otherwise protects "special" characters:
#
# " Quoted string encoding where quote(") and
# backslash(\) characters are \-escaped while
# CR, LF, and TAB characters are encoded as \r,
# \n, and \t two-character sequences.
#
# [ Custom Squid encoding where percent(%), square
# brackets([]), backslash(\) and characters with
# codes outside of [32,126] range are %-encoded.
# SP is not encoded. Used by log_mime_hdrs.
#
# # URL encoding (a.k.a. percent-encoding) where
# all URL unsafe and control characters (per RFC
# 1738) are %-encoded.
#
# / Shell-like encoding where quote(") and
# backslash(\) characters are \-escaped while CR
# and LF characters are encoded as \r and \n
# two-character sequences. Values containing SP
# character(s) are surrounded by quotes(").
#
# ' Raw/as-is encoding with no escaping/quoting.
#
# Default encoding: When no explicit encoding is
# specified, each %code determines its own encoding.
# Most %codes use raw/as-is encoding, but some codes use
# a so called "pass-through URL encoding" where all URL
# unsafe and control characters (per RFC 1738) are
# %-encoded, but the percent character(%) is left as is.
#
# - left aligned
#
# width minimum and/or maximum field width:
# [width_min][.width_max]
# When minimum starts with 0, the field is zero-padded.
# String values exceeding maximum width are truncated.
#
# {arg} argument such as header name etc. This field may be
# placed before or after the token, but not both at once.
#
# Format codes:
#
# % a literal % character
# sn Unique sequence number per log line entry
# err_code The ID of an error response served by Squid or
# a similar internal error identifier.
# err_detail Additional err_code-dependent error information.
# note The annotation specified by the argument. Also
# logs the adaptation meta headers set by the
# adaptation_meta configuration parameter.
# If no argument given all annotations logged.
# The argument may include a separator to use with
# annotation values:
# name[:separator]
# By default, multiple note values are separated with ","
# and multiple notes are separated with "\r\n".
# When logging named notes with %{name}note, the
# explicitly configured separator is used between note
# values. When logging all notes with %note, the
# explicitly configured separator is used between
# individual notes. There is currently no way to
# specify both value and notes separators when logging
# all notes with %note.
# master_xaction The master transaction identifier is an unsigned
# integer. These IDs are guaranteed to monotonically
# increase within a single worker process lifetime, with
# higher values corresponding to transactions that were
# accepted or initiated later. Due to current implementation
# deficiencies, some IDs are skipped (i.e. never logged).
# Concurrent workers and restarted workers use similar,
# overlapping sequences of master transaction IDs.
#
# Connection related format codes:
#
# >a Client source IP address
# >A Client FQDN
# >p Client source port
# >eui Client source EUI (MAC address, EUI-48 or EUI-64 identifier)
# >la Local IP address the client connected to
# >lp Local port number the client connected to
# >qos Client connection TOS/DSCP value set by Squid
# >nfmark Client connection netfilter packet MARK set by Squid
#
# la Local listening IP address the client connection was connected to.
# lp Local listening port number the client connection was connected to.
#
# <a Server IP address of the last server or peer connection
# <A Server FQDN or peer name
# <p Server port number of the last server or peer connection
# <la Local IP address of the last server or peer connection
# <lp Local port number of the last server or peer connection
# <qos Server connection TOS/DSCP value set by Squid
# <nfmark Server connection netfilter packet MARK set by Squid
#
# >handshake Raw client handshake
# Initial client bytes received by Squid on a newly
# accepted TCP connection or inside a just established
# CONNECT tunnel. Squid stops accumulating handshake
# bytes as soon as the handshake parser succeeds or
# fails (determining whether the client is using the
# expected protocol).
#
# For HTTP clients, the handshake is the request line.
# For TLS clients, the handshake consists of all TLS
# records up to and including the TLS record that
# contains the last byte of the first ClientHello
# message. For clients using an unsupported protocol,
# this field contains the bytes received by Squid at the
# time of the handshake parsing failure.
#
# See the on_unsupported_protocol directive for more
# information on Squid handshake traffic expectations.
#
# Current support is limited to these contexts:
# - http_port connections, but only when the
# on_unsupported_protocol directive is in use.
# - https_port connections (and CONNECT tunnels) that
# are subject to the ssl_bump peek or stare action.
#
# To protect binary handshake data, this field is always
# base64-encoded (RFC 4648 Section 4). If logformat
# field encoding is configured, that encoding is applied
# on top of base64. Otherwise, the computed base64 value
# is recorded as is.
#
# Time related format codes:
#
# ts Seconds since epoch
# tu subsecond time (milliseconds)
# tl Local time. Optional strftime format argument
# default %d/%b/%Y:%H:%M:%S %z
# tg GMT time. Optional strftime format argument
# default %d/%b/%Y:%H:%M:%S %z
# tr Response time (milliseconds)
# dt Total time spent making DNS lookups (milliseconds)
# tS Approximate master transaction start time in
# <full seconds since epoch>.<fractional seconds> format.
# Currently, Squid considers the master transaction
# started when a complete HTTP request header initiating
# the transaction is received from the client. This is
# the same value that Squid uses to calculate transaction
# response time when logging %tr to access.log. Currently,
# Squid uses millisecond resolution for %tS values,
# similar to the default access.log "current time" field
# (%ts.%03tu).
#
# Access Control related format codes:
#
# et Tag returned by external acl
# ea Log string returned by external acl
# un User name (any available)
# ul User name from authentication
# ue User name from external acl helper
# ui User name from ident
# un A user name. Expands to the first available name
# from the following list of information sources:
# - authenticated user name, like %ul
# - user name supplied by an external ACL, like %ue
# - SSL client name, like %us
# - ident user name, like %ui
# credentials Client credentials. The exact meaning depends on
# the authentication scheme: For Basic authentication,
# it is the password; for Digest, the realm sent by the
# client; for NTLM and Negotiate, the client challenge
# or client credentials prefixed with "YR " or "KK ".
#
# HTTP related format codes:
#
# REQUEST
#
# [http::]rm Request method (GET/POST etc)
# [http::]>rm Request method from client
# [http::]<rm Request method sent to server or peer
#
# [http::]ru Request URL received (or computed) and sanitized
#
# Logs request URI received from the client, a
# request adaptation service, or a request
# redirector (whichever was applied last).
#
# Computed URLs are URIs of internally generated
# requests and various "error:..." URIs.
#
# Honors strip_query_terms and uri_whitespace.
#
# This field is not encoded by default. Encoding
# this field using variants of %-encoding will
# clash with uri_whitespace modifications that
# also use %-encoding.
#
# [http::]>ru Request URL received from the client (or computed)
#
# Computed URLs are URIs of internally generated
# requests and various "error:..." URIs.
#
# Unlike %ru, this request URI is not affected
# by request adaptation, URL rewriting services,
# and strip_query_terms.
#
# Honors uri_whitespace.
#
# This field is using pass-through URL encoding
# by default. Encoding this field using other
# variants of %-encoding will clash with
# uri_whitespace modifications that also use
# %-encoding.
#
# [http::]<ru Request URL sent to server or peer
# [http::]>rs Request URL scheme from client
# [http::]<rs Request URL scheme sent to server or peer
# [http::]>rd Request URL domain from client
# [http::]<rd Request URL domain sent to server or peer
# [http::]>rP Request URL port from client
# [http::]<rP Request URL port sent to server or peer
# [http::]rp Request URL path excluding hostname
# [http::]>rp Request URL path excluding hostname from client
# [http::]<rp Request URL path excluding hostname sent to server or peer
# [http::]rv Request protocol version
# [http::]>rv Request protocol version from client
# [http::]<rv Request protocol version sent to server or peer
#
# [http::]>h Original received request header.
# Usually differs from the request header sent by
# Squid, although most fields are often preserved.
# Accepts optional header field name/value filter
# argument using name[:[separator]element] format.
# [http::]>ha Received request header after adaptation and
# redirection (pre-cache REQMOD vectoring point).
# Usually differs from the request header sent by
# Squid, although most fields are often preserved.
# Optional header name argument as for >h
#
# RESPONSE
#
# [http::]<Hs HTTP status code received from the next hop
# [http::]>Hs HTTP status code sent to the client
#
# [http::]<h Reply header. Optional header name argument
# as for >h
#
# [http::]mt MIME content type
#
#
# SIZE COUNTERS
#
# [http::]st Total size of request + reply traffic with client
# [http::]>st Total size of request received from client.
# Excluding chunked encoding bytes.
# [http::]<st Total size of reply sent to client (after adaptation)
#
# [http::]>sh Size of request headers received from client
# [http::]<sh Size of reply headers sent to client (after adaptation)
#
# [http::]<sH Reply high offset sent
# [http::]<sS Upstream object size
#
# [http::]<bs Number of HTTP-equivalent message body bytes
# received from the next hop, excluding chunked
# transfer encoding and control messages.
# Generated FTP/Gopher listings are treated as
# received bodies.
#
# TIMING
#
# [http::]<pt Peer response time in milliseconds. The timer starts
# when the last request byte is sent to the next hop
# and stops when the last response byte is received.
# [http::]<tt Total time in milliseconds. The timer
# starts with the first connect request (or write I/O)
# sent to the first selected peer. The timer stops
# with the last I/O with the last peer.
#
# Squid handling related format codes:
#
# Ss Squid request status (TCP_MISS etc)
# Sh Squid hierarchy status (DEFAULT_PARENT etc)
#
# SSL-related format codes:
#
# ssl::bump_mode SslBump decision for the transaction:
#
# For CONNECT requests that initiated bumping of
# a connection and for any request received on
# an already bumped connection, Squid logs the
# corresponding SslBump mode ("splice", "bump",
# "peek", "stare", "terminate", "server-first"
# or "client-first"). See the ssl_bump option
# for more information about these modes.
#
# A "none" token is logged for requests that
# triggered "ssl_bump" ACL evaluation matching
# a "none" rule.
#
# In all other cases, a single dash ("-") is
# logged.
#
# ssl::>sni SSL client SNI sent to Squid.
#
# ssl::>cert_subject
# The Subject field of the received client
# SSL certificate or a dash ('-') if Squid has
# received an invalid/malformed certificate or
# no certificate at all. Consider encoding the
# logged value because Subject often has spaces.
#
# ssl::>cert_issuer
# The Issuer field of the received client
# SSL certificate or a dash ('-') if Squid has
# received an invalid/malformed certificate or
# no certificate at all. Consider encoding the
# logged value because Issuer often has spaces.
#
# ssl::<cert_subject
# The Subject field of the received server
# TLS certificate or a dash ('-') if this is
# not available. Consider encoding the logged
# value because Subject often has spaces.
#
# ssl::<cert_issuer
# The Issuer field of the received server
# TLS certificate or a dash ('-') if this is
# not available. Consider encoding the logged
# value because Issuer often has spaces.
#
# ssl::<cert
# The received server x509 certificate in PEM
# format, including BEGIN and END lines (or a
# dash ('-') if the certificate is unavailable).
#
# WARNING: Large certificates will exceed the
# current 8KB access.log record limit, resulting
# in truncated records. Such truncation usually
# happens in the middle of a record field. The
# limit applies to all access logging modules.
#
# The logged certificate may have failed
# validation and may not be trusted by Squid.
# This field does not include any intermediate
# certificates that may have been received from
# the server or fetched during certificate
# validation process.
#
# Currently, Squid only collects server
# certificates during step3 of SslBump
# processing; connections that were not subject
# to ssl_bump rules or that did not match a peek
# or stare rule at step2 will not have the
# server certificate information.
#
# This field is using pass-through URL encoding
# by default.
#
# ssl::<cert_errors
# The list of certificate validation errors
# detected by Squid (including OpenSSL and
# certificate validation helper components). The
# errors are listed in the discovery order. By
# default, the error codes are separated by ':'.
# Accepts an optional separator argument.
#
# %ssl::>negotiated_version The negotiated TLS version of the
# client connection.
#
# %ssl::<negotiated_version The negotiated TLS version of the
# last server or peer connection.
#
# %ssl::>received_hello_version The TLS version of the Hello
# message received from TLS client.
#
# %ssl::<received_hello_version The TLS version of the Hello
# message received from TLS server.
#
# %ssl::>received_supported_version The maximum TLS version
# supported by the TLS client.
#
# %ssl::<received_supported_version The maximum TLS version
# supported by the TLS server.
#
# %ssl::>negotiated_cipher The negotiated cipher of the
# client connection.
#
# %ssl::<negotiated_cipher The negotiated cipher of the
# last server or peer connection.
#
# If ICAP is enabled, the following code becomes available (as
# well as ICAP log codes documented with the icap_log option):
#
# icap::tt Total ICAP processing time for the HTTP
# transaction. The timer ticks when ICAP
# ACLs are checked and when ICAP
# transaction is in progress.
#
# If adaptation is enabled the following codes become available:
#
# adapt::<last_h The header of the last ICAP response or
# meta-information from the last eCAP
# transaction related to the HTTP transaction.
# Like <h, accepts an optional header name
# argument.
#
# adapt::sum_trs Summed adaptation transaction response
# times recorded as a comma-separated list in
# the order of transaction start time. Each time
# value is recorded as an integer number,
# representing response time of one or more
# adaptation (ICAP or eCAP) transaction in
# milliseconds. When a failed transaction is
# being retried or repeated, its time is not
# logged individually but added to the
# replacement (next) transaction. See also:
# adapt::all_trs.
#
# adapt::all_trs All adaptation transaction response times.
# Same as adaptation_strs but response times of
# individual transactions are never added
# together. Instead, all transaction response
# times are recorded individually.
#
# You can prefix adapt::*_trs format codes with adaptation
# service name in curly braces to record response time(s) specific
# to that service. For example: %{my_service}adapt::sum_trs
#
# Format codes related to the PROXY protocol:
#
# proxy_protocol::>h PROXY protocol header, including optional TLVs.
#
# Supports the same field and element reporting/extraction logic
# as %http::>h. For configuration and reporting purposes, Squid
# maps each PROXY TLV to an HTTP header field: the TLV type
# (configured as a decimal integer) is the field name, and the
# TLV value is the field value. All TLVs of "LOCAL" connections
# (in PROXY protocol terminology) are currently skipped/ignored.
#
# Squid also maps the following standard PROXY protocol header
# blocks to pseudo HTTP headers (their names use PROXY
# terminology and start with a colon, following HTTP tradition
# for pseudo headers): :command, :version, :src_addr, :dst_addr,
# :src_port, and :dst_port.
#
# Without optional parameters, this logformat code logs
# pseudo headers and TLVs.
#
# This format code uses pass-through URL encoding by default.
#
# Example:
# # relay custom PROXY TLV #224 to adaptation services
# adaptation_meta Client-Foo "%proxy_protocol::>h{224}"
#
# See also: %http::>h
#
# The default formats available (which do not need re-defining) are:
#
#logformat squid %ts.%03tu %6tr %>a %Ss/%03>Hs %<st %rm %ru %[un %Sh/%<a %mt
#logformat common %>a %[ui %[un [%tl] "%rm %ru HTTP/%rv" %>Hs %<st %Ss:%Sh
#logformat combined %>a %[ui %[un [%tl] "%rm %ru HTTP/%rv" %>Hs %<st "%{Referer}>h" "%{User-Agent}>h" %Ss:%Sh
#logformat referrer %ts.%03tu %>a %{Referer}>h %ru
#logformat useragent %>a [%tl] "%{User-Agent}>h"
#
# NOTE: When the log_mime_hdrs directive is set to ON.
# The squid, common and combined formats have a safely encoded copy
# of the mime headers appended to each line within a pair of brackets.
#
# NOTE: The common and combined formats are not quite true to the Apache definition.
# The logs from Squid contain an extra status and hierarchy code appended.
#
#Default:
# The format definitions squid, common, combined, referrer, useragent are built in.
# TAG: access_log
# Configures whether and how Squid logs HTTP and ICP transactions.
# If access logging is enabled, a single line is logged for every
# matching HTTP or ICP request. The recommended directive formats are:
#
# access_log <module>:<place> [option ...] [acl acl ...]
# access_log none [acl acl ...]
#
# The following directive format is accepted but may be deprecated:
# access_log <module>:<place> [<logformat name> [acl acl ...]]
#
# In most cases, the first ACL name must not contain the '=' character
# and should not be equal to an existing logformat name. You can always
# start with an 'all' ACL to work around those restrictions.
#
# Will log to the specified module:place using the specified format (which
# must be defined in a logformat directive) those entries which match
# ALL the acl's specified (which must be defined in acl clauses).
# If no acl is specified, all requests will be logged to this destination.
#
# ===== Available options for the recommended directive format =====
#
# logformat=name Names log line format (either built-in or
# defined by a logformat directive). Defaults
# to 'squid'.
#
# buffer-size=64KB Defines approximate buffering limit for log
# records (see buffered_logs). Squid should not
# keep more than the specified size and, hence,
# should flush records before the buffer becomes
# full to avoid overflows under normal
# conditions (the exact flushing algorithm is
# module-dependent though). The on-error option
# controls overflow handling.
#
# on-error=die|drop Defines action on unrecoverable errors. The
# 'drop' action ignores (i.e., does not log)
# affected log records. The default 'die' action
# kills the affected worker. The drop action
# support has not been tested for modules other
# than tcp.
#
# rotate=N Specifies the number of log file rotations to
# make when you run 'squid -k rotate'. The default
# is to obey the logfile_rotate directive. Setting
# rotate=0 will disable the file name rotation,
# but the log files are still closed and re-opened.
# This will enable you to rename the logfiles
# yourself just before sending the rotate signal.
# Only supported by the stdio module.
#
# ===== Modules Currently available =====
#
# none Do not log any requests matching these ACL.
# Do not specify Place or logformat name.
#
# stdio Write each log line to disk immediately at the completion of
# each request.
# Place: the filename and path to be written.
#
# daemon Very similar to stdio. But instead of writing to disk the log
# line is passed to a daemon helper for asychronous handling instead.
# Place: varies depending on the daemon.
#
# log_file_daemon Place: the file name and path to be written.
#
# syslog To log each request via syslog facility.
# Place: The syslog facility and priority level for these entries.
# Place Format: facility.priority
#
# where facility could be any of:
# authpriv, daemon, local0 ... local7 or user.
#
# And priority could be any of:
# err, warning, notice, info, debug.
#
# udp To send each log line as text data to a UDP receiver.
# Place: The destination host name or IP and port.
# Place Format: //host:port
#
# tcp To send each log line as text data to a TCP receiver.
# Lines may be accumulated before sending (see buffered_logs).
# Place: The destination host name or IP and port.
# Place Format: //host:port
#
# Default:
# access_log daemon:/var/log/squid/access.log squid
#Default:
# access_log daemon:/var/log/squid/access.log squid
# TAG: icap_log
# ICAP log files record ICAP transaction summaries, one line per
# transaction.
#
# The icap_log option format is:
# icap_log <filepath> [<logformat name> [acl acl ...]]
# icap_log none [acl acl ...]]
#
# Please see access_log option documentation for details. The two
# kinds of logs share the overall configuration approach and many
# features.
#
# ICAP processing of a single HTTP message or transaction may
# require multiple ICAP transactions. In such cases, multiple
# ICAP transaction log lines will correspond to a single access
# log line.
#
# ICAP log supports many access.log logformat %codes. In ICAP context,
# HTTP message-related %codes are applied to the HTTP message embedded
# in an ICAP message. Logformat "%http::>..." codes are used for HTTP
# messages embedded in ICAP requests while "%http::<..." codes are used
# for HTTP messages embedded in ICAP responses. For example:
#
# http::>h To-be-adapted HTTP message headers sent by Squid to
# the ICAP service. For REQMOD transactions, these are
# HTTP request headers. For RESPMOD, these are HTTP
# response headers, but Squid currently cannot log them
# (i.e., %http::>h will expand to "-" for RESPMOD).
#
# http::<h Adapted HTTP message headers sent by the ICAP
# service to Squid (i.e., HTTP request headers in regular
# REQMOD; HTTP response headers in RESPMOD and during
# request satisfaction in REQMOD).
#
# ICAP OPTIONS transactions do not embed HTTP messages.
#
# Several logformat codes below deal with ICAP message bodies. An ICAP
# message body, if any, typically includes a complete HTTP message
# (required HTTP headers plus optional HTTP message body). When
# computing HTTP message body size for these logformat codes, Squid
# either includes or excludes chunked encoding overheads; see
# code-specific documentation for details.
#
# For Secure ICAP services, all size-related information is currently
# computed before/after TLS encryption/decryption, as if TLS was not
# in use at all.
#
# The following format codes are also available for ICAP logs:
#
# icap::<A ICAP server IP address. Similar to <A.
#
# icap::<service_name ICAP service name from the icap_service
# option in Squid configuration file.
#
# icap::ru ICAP Request-URI. Similar to ru.
#
# icap::rm ICAP request method (REQMOD, RESPMOD, or
# OPTIONS). Similar to existing rm.
#
# icap::>st The total size of the ICAP request sent to the ICAP
# server (ICAP headers + ICAP body), including chunking
# metadata (if any).
#
# icap::<st The total size of the ICAP response received from the
# ICAP server (ICAP headers + ICAP body), including
# chunking metadata (if any).
#
# icap::<bs The size of the ICAP response body received from the
# ICAP server, excluding chunking metadata (if any).
#
# icap::tr Transaction response time (in
# milliseconds). The timer starts when
# the ICAP transaction is created and
# stops when the transaction is completed.
# Similar to tr.
#
# icap::tio Transaction I/O time (in milliseconds). The
# timer starts when the first ICAP request
# byte is scheduled for sending. The timers
# stops when the last byte of the ICAP response
# is received.
#
# icap::to Transaction outcome: ICAP_ERR* for all
# transaction errors, ICAP_OPT for OPTION
# transactions, ICAP_ECHO for 204
# responses, ICAP_MOD for message
# modification, and ICAP_SAT for request
# satisfaction. Similar to Ss.
#
# icap::Hs ICAP response status code. Similar to Hs.
#
# icap::>h ICAP request header(s). Similar to >h.
#
# icap::<h ICAP response header(s). Similar to <h.
#
# The default ICAP log format, which can be used without an explicit
# definition, is called icap_squid:
#
#logformat icap_squid %ts.%03tu %6icap::tr %>A %icap::to/%03icap::Hs %icap::<st %icap::rm %icap::ru %un -/%icap::<A -
#
# See also: logformat and %adapt::<last_h
#Default:
# none
# TAG: logfile_daemon
# Specify the path to the logfile-writing daemon. This daemon is
# used to write the access and store logs, if configured.
#
# Squid sends a number of commands to the log daemon:
# L<data>\n - logfile data
# R\n - rotate file
# T\n - truncate file
# O\n - reopen file
# F\n - flush file
# r<n>\n - set rotate count to <n>
# b<n>\n - 1 = buffer output, 0 = don't buffer output
#
# No responses is expected.
#Default:
# logfile_daemon /usr/lib/squid/log_file_daemon
# TAG: stats_collection allow|deny acl acl...
# This options allows you to control which requests gets accounted
# in performance counters.
#
# This clause only supports fast acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#Default:
# Allow logging for all transactions.
# TAG: cache_store_log
# Logs the activities of the storage manager. Shows which
# objects are ejected from the cache, and which objects are
# saved and for how long.
# There are not really utilities to analyze this data, so you can safely
# disable it (the default).
#
# Store log uses modular logging outputs. See access_log for the list
# of modules supported.
#
# Example:
# cache_store_log stdio:/var/log/squid/store.log
# cache_store_log daemon:/var/log/squid/store.log
#Default:
# none
# TAG: cache_swap_state
# Location for the cache "swap.state" file. This index file holds
# the metadata of objects saved on disk. It is used to rebuild
# the cache during startup. Normally this file resides in each
# 'cache_dir' directory, but you may specify an alternate
# pathname here. Note you must give a full filename, not just
# a directory. Since this is the index for the whole object
# list you CANNOT periodically rotate it!
#
# If %s can be used in the file name it will be replaced with a
# a representation of the cache_dir name where each / is replaced
# with '.'. This is needed to allow adding/removing cache_dir
# lines when cache_swap_log is being used.
#
# If have more than one 'cache_dir', and %s is not used in the name
# these swap logs will have names such as:
#
# cache_swap_log.00
# cache_swap_log.01
# cache_swap_log.02
#
# The numbered extension (which is added automatically)
# corresponds to the order of the 'cache_dir' lines in this
# configuration file. If you change the order of the 'cache_dir'
# lines in this file, these index files will NOT correspond to
# the correct 'cache_dir' entry (unless you manually rename
# them). We recommend you do NOT use this option. It is
# better to keep these index files in each 'cache_dir' directory.
#Default:
# Store the journal inside its cache_dir
# TAG: logfile_rotate
# Specifies the default number of logfile rotations to make when you
# type 'squid -k rotate'. The default is 10, which will rotate
# with extensions 0 through 9. Setting logfile_rotate to 0 will
# disable the file name rotation, but the logfiles are still closed
# and re-opened. This will enable you to rename the logfiles
# yourself just before sending the rotate signal.
#
# Note, from Squid-3.1 this option is only a default for cache.log,
# that log can be rotated separately by using debug_options.
#
# Note, from Squid-4 this option is only a default for access.log
# recorded by stdio: module. Those logs can be rotated separately by
# using the rotate=N option on their access_log directive.
#
# Note, the 'squid -k rotate' command normally sends a USR1
# signal to the running squid process. In certain situations
# (e.g. on Linux with Async I/O), USR1 is used for other
# purposes, so -k rotate uses another signal. It is best to get
# in the habit of using 'squid -k rotate' instead of 'kill -USR1
# <pid>'.
#
# Note, for Debian/Linux the default of logfile_rotate is
# zero, since it includes external logfile-rotation methods.
#Default:
# logfile_rotate 0
# TAG: mime_table
# Path to Squid's icon configuration file.
#
# You shouldn't need to change this, but the default file contains
# examples and formatting information if you do.
#Default:
# mime_table /usr/share/squid/mime.conf
# TAG: log_mime_hdrs on|off
# The Cache can record both the request and the response MIME
# headers for each HTTP transaction. The headers are encoded
# safely and will appear as two bracketed fields at the end of
# the access log (for either the native or httpd-emulated log
# formats). To enable this logging set log_mime_hdrs to 'on'.
#Default:
# log_mime_hdrs off
# TAG: pid_filename
# A filename to write the process-id to. To disable, enter "none".
#Default:
# pid_filename /run/squid.pid
# TAG: client_netmask
# A netmask for client addresses in logfiles and cachemgr output.
# Change this to protect the privacy of your cache clients.
# A netmask of 255.255.255.0 will log all IP's in that range with
# the last digit set to '0'.
#Default:
# Log full client IP address
# TAG: strip_query_terms
# By default, Squid strips query terms from requested URLs before
# logging. This protects your user's privacy and reduces log size.
#
# When investigating HIT/MISS or other caching behaviour you
# will need to disable this to see the full URL used by Squid.
#Default:
# strip_query_terms on
# TAG: buffered_logs on|off
# Whether to write/send access_log records ASAP or accumulate them and
# then write/send them in larger chunks. Buffering may improve
# performance because it decreases the number of I/Os. However,
# buffering increases the delay before log records become available to
# the final recipient (e.g., a disk file or logging daemon) and,
# hence, increases the risk of log records loss.
#
# Note that even when buffered_logs are off, Squid may have to buffer
# records if it cannot write/send them immediately due to pending I/Os
# (e.g., the I/O writing the previous log record) or connectivity loss.
#
# Currently honored by 'daemon' and 'tcp' access_log modules only.
#Default:
# buffered_logs off
# TAG: netdb_filename
# Where Squid stores it's netdb journal.
# When enabled this journal preserves netdb state between restarts.
#
# To disable, enter "none".
#Default:
# netdb_filename stdio:/var/spool/squid/netdb.state
# OPTIONS FOR TROUBLESHOOTING
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: cache_log
# Squid administrative logging file.
#
# This is where general information about Squid behavior goes. You can
# increase the amount of data logged to this file and how often it is
# rotated with "debug_options"
#Default:
# cache_log /var/log/squid/cache.log
# TAG: debug_options
# Logging options are set as section,level where each source file
# is assigned a unique section. Lower levels result in less
# output, Full debugging (level 9) can result in a very large
# log file, so be careful.
#
# The magic word "ALL" sets debugging levels for all sections.
# The default is to run with "ALL,1" to record important warnings.
#
# The rotate=N option can be used to keep more or less of these logs
# than would otherwise be kept by logfile_rotate.
# For most uses a single log should be enough to monitor current
# events affecting Squid.
#Default:
# Log all critical and important messages.
# TAG: coredump_dir
# By default Squid leaves core files in the directory from where
# it was started. If you set 'coredump_dir' to a directory
# that exists, Squid will chdir() to that directory at startup
# and coredump files will be left there.
#
#Default:
# Use the directory from where Squid was started.
#
# Leave coredumps in the first cache dir
coredump_dir /var/spool/squid
# OPTIONS FOR FTP GATEWAYING
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: ftp_user
# If you want the anonymous login password to be more informative
# (and enable the use of picky FTP servers), set this to something
# reasonable for your domain, like wwwuser@somewhere.net
#
# The reason why this is domainless by default is the
# request can be made on the behalf of a user in any domain,
# depending on how the cache is used.
# Some FTP server also validate the email address is valid
# (for example perl.com).
#Default:
# ftp_user Squid@
# TAG: ftp_passive
# If your firewall does not allow Squid to use passive
# connections, turn off this option.
#
# Use of ftp_epsv_all option requires this to be ON.
#Default:
# ftp_passive on
# TAG: ftp_epsv_all
# FTP Protocol extensions permit the use of a special "EPSV ALL" command.
#
# NATs may be able to put the connection on a "fast path" through the
# translator, as the EPRT command will never be used and therefore,
# translation of the data portion of the segments will never be needed.
#
# When a client only expects to do two-way FTP transfers this may be
# useful.
# If squid finds that it must do a three-way FTP transfer after issuing
# an EPSV ALL command, the FTP session will fail.
#
# If you have any doubts about this option do not use it.
# Squid will nicely attempt all other connection methods.
#
# Requires ftp_passive to be ON (default) for any effect.
#Default:
# ftp_epsv_all off
# TAG: ftp_epsv
# FTP Protocol extensions permit the use of a special "EPSV" command.
#
# NATs may be able to put the connection on a "fast path" through the
# translator using EPSV, as the EPRT command will never be used
# and therefore, translation of the data portion of the segments
# will never be needed.
#
# EPSV is often required to interoperate with FTP servers on IPv6
# networks. On the other hand, it may break some IPv4 servers.
#
# By default, EPSV may try EPSV with any FTP server. To fine tune
# that decision, you may restrict EPSV to certain clients or servers
# using ACLs:
#
# ftp_epsv allow|deny al1 acl2 ...
#
# WARNING: Disabling EPSV may cause problems with external NAT and IPv6.
#
# Only fast ACLs are supported.
# Requires ftp_passive to be ON (default) for any effect.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: ftp_eprt
# FTP Protocol extensions permit the use of a special "EPRT" command.
#
# This extension provides a protocol neutral alternative to the
# IPv4-only PORT command. When supported it enables active FTP data
# channels over IPv6 and efficient NAT handling.
#
# Turning this OFF will prevent EPRT being attempted and will skip
# straight to using PORT for IPv4 servers.
#
# Some devices are known to not handle this extension correctly and
# may result in crashes. Devices which suport EPRT enough to fail
# cleanly will result in Squid attempting PORT anyway. This directive
# should only be disabled when EPRT results in device failures.
#
# WARNING: Doing so will convert Squid back to the old behavior with all
# the related problems with external NAT devices/layers and IPv4-only FTP.
#Default:
# ftp_eprt on
# TAG: ftp_sanitycheck
# For security and data integrity reasons Squid by default performs
# sanity checks of the addresses of FTP data connections ensure the
# data connection is to the requested server. If you need to allow
# FTP connections to servers using another IP address for the data
# connection turn this off.
#Default:
# ftp_sanitycheck on
# TAG: ftp_telnet_protocol
# The FTP protocol is officially defined to use the telnet protocol
# as transport channel for the control connection. However, many
# implementations are broken and does not respect this aspect of
# the FTP protocol.
#
# If you have trouble accessing files with ASCII code 255 in the
# path or similar problems involving this ASCII code you can
# try setting this directive to off. If that helps, report to the
# operator of the FTP server in question that their FTP server
# is broken and does not follow the FTP standard.
#Default:
# ftp_telnet_protocol on
# OPTIONS FOR EXTERNAL SUPPORT PROGRAMS
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: diskd_program
# Specify the location of the diskd executable.
# Note this is only useful if you have compiled in
# diskd as one of the store io modules.
#Default:
# diskd_program /usr/lib/squid/diskd
# TAG: unlinkd_program
# Specify the location of the executable for file deletion process.
#Default:
# unlinkd_program /usr/lib/squid/unlinkd
# TAG: pinger_program
# Specify the location of the executable for the pinger process.
#Default:
# pinger_program /usr/lib/squid/pinger
# TAG: pinger_enable
# Control whether the pinger is active at run-time.
# Enables turning ICMP pinger on and off with a simple
# squid -k reconfigure.
#Default:
# pinger_enable on
# OPTIONS FOR URL REWRITING
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: url_rewrite_program
# The name and command line parameters of an admin-provided executable
# for redirecting clients or adjusting/replacing client request URLs.
#
# This helper is consulted after the received request is cleared by
# http_access and adapted using eICAP/ICAP services (if any). If the
# helper does not redirect the client, Squid checks adapted_http_access
# and may consult the cache or forward the request to the next hop.
#
#
# For each request, the helper gets one line in the following format:
#
# [channel-ID <SP>] request-URL [<SP> extras] <NL>
#
# Use url_rewrite_extras to configure what Squid sends as 'extras'.
#
#
# The helper must reply to each query using a single line:
#
# [channel-ID <SP>] result [<SP> kv-pairs] <NL>
#
# The result section must match exactly one of the following outcomes:
#
# OK [status=30N] url="..."
#
# Redirect the client to a URL supplied in the 'url' parameter.
# Optional 'status' specifies the status code to send to the
# client in Squid's HTTP redirect response. It must be one of
# the standard HTTP redirect status codes: 301, 302, 303, 307,
# or 308. When no specific status is requested, Squid uses 302.
#
# OK rewrite-url="..."
#
# Replace the current request URL with the one supplied in the
# 'rewrite-url' parameter. Squid fetches the resource specified
# by the new URL and forwards the received response (or its
# cached copy) to the client.
#
# WARNING: Avoid rewriting URLs! When possible, redirect the
# client using an "OK url=..." helper response instead.
# Rewriting URLs may create inconsistent requests and/or break
# synchronization between internal client and origin server
# states, especially when URLs or other message parts contain
# snippets of that state. For example, Squid does not adjust
# Location headers and embedded URLs after the helper rewrites
# the request URL.
#
# OK
# Keep the client request intact.
#
# ERR
# Keep the client request intact.
#
# BH [message="..."]
# A helper problem that should be reported to the Squid admin
# via a level-1 cache.log message. The 'message' parameter is
# reserved for specifying the log message.
#
# In addition to the kv-pairs mentioned above, Squid also understands
# the following optional kv-pairs in URL rewriter responses:
#
# clt_conn_tag=TAG
# Associates a TAG with the client TCP connection.
#
# The clt_conn_tag=TAG pair is treated as a regular transaction
# annotation for the current request and also annotates future
# requests on the same client connection. A helper may update
# the TAG during subsequent requests by returning a new kv-pair.
#
#
# Helper messages contain the channel-ID part if and only if the
# url_rewrite_children directive specifies positive concurrency. As a
# channel-ID value, Squid sends a number between 0 and concurrency-1.
# The helper must echo back the received channel-ID in its response.
#
# By default, Squid does not use a URL rewriter.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: url_rewrite_children
# Specifies the maximum number of redirector processes that Squid may
# spawn (numberofchildren) and several related options. Using too few of
# these helper processes (a.k.a. "helpers") creates request queues.
# Using too many helpers wastes your system resources.
#
# Usage: numberofchildren [option]...
#
# The startup= and idle= options allow some measure of skew in your
# tuning.
#
# startup=
#
# Sets a minimum of how many processes are to be spawned when Squid
# starts or reconfigures. When set to zero the first request will
# cause spawning of the first child process to handle it.
#
# Starting too few will cause an initial slowdown in traffic as Squid
# attempts to simultaneously spawn enough processes to cope.
#
# idle=
#
# Sets a minimum of how many processes Squid is to try and keep available
# at all times. When traffic begins to rise above what the existing
# processes can handle this many more will be spawned up to the maximum
# configured. A minimum setting of 1 is required.
#
# concurrency=
#
# The number of requests each redirector helper can handle in
# parallel. Defaults to 0 which indicates the redirector
# is a old-style single threaded redirector.
#
# When this directive is set to a value >= 1 then the protocol
# used to communicate with the helper is modified to include
# an ID in front of the request/response. The ID from the request
# must be echoed back with the response to that request.
#
# queue-size=N
#
# Sets the maximum number of queued requests. A request is queued when
# no existing child can accept it due to concurrency limit and no new
# child can be started due to numberofchildren limit. The default
# maximum is zero if url_rewrite_bypass is enabled and
# 2*numberofchildren otherwise. If the queued requests exceed queue size
# and redirector_bypass configuration option is set, then redirector is
# bypassed. Otherwise, Squid is allowed to temporarily exceed the
# configured maximum, marking the affected helper as "overloaded". If
# the helper overload lasts more than 3 minutes, the action prescribed
# by the on-persistent-overload option applies.
#
# on-persistent-overload=action
#
# Specifies Squid reaction to a new helper request arriving when the helper
# has been overloaded for more that 3 minutes already. The number of queued
# requests determines whether the helper is overloaded (see the queue-size
# option).
#
# Two actions are supported:
#
# die Squid worker quits. This is the default behavior.
#
# ERR Squid treats the helper request as if it was
# immediately submitted, and the helper immediately
# replied with an ERR response. This action has no effect
# on the already queued and in-progress helper requests.
#Default:
# url_rewrite_children 20 startup=0 idle=1 concurrency=0
# TAG: url_rewrite_host_header
# To preserve same-origin security policies in browsers and
# prevent Host: header forgery by redirectors Squid rewrites
# any Host: header in redirected requests.
#
# If you are running an accelerator this may not be a wanted
# effect of a redirector. This directive enables you disable
# Host: alteration in reverse-proxy traffic.
#
# WARNING: Entries are cached on the result of the URL rewriting
# process, so be careful if you have domain-virtual hosts.
#
# WARNING: Squid and other software verifies the URL and Host
# are matching, so be careful not to relay through other proxies
# or inspecting firewalls with this disabled.
#Default:
# url_rewrite_host_header on
# TAG: url_rewrite_access
# If defined, this access list specifies which requests are
# sent to the redirector processes.
#
# This clause supports both fast and slow acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#Default:
# Allow, unless rules exist in squid.conf.
# TAG: url_rewrite_bypass
# When this is 'on', a request will not go through the
# redirector if all the helpers are busy. If this is 'off' and the
# redirector queue grows too large, the action is prescribed by the
# on-persistent-overload option. You should only enable this if the
# redirectors are not critical to your caching system. If you use
# redirectors for access control, and you enable this option,
# users may have access to pages they should not
# be allowed to request.
#
# Enabling this option sets the default url_rewrite_children queue-size
# option value to 0.
#Default:
# url_rewrite_bypass off
# TAG: url_rewrite_extras
# Specifies a string to be append to request line format for the
# rewriter helper. "Quoted" format values may contain spaces and
# logformat %macros. In theory, any logformat %macro can be used.
# In practice, a %macro expands as a dash (-) if the helper request is
# sent before the required macro information is available to Squid.
#Default:
# url_rewrite_extras "%>a/%>A %un %>rm myip=%la myport=%lp"
# TAG: url_rewrite_timeout
# Squid times active requests to redirector. The timeout value and Squid
# reaction to a timed out request are configurable using the following
# format:
#
# url_rewrite_timeout timeout time-units on_timeout=<action> [response=<quoted-response>]
#
# supported timeout actions:
# fail Squid return a ERR_GATEWAY_FAILURE error page
#
# bypass Do not re-write the URL
#
# retry Send the lookup to the helper again
#
# use_configured_response
# Use the <quoted-response> as helper response
#Default:
# Squid waits for the helper response forever
# OPTIONS FOR STORE ID
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: store_id_program
# Specify the location of the executable StoreID helper to use.
# Since they can perform almost any function there isn't one included.
#
# For each requested URL, the helper will receive one line with the format
#
# [channel-ID <SP>] URL [<SP> extras]<NL>
#
#
# After processing the request the helper must reply using the following format:
#
# [channel-ID <SP>] result [<SP> kv-pairs]
#
# The result code can be:
#
# OK store-id="..."
# Use the StoreID supplied in 'store-id='.
#
# ERR
# The default is to use HTTP request URL as the store ID.
#
# BH
# An internal error occurred in the helper, preventing
# a result being identified.
#
# In addition to the above kv-pairs Squid also understands the following
# optional kv-pairs received from URL rewriters:
# clt_conn_tag=TAG
# Associates a TAG with the client TCP connection.
# Please see url_rewrite_program related documentation for this
# kv-pair
#
# Helper programs should be prepared to receive and possibly ignore
# additional whitespace-separated tokens on each input line.
#
# When using the concurrency= option the protocol is changed by
# introducing a query channel tag in front of the request/response.
# The query channel tag is a number between 0 and concurrency-1.
# This value must be echoed back unchanged to Squid as the first part
# of the response relating to its request.
#
# NOTE: when using StoreID refresh_pattern will apply to the StoreID
# returned from the helper and not the URL.
#
# WARNING: Wrong StoreID value returned by a careless helper may result
# in the wrong cached response returned to the user.
#
# By default, a StoreID helper is not used.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: store_id_extras
# Specifies a string to be append to request line format for the
# StoreId helper. "Quoted" format values may contain spaces and
# logformat %macros. In theory, any logformat %macro can be used.
# In practice, a %macro expands as a dash (-) if the helper request is
# sent before the required macro information is available to Squid.
#Default:
# store_id_extras "%>a/%>A %un %>rm myip=%la myport=%lp"
# TAG: store_id_children
# Specifies the maximum number of StoreID helper processes that Squid
# may spawn (numberofchildren) and several related options. Using
# too few of these helper processes (a.k.a. "helpers") creates request
# queues. Using too many helpers wastes your system resources.
#
# Usage: numberofchildren [option]...
#
# The startup= and idle= options allow some measure of skew in your
# tuning.
#
# startup=
#
# Sets a minimum of how many processes are to be spawned when Squid
# starts or reconfigures. When set to zero the first request will
# cause spawning of the first child process to handle it.
#
# Starting too few will cause an initial slowdown in traffic as Squid
# attempts to simultaneously spawn enough processes to cope.
#
# idle=
#
# Sets a minimum of how many processes Squid is to try and keep available
# at all times. When traffic begins to rise above what the existing
# processes can handle this many more will be spawned up to the maximum
# configured. A minimum setting of 1 is required.
#
# concurrency=
#
# The number of requests each storeID helper can handle in
# parallel. Defaults to 0 which indicates the helper
# is a old-style single threaded program.
#
# When this directive is set to a value >= 1 then the protocol
# used to communicate with the helper is modified to include
# an ID in front of the request/response. The ID from the request
# must be echoed back with the response to that request.
#
# queue-size=N
#
# Sets the maximum number of queued requests to N. A request is queued
# when no existing child can accept it due to concurrency limit and no
# new child can be started due to numberofchildren limit. The default
# maximum is 2*numberofchildren. If the queued requests exceed queue
# size and redirector_bypass configuration option is set, then
# redirector is bypassed. Otherwise, Squid is allowed to temporarily
# exceed the configured maximum, marking the affected helper as
# "overloaded". If the helper overload lasts more than 3 minutes, the
# action prescribed by the on-persistent-overload option applies.
#
# on-persistent-overload=action
#
# Specifies Squid reaction to a new helper request arriving when the helper
# has been overloaded for more that 3 minutes already. The number of queued
# requests determines whether the helper is overloaded (see the queue-size
# option).
#
# Two actions are supported:
#
# die Squid worker quits. This is the default behavior.
#
# ERR Squid treats the helper request as if it was
# immediately submitted, and the helper immediately
# replied with an ERR response. This action has no effect
# on the already queued and in-progress helper requests.
#Default:
# store_id_children 20 startup=0 idle=1 concurrency=0
# TAG: store_id_access
# If defined, this access list specifies which requests are
# sent to the StoreID processes. By default all requests
# are sent.
#
# This clause supports both fast and slow acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#Default:
# Allow, unless rules exist in squid.conf.
# TAG: store_id_bypass
# When this is 'on', a request will not go through the
# helper if all helpers are busy. If this is 'off' and the helper
# queue grows too large, the action is prescribed by the
# on-persistent-overload option. You should only enable this if the
# helpers are not critical to your caching system. If you use
# helpers for critical caching components, and you enable this
# option, users may not get objects from cache.
# This options sets default queue-size option of the store_id_children
# to 0.
#Default:
# store_id_bypass on
# OPTIONS FOR TUNING THE CACHE
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: cache
# Requests denied by this directive will not be served from the cache
# and their responses will not be stored in the cache. This directive
# has no effect on other transactions and on already cached responses.
#
# This clause supports both fast and slow acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#
# This and the two other similar caching directives listed below are
# checked at different transaction processing stages, have different
# access to response information, affect different cache operations,
# and differ in slow ACLs support:
#
# * cache: Checked before Squid makes a hit/miss determination.
# No access to reply information!
# Denies both serving a hit and storing a miss.
# Supports both fast and slow ACLs.
# * send_hit: Checked after a hit was detected.
# Has access to reply (hit) information.
# Denies serving a hit only.
# Supports fast ACLs only.
# * store_miss: Checked before storing a cachable miss.
# Has access to reply (miss) information.
# Denies storing a miss only.
# Supports fast ACLs only.
#
# If you are not sure which of the three directives to use, apply the
# following decision logic:
#
# * If your ACL(s) are of slow type _and_ need response info, redesign.
# Squid does not support that particular combination at this time.
# Otherwise:
# * If your directive ACL(s) are of slow type, use "cache"; and/or
# * if your directive ACL(s) need no response info, use "cache".
# Otherwise:
# * If you do not want the response cached, use store_miss; and/or
# * if you do not want a hit on a cached response, use send_hit.
#Default:
# By default, this directive is unused and has no effect.
# TAG: send_hit
# Responses denied by this directive will not be served from the cache
# (but may still be cached, see store_miss). This directive has no
# effect on the responses it allows and on the cached objects.
#
# Please see the "cache" directive for a summary of differences among
# store_miss, send_hit, and cache directives.
#
# Unlike the "cache" directive, send_hit only supports fast acl
# types. See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#
# For example:
#
# # apply custom Store ID mapping to some URLs
# acl MapMe dstdomain .c.example.com
# store_id_program ...
# store_id_access allow MapMe
#
# # but prevent caching of special responses
# # such as 302 redirects that cause StoreID loops
# acl Ordinary http_status 200-299
# store_miss deny MapMe !Ordinary
#
# # and do not serve any previously stored special responses
# # from the cache (in case they were already cached before
# # the above store_miss rule was in effect).
# send_hit deny MapMe !Ordinary
#Default:
# By default, this directive is unused and has no effect.
# TAG: store_miss
# Responses denied by this directive will not be cached (but may still
# be served from the cache, see send_hit). This directive has no
# effect on the responses it allows and on the already cached responses.
#
# Please see the "cache" directive for a summary of differences among
# store_miss, send_hit, and cache directives. See the
# send_hit directive for a usage example.
#
# Unlike the "cache" directive, store_miss only supports fast acl
# types. See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#Default:
# By default, this directive is unused and has no effect.
# TAG: max_stale time-units
# This option puts an upper limit on how stale content Squid
# will serve from the cache if cache validation fails.
# Can be overriden by the refresh_pattern max-stale option.
#Default:
# max_stale 1 week
# TAG: refresh_pattern
# usage: refresh_pattern [-i] regex min percent max [options]
#
# By default, regular expressions are CASE-SENSITIVE. To make
# them case-insensitive, use the -i option.
#
# 'Min' is the time (in minutes) an object without an explicit
# expiry time should be considered fresh. The recommended
# value is 0, any higher values may cause dynamic applications
# to be erroneously cached unless the application designer
# has taken the appropriate actions.
#
# 'Percent' is a percentage of the objects age (time since last
# modification age) an object without explicit expiry time
# will be considered fresh.
#
# 'Max' is an upper limit on how long objects without an explicit
# expiry time will be considered fresh. The value is also used
# to form Cache-Control: max-age header for a request sent from
# Squid to origin/parent.
#
# options: override-expire
# override-lastmod
# reload-into-ims
# ignore-reload
# ignore-no-store
# ignore-private
# max-stale=NN
# refresh-ims
# store-stale
#
# override-expire enforces min age even if the server
# sent an explicit expiry time (e.g., with the
# Expires: header or Cache-Control: max-age). Doing this
# VIOLATES the HTTP standard. Enabling this feature
# could make you liable for problems which it causes.
#
# Note: override-expire does not enforce staleness - it only extends
# freshness / min. If the server returns a Expires time which
# is longer than your max time, Squid will still consider
# the object fresh for that period of time.
#
# override-lastmod enforces min age even on objects
# that were modified recently.
#
# reload-into-ims changes a client no-cache or ``reload''
# request for a cached entry into a conditional request using
# If-Modified-Since and/or If-None-Match headers, provided the
# cached entry has a Last-Modified and/or a strong ETag header.
# Doing this VIOLATES the HTTP standard. Enabling this feature
# could make you liable for problems which it causes.
#
# ignore-reload ignores a client no-cache or ``reload''
# header. Doing this VIOLATES the HTTP standard. Enabling
# this feature could make you liable for problems which
# it causes.
#
# ignore-no-store ignores any ``Cache-control: no-store''
# headers received from a server. Doing this VIOLATES
# the HTTP standard. Enabling this feature could make you
# liable for problems which it causes.
#
# ignore-private ignores any ``Cache-control: private''
# headers received from a server. Doing this VIOLATES
# the HTTP standard. Enabling this feature could make you
# liable for problems which it causes.
#
# refresh-ims causes squid to contact the origin server
# when a client issues an If-Modified-Since request. This
# ensures that the client will receive an updated version
# if one is available.
#
# store-stale stores responses even if they don't have explicit
# freshness or a validator (i.e., Last-Modified or an ETag)
# present, or if they're already stale. By default, Squid will
# not cache such responses because they usually can't be
# reused. Note that such responses will be stale by default.
#
# max-stale=NN provide a maximum staleness factor. Squid won't
# serve objects more stale than this even if it failed to
# validate the object. Default: use the max_stale global limit.
#
# Basically a cached object is:
#
# FRESH if expire > now, else STALE
# STALE if age > max
# FRESH if lm-factor < percent, else STALE
# FRESH if age < min
# else STALE
#
# The refresh_pattern lines are checked in the order listed here.
# The first entry which matches is used. If none of the entries
# match the default will be used.
#
# Note, you must uncomment all the default lines if you want
# to change one. The default setting is only active if none is
# used.
#
#
#
# Add any of your own refresh_pattern entries above these.
#
refresh_pattern ^ftp: 1440 20% 10080
refresh_pattern ^gopher: 1440 0% 1440
refresh_pattern -i (/cgi-bin/|\?) 0 0% 0
refresh_pattern \/(Packages|Sources)(|\.bz2|\.gz|\.xz)$ 0 0% 0 refresh-ims
refresh_pattern \/Release(|\.gpg)$ 0 0% 0 refresh-ims
refresh_pattern \/InRelease$ 0 0% 0 refresh-ims
refresh_pattern \/(Translation-.*)(|\.bz2|\.gz|\.xz)$ 0 0% 0 refresh-ims
# example pattern for deb packages
#refresh_pattern (\.deb|\.udeb)$ 129600 100% 129600
refresh_pattern . 0 20% 4320
# TAG: quick_abort_min (KB)
#Default:
# quick_abort_min 16 KB
# TAG: quick_abort_max (KB)
#Default:
# quick_abort_max 16 KB
# TAG: quick_abort_pct (percent)
# The cache by default continues downloading aborted requests
# which are almost completed (less than 16 KB remaining). This
# may be undesirable on slow (e.g. SLIP) links and/or very busy
# caches. Impatient users may tie up file descriptors and
# bandwidth by repeatedly requesting and immediately aborting
# downloads.
#
# When the user aborts a request, Squid will check the
# quick_abort values to the amount of data transferred until
# then.
#
# If the transfer has less than 'quick_abort_min' KB remaining,
# it will finish the retrieval.
#
# If the transfer has more than 'quick_abort_max' KB remaining,
# it will abort the retrieval.
#
# If more than 'quick_abort_pct' of the transfer has completed,
# it will finish the retrieval.
#
# If you do not want any retrieval to continue after the client
# has aborted, set both 'quick_abort_min' and 'quick_abort_max'
# to '0 KB'.
#
# If you want retrievals to always continue if they are being
# cached set 'quick_abort_min' to '-1 KB'.
#Default:
# quick_abort_pct 95
# TAG: read_ahead_gap buffer-size
# The amount of data the cache will buffer ahead of what has been
# sent to the client when retrieving an object from another server.
#Default:
# read_ahead_gap 16 KB
# TAG: negative_ttl time-units
# Set the Default Time-to-Live (TTL) for failed requests.
# Certain types of failures (such as "connection refused" and
# "404 Not Found") are able to be negatively-cached for a short time.
# Modern web servers should provide Expires: header, however if they
# do not this can provide a minimum TTL.
# The default is not to cache errors with unknown expiry details.
#
# Note that this is different from negative caching of DNS lookups.
#
# WARNING: Doing this VIOLATES the HTTP standard. Enabling
# this feature could make you liable for problems which it
# causes.
#Default:
# negative_ttl 0 seconds
# TAG: positive_dns_ttl time-units
# Upper limit on how long Squid will cache positive DNS responses.
# Default is 6 hours (360 minutes). This directive must be set
# larger than negative_dns_ttl.
#Default:
# positive_dns_ttl 6 hours
# TAG: negative_dns_ttl time-units
# Time-to-Live (TTL) for negative caching of failed DNS lookups.
# This also sets the lower cache limit on positive lookups.
# Minimum value is 1 second, and it is not recommendable to go
# much below 10 seconds.
#Default:
# negative_dns_ttl 1 minutes
# TAG: range_offset_limit size [acl acl...]
# usage: (size) [units] [[!]aclname]
#
# Sets an upper limit on how far (number of bytes) into the file
# a Range request may be to cause Squid to prefetch the whole file.
# If beyond this limit, Squid forwards the Range request as it is and
# the result is NOT cached.
#
# This is to stop a far ahead range request (lets say start at 17MB)
# from making Squid fetch the whole object up to that point before
# sending anything to the client.
#
# Multiple range_offset_limit lines may be specified, and they will
# be searched from top to bottom on each request until a match is found.
# The first match found will be used. If no line matches a request, the
# default limit of 0 bytes will be used.
#
# 'size' is the limit specified as a number of units.
#
# 'units' specifies whether to use bytes, KB, MB, etc.
# If no units are specified bytes are assumed.
#
# A size of 0 causes Squid to never fetch more than the
# client requested. (default)
#
# A size of 'none' causes Squid to always fetch the object from the
# beginning so it may cache the result. (2.0 style)
#
# 'aclname' is the name of a defined ACL.
#
# NP: Using 'none' as the byte value here will override any quick_abort settings
# that may otherwise apply to the range request. The range request will
# be fully fetched from start to finish regardless of the client
# actions. This affects bandwidth usage.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: minimum_expiry_time (seconds)
# The minimum caching time according to (Expires - Date)
# headers Squid honors if the object can't be revalidated.
# The default is 60 seconds.
#
# In reverse proxy environments it might be desirable to honor
# shorter object lifetimes. It is most likely better to make
# your server return a meaningful Last-Modified header however.
#
# In ESI environments where page fragments often have short
# lifetimes, this will often be best set to 0.
#Default:
# minimum_expiry_time 60 seconds
# TAG: store_avg_object_size (bytes)
# Average object size, used to estimate number of objects your
# cache can hold. The default is 13 KB.
#
# This is used to pre-seed the cache index memory allocation to
# reduce expensive reallocate operations while handling clients
# traffic. Too-large values may result in memory allocation during
# peak traffic, too-small values will result in wasted memory.
#
# Check the cache manager 'info' report metrics for the real
# object sizes seen by your Squid before tuning this.
#Default:
# store_avg_object_size 13 KB
# TAG: store_objects_per_bucket
# Target number of objects per bucket in the store hash table.
# Lowering this value increases the total number of buckets and
# also the storage maintenance rate. The default is 20.
#Default:
# store_objects_per_bucket 20
# HTTP OPTIONS
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: request_header_max_size (KB)
# This specifies the maximum size for HTTP headers in a request.
# Request headers are usually relatively small (about 512 bytes).
# Placing a limit on the request header size will catch certain
# bugs (for example with persistent connections) and possibly
# buffer-overflow or denial-of-service attacks.
#Default:
# request_header_max_size 64 KB
# TAG: reply_header_max_size (KB)
# This specifies the maximum size for HTTP headers in a reply.
# Reply headers are usually relatively small (about 512 bytes).
# Placing a limit on the reply header size will catch certain
# bugs (for example with persistent connections) and possibly
# buffer-overflow or denial-of-service attacks.
#Default:
# reply_header_max_size 64 KB
# TAG: request_body_max_size (bytes)
# This specifies the maximum size for an HTTP request body.
# In other words, the maximum size of a PUT/POST request.
# A user who attempts to send a request with a body larger
# than this limit receives an "Invalid Request" error message.
# If you set this parameter to a zero (the default), there will
# be no limit imposed.
#
# See also client_request_buffer_max_size for an alternative
# limitation on client uploads which can be configured.
#Default:
# No limit.
# TAG: client_request_buffer_max_size (bytes)
# This specifies the maximum buffer size of a client request.
# It prevents squid eating too much memory when somebody uploads
# a large file.
#Default:
# client_request_buffer_max_size 512 KB
# TAG: broken_posts
# A list of ACL elements which, if matched, causes Squid to send
# an extra CRLF pair after the body of a PUT/POST request.
#
# Some HTTP servers has broken implementations of PUT/POST,
# and rely on an extra CRLF pair sent by some WWW clients.
#
# Quote from RFC2616 section 4.1 on this matter:
#
# Note: certain buggy HTTP/1.0 client implementations generate an
# extra CRLF's after a POST request. To restate what is explicitly
# forbidden by the BNF, an HTTP/1.1 client must not preface or follow
# a request with an extra CRLF.
#
# This clause only supports fast acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#
#Example:
# acl buggy_server url_regex ^http://....
# broken_posts allow buggy_server
#Default:
# Obey RFC 2616.
# TAG: adaptation_uses_indirect_client on|off
# Controls whether the indirect client IP address (instead of the direct
# client IP address) is passed to adaptation services.
#
# See also: follow_x_forwarded_for adaptation_send_client_ip
#Default:
# adaptation_uses_indirect_client on
# TAG: via on|off
# If set (default), Squid will include a Via header in requests and
# replies as required by RFC2616.
#Default:
# via on
# TAG: vary_ignore_expire on|off
# Many HTTP servers supporting Vary gives such objects
# immediate expiry time with no cache-control header
# when requested by a HTTP/1.0 client. This option
# enables Squid to ignore such expiry times until
# HTTP/1.1 is fully implemented.
#
# WARNING: If turned on this may eventually cause some
# varying objects not intended for caching to get cached.
#Default:
# vary_ignore_expire off
# TAG: request_entities
# Squid defaults to deny GET and HEAD requests with request entities,
# as the meaning of such requests are undefined in the HTTP standard
# even if not explicitly forbidden.
#
# Set this directive to on if you have clients which insists
# on sending request entities in GET or HEAD requests. But be warned
# that there is server software (both proxies and web servers) which
# can fail to properly process this kind of request which may make you
# vulnerable to cache pollution attacks if enabled.
#Default:
# request_entities off
# TAG: request_header_access
# Usage: request_header_access header_name allow|deny [!]aclname ...
#
# WARNING: Doing this VIOLATES the HTTP standard. Enabling
# this feature could make you liable for problems which it
# causes.
#
# This option replaces the old 'anonymize_headers' and the
# older 'http_anonymizer' option with something that is much
# more configurable. A list of ACLs for each header name allows
# removal of specific header fields under specific conditions.
#
# This option only applies to outgoing HTTP request headers (i.e.,
# headers sent by Squid to the next HTTP hop such as a cache peer
# or an origin server). The option has no effect during cache hit
# detection. The equivalent adaptation vectoring point in ICAP
# terminology is post-cache REQMOD.
#
# The option is applied to individual outgoing request header
# fields. For each request header field F, Squid uses the first
# qualifying sets of request_header_access rules:
#
# 1. Rules with header_name equal to F's name.
# 2. Rules with header_name 'Other', provided F's name is not
# on the hard-coded list of commonly used HTTP header names.
# 3. Rules with header_name 'All'.
#
# Within that qualifying rule set, rule ACLs are checked as usual.
# If ACLs of an "allow" rule match, the header field is allowed to
# go through as is. If ACLs of a "deny" rule match, the header is
# removed and request_header_replace is then checked to identify
# if the removed header has a replacement. If no rules within the
# set have matching ACLs, the header field is left as is.
#
# For example, to achieve the same behavior as the old
# 'http_anonymizer standard' option, you should use:
#
# request_header_access From deny all
# request_header_access Referer deny all
# request_header_access User-Agent deny all
#
# Or, to reproduce the old 'http_anonymizer paranoid' feature
# you should use:
#
# request_header_access Authorization allow all
# request_header_access Proxy-Authorization allow all
# request_header_access Cache-Control allow all
# request_header_access Content-Length allow all
# request_header_access Content-Type allow all
# request_header_access Date allow all
# request_header_access Host allow all
# request_header_access If-Modified-Since allow all
# request_header_access Pragma allow all
# request_header_access Accept allow all
# request_header_access Accept-Charset allow all
# request_header_access Accept-Encoding allow all
# request_header_access Accept-Language allow all
# request_header_access Connection allow all
# request_header_access All deny all
#
# HTTP reply headers are controlled with the reply_header_access directive.
#
# By default, all headers are allowed (no anonymizing is performed).
#Default:
# No limits.
# TAG: reply_header_access
# Usage: reply_header_access header_name allow|deny [!]aclname ...
#
# WARNING: Doing this VIOLATES the HTTP standard. Enabling
# this feature could make you liable for problems which it
# causes.
#
# This option only applies to reply headers, i.e., from the
# server to the client.
#
# This is the same as request_header_access, but in the other
# direction. Please see request_header_access for detailed
# documentation.
#
# For example, to achieve the same behavior as the old
# 'http_anonymizer standard' option, you should use:
#
# reply_header_access Server deny all
# reply_header_access WWW-Authenticate deny all
# reply_header_access Link deny all
#
# Or, to reproduce the old 'http_anonymizer paranoid' feature
# you should use:
#
# reply_header_access Allow allow all
# reply_header_access WWW-Authenticate allow all
# reply_header_access Proxy-Authenticate allow all
# reply_header_access Cache-Control allow all
# reply_header_access Content-Encoding allow all
# reply_header_access Content-Length allow all
# reply_header_access Content-Type allow all
# reply_header_access Date allow all
# reply_header_access Expires allow all
# reply_header_access Last-Modified allow all
# reply_header_access Location allow all
# reply_header_access Pragma allow all
# reply_header_access Content-Language allow all
# reply_header_access Retry-After allow all
# reply_header_access Title allow all
# reply_header_access Content-Disposition allow all
# reply_header_access Connection allow all
# reply_header_access All deny all
#
# HTTP request headers are controlled with the request_header_access directive.
#
# By default, all headers are allowed (no anonymizing is
# performed).
#Default:
# No limits.
# TAG: request_header_replace
# Usage: request_header_replace header_name message
# Example: request_header_replace User-Agent Nutscrape/1.0 (CP/M; 8-bit)
#
# This option allows you to change the contents of headers
# denied with request_header_access above, by replacing them
# with some fixed string.
#
# This only applies to request headers, not reply headers.
#
# By default, headers are removed if denied.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: reply_header_replace
# Usage: reply_header_replace header_name message
# Example: reply_header_replace Server Foo/1.0
#
# This option allows you to change the contents of headers
# denied with reply_header_access above, by replacing them
# with some fixed string.
#
# This only applies to reply headers, not request headers.
#
# By default, headers are removed if denied.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: request_header_add
# Usage: request_header_add field-name field-value [ acl ... ]
# Example: request_header_add X-Client-CA "CA=%ssl::>cert_issuer" all
#
# This option adds header fields to outgoing HTTP requests (i.e.,
# request headers sent by Squid to the next HTTP hop such as a
# cache peer or an origin server). The option has no effect during
# cache hit detection. The equivalent adaptation vectoring point
# in ICAP terminology is post-cache REQMOD.
#
# Field-name is a token specifying an HTTP header name. If a
# standard HTTP header name is used, Squid does not check whether
# the new header conflicts with any existing headers or violates
# HTTP rules. If the request to be modified already contains a
# field with the same name, the old field is preserved but the
# header field values are not merged.
#
# Field-value is either a token or a quoted string. If quoted
# string format is used, then the surrounding quotes are removed
# while escape sequences and %macros are processed.
#
# One or more Squid ACLs may be specified to restrict header
# injection to matching requests. As always in squid.conf, all
# ACLs in the ACL list must be satisfied for the insertion to
# happen. The request_header_add supports fast ACLs only.
#
# See also: reply_header_add.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: reply_header_add
# Usage: reply_header_add field-name field-value [ acl ... ]
# Example: reply_header_add X-Client-CA "CA=%ssl::>cert_issuer" all
#
# This option adds header fields to outgoing HTTP responses (i.e., response
# headers delivered by Squid to the client). This option has no effect on
# cache hit detection. The equivalent adaptation vectoring point in
# ICAP terminology is post-cache RESPMOD. This option does not apply to
# successful CONNECT replies.
#
# Field-name is a token specifying an HTTP header name. If a
# standard HTTP header name is used, Squid does not check whether
# the new header conflicts with any existing headers or violates
# HTTP rules. If the response to be modified already contains a
# field with the same name, the old field is preserved but the
# header field values are not merged.
#
# Field-value is either a token or a quoted string. If quoted
# string format is used, then the surrounding quotes are removed
# while escape sequences and %macros are processed.
#
# One or more Squid ACLs may be specified to restrict header
# injection to matching responses. As always in squid.conf, all
# ACLs in the ACL list must be satisfied for the insertion to
# happen. The reply_header_add option supports fast ACLs only.
#
# See also: request_header_add.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: note
# This option used to log custom information about the master
# transaction. For example, an admin may configure Squid to log
# which "user group" the transaction belongs to, where "user group"
# will be determined based on a set of ACLs and not [just]
# authentication information.
# Values of key/value pairs can be logged using %{key}note macros:
#
# note key value acl ...
# logformat myFormat ... %{key}note ...
#
# This clause only supports fast acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: relaxed_header_parser on|off|warn
# In the default "on" setting Squid accepts certain forms
# of non-compliant HTTP messages where it is unambiguous
# what the sending application intended even if the message
# is not correctly formatted. The messages is then normalized
# to the correct form when forwarded by Squid.
#
# If set to "warn" then a warning will be emitted in cache.log
# each time such HTTP error is encountered.
#
# If set to "off" then such HTTP errors will cause the request
# or response to be rejected.
#Default:
# relaxed_header_parser on
# TAG: collapsed_forwarding (on|off)
# This option controls whether Squid is allowed to merge multiple
# potentially cachable requests for the same URI before Squid knows
# whether the response is going to be cachable.
#
# When enabled, instead of forwarding each concurrent request for
# the same URL, Squid just sends the first of them. The other, so
# called "collapsed" requests, wait for the response to the first
# request and, if it happens to be cachable, use that response.
# Here, "concurrent requests" means "received after the first
# request headers were parsed and before the corresponding response
# headers were parsed".
#
# This feature is disabled by default: enabling collapsed
# forwarding needlessly delays forwarding requests that look
# cachable (when they are collapsed) but then need to be forwarded
# individually anyway because they end up being for uncachable
# content. However, in some cases, such as acceleration of highly
# cachable content with periodic or grouped expiration times, the
# gains from collapsing [large volumes of simultaneous refresh
# requests] outweigh losses from such delays.
#
# Squid collapses two kinds of requests: regular client requests
# received on one of the listening ports and internal "cache
# revalidation" requests which are triggered by those regular
# requests hitting a stale cached object. Revalidation collapsing
# is currently disabled for Squid instances containing SMP-aware
# disk or memory caches and for Vary-controlled cached objects.
#Default:
# collapsed_forwarding off
# TAG: collapsed_forwarding_access
# Use this directive to restrict collapsed forwarding to a subset of
# eligible requests. The directive is checked for regular HTTP
# requests, internal revalidation requests, and HTCP/ICP requests.
#
# collapsed_forwarding_access allow|deny [!]aclname ...
#
# This directive cannot force collapsing. It has no effect on
# collapsing unless collapsed_forwarding is 'on', and all other
# collapsing preconditions are satisfied.
#
# * A denied request will not collapse, and future transactions will
# not collapse on it (even if they are allowed to collapse).
#
# * An allowed request may collapse, or future transactions may
# collapse on it (provided they are allowed to collapse).
#
# This directive is evaluated before receiving HTTP response headers
# and without access to Squid-to-peer connection (if any).
#
# Only fast ACLs are supported.
#
# See also: collapsed_forwarding.
#Default:
# Requests may be collapsed if collapsed_forwarding is on.
# TAG: shared_transient_entries_limit (number of entries)
# This directive limits the size of a table used for sharing current
# transaction information among SMP workers. A table entry stores meta
# information about a single cache entry being delivered to Squid
# client(s) by one or more SMP workers. A single table entry consumes
# less than 128 shared memory bytes.
#
# The limit should be significantly larger than the number of
# concurrent non-collapsed cachable responses leaving Squid. For a
# cache that handles less than 5000 concurrent requests, the default
# setting of 16384 should be plenty.
#
# Using excessively large values wastes shared memory. Limiting the
# table size too much results in hash collisions, leading to lower hit
# ratio and missed SMP request collapsing opportunities: Transactions
# left without a table entry cannot cache their responses and are
# invisible to other concurrent requests for the same resource.
#
# A zero limit is allowed but unsupported. A positive small limit
# lowers hit ratio, but zero limit disables a lot of essential
# synchronization among SMP workers, leading to HTTP violations (e.g.,
# stale hit responses). It also disables shared collapsed forwarding:
# A worker becomes unable to collapse its requests on transactions in
# other workers, resulting in more trips to the origin server and more
# cache thrashing.
#Default:
# shared_transient_entries_limit 16384
# TIMEOUTS
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: forward_timeout time-units
# This parameter specifies how long Squid should at most attempt in
# finding a forwarding path for the request before giving up.
#Default:
# forward_timeout 4 minutes
# TAG: connect_timeout time-units
# This parameter specifies how long to wait for the TCP connect to
# the requested server or peer to complete before Squid should
# attempt to find another path where to forward the request.
#Default:
# connect_timeout 1 minute
# TAG: peer_connect_timeout time-units
# This parameter specifies how long to wait for a pending TCP
# connection to a peer cache. The default is 30 seconds. You
# may also set different timeout values for individual neighbors
# with the 'connect-timeout' option on a 'cache_peer' line.
#Default:
# peer_connect_timeout 30 seconds
# TAG: read_timeout time-units
# Applied on peer server connections.
#
# After each successful read(), the timeout will be extended by this
# amount. If no data is read again after this amount of time,
# the request is aborted and logged with ERR_READ_TIMEOUT.
#
# The default is 15 minutes.
#Default:
# read_timeout 15 minutes
# TAG: write_timeout time-units
# This timeout is tracked for all connections that have data
# available for writing and are waiting for the socket to become
# ready. After each successful write, the timeout is extended by
# the configured amount. If Squid has data to write but the
# connection is not ready for the configured duration, the
# transaction associated with the connection is terminated. The
# default is 15 minutes.
#Default:
# write_timeout 15 minutes
# TAG: request_timeout
# How long to wait for complete HTTP request headers after initial
# connection establishment.
#Default:
# request_timeout 5 minutes
# TAG: request_start_timeout
# How long to wait for the first request byte after initial
# connection establishment.
#Default:
# request_start_timeout 5 minutes
# TAG: client_idle_pconn_timeout
# How long to wait for the next HTTP request on a persistent
# client connection after the previous request completes.
#Default:
# client_idle_pconn_timeout 2 minutes
# TAG: ftp_client_idle_timeout
# How long to wait for an FTP request on a connection to Squid ftp_port.
# Many FTP clients do not deal with idle connection closures well,
# necessitating a longer default timeout than client_idle_pconn_timeout
# used for incoming HTTP requests.
#Default:
# ftp_client_idle_timeout 30 minutes
# TAG: client_lifetime time-units
# The maximum amount of time a client (browser) is allowed to
# remain connected to the cache process. This protects the Cache
# from having a lot of sockets (and hence file descriptors) tied up
# in a CLOSE_WAIT state from remote clients that go away without
# properly shutting down (either because of a network failure or
# because of a poor client implementation). The default is one
# day, 1440 minutes.
#
# NOTE: The default value is intended to be much larger than any
# client would ever need to be connected to your cache. You
# should probably change client_lifetime only as a last resort.
# If you seem to have many client connections tying up
# filedescriptors, we recommend first tuning the read_timeout,
# request_timeout, persistent_request_timeout and quick_abort values.
#Default:
# client_lifetime 1 day
# TAG: pconn_lifetime time-units
# Desired maximum lifetime of a persistent connection.
# When set, Squid will close a now-idle persistent connection that
# exceeded configured lifetime instead of moving the connection into
# the idle connection pool (or equivalent). No effect on ongoing/active
# transactions. Connection lifetime is the time period from the
# connection acceptance or opening time until "now".
#
# This limit is useful in environments with long-lived connections
# where Squid configuration or environmental factors change during a
# single connection lifetime. If unrestricted, some connections may
# last for hours and even days, ignoring those changes that should
# have affected their behavior or their existence.
#
# Currently, a new lifetime value supplied via Squid reconfiguration
# has no effect on already idle connections unless they become busy.
#
# When set to '0' this limit is not used.
#Default:
# pconn_lifetime 0 seconds
# TAG: half_closed_clients
# Some clients may shutdown the sending side of their TCP
# connections, while leaving their receiving sides open. Sometimes,
# Squid can not tell the difference between a half-closed and a
# fully-closed TCP connection.
#
# By default, Squid will immediately close client connections when
# read(2) returns "no more data to read."
#
# Change this option to 'on' and Squid will keep open connections
# until a read(2) or write(2) on the socket returns an error.
# This may show some benefits for reverse proxies. But if not
# it is recommended to leave OFF.
#Default:
# half_closed_clients off
# TAG: server_idle_pconn_timeout
# Timeout for idle persistent connections to servers and other
# proxies.
#Default:
# server_idle_pconn_timeout 1 minute
# TAG: ident_timeout
# Maximum time to wait for IDENT lookups to complete.
#
# If this is too high, and you enabled IDENT lookups from untrusted
# users, you might be susceptible to denial-of-service by having
# many ident requests going at once.
#Default:
# ident_timeout 10 seconds
# TAG: shutdown_lifetime time-units
# When SIGTERM or SIGHUP is received, the cache is put into
# "shutdown pending" mode until all active sockets are closed.
# This value is the lifetime to set for all open descriptors
# during shutdown mode. Any active clients after this many
# seconds will receive a 'timeout' message.
#Default:
# shutdown_lifetime 30 seconds
# ADMINISTRATIVE PARAMETERS
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: cache_mgr
# Email-address of local cache manager who will receive
# mail if the cache dies. The default is "webmaster".
#Default:
# cache_mgr webmaster
# TAG: mail_from
# From: email-address for mail sent when the cache dies.
# The default is to use 'squid@unique_hostname'.
#
# See also: unique_hostname directive.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: mail_program
# Email program used to send mail if the cache dies.
# The default is "mail". The specified program must comply
# with the standard Unix mail syntax:
# mail-program recipient < mailfile
#
# Optional command line options can be specified.
#Default:
# mail_program mail
# TAG: cache_effective_user
# If you start Squid as root, it will change its effective/real
# UID/GID to the user specified below. The default is to change
# to UID of proxy.
# see also; cache_effective_group
#Default:
# cache_effective_user proxy
# TAG: cache_effective_group
# Squid sets the GID to the effective user's default group ID
# (taken from the password file) and supplementary group list
# from the groups membership.
#
# If you want Squid to run with a specific GID regardless of
# the group memberships of the effective user then set this
# to the group (or GID) you want Squid to run as. When set
# all other group privileges of the effective user are ignored
# and only this GID is effective. If Squid is not started as
# root the user starting Squid MUST be member of the specified
# group.
#
# This option is not recommended by the Squid Team.
# Our preference is for administrators to configure a secure
# user account for squid with UID/GID matching system policies.
#Default:
# Use system group memberships of the cache_effective_user account
# TAG: httpd_suppress_version_string on|off
# Suppress Squid version string info in HTTP headers and HTML error pages.
#Default:
# httpd_suppress_version_string off
# TAG: visible_hostname
# If you want to present a special hostname in error messages, etc,
# define this. Otherwise, the return value of gethostname()
# will be used. If you have multiple caches in a cluster and
# get errors about IP-forwarding you must set them to have individual
# names with this setting.
#Default:
# Automatically detect the system host name
# TAG: unique_hostname
# If you want to have multiple machines with the same
# 'visible_hostname' you must give each machine a different
# 'unique_hostname' so forwarding loops can be detected.
#Default:
# Copy the value from visible_hostname
# TAG: hostname_aliases
# A list of other DNS names your cache has.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: umask
# Minimum umask which should be enforced while the proxy
# is running, in addition to the umask set at startup.
#
# For a traditional octal representation of umasks, start
# your value with 0.
#Default:
# umask 027
# OPTIONS FOR THE CACHE REGISTRATION SERVICE
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
#
# This section contains parameters for the (optional) cache
# announcement service. This service is provided to help
# cache administrators locate one another in order to join or
# create cache hierarchies.
#
# An 'announcement' message is sent (via UDP) to the registration
# service by Squid. By default, the announcement message is NOT
# SENT unless you enable it with 'announce_period' below.
#
# The announcement message includes your hostname, plus the
# following information from this configuration file:
#
# http_port
# icp_port
# cache_mgr
#
# All current information is processed regularly and made
# available on the Web at http://www.ircache.net/Cache/Tracker/.
# TAG: announce_period
# This is how frequently to send cache announcements.
#
# To enable announcing your cache, just set an announce period.
#
# Example:
# announce_period 1 day
#Default:
# Announcement messages disabled.
# TAG: announce_host
# Set the hostname where announce registration messages will be sent.
#
# See also announce_port and announce_file
#Default:
# announce_host tracker.ircache.net
# TAG: announce_file
# The contents of this file will be included in the announce
# registration messages.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: announce_port
# Set the port where announce registration messages will be sent.
#
# See also announce_host and announce_file
#Default:
# announce_port 3131
# HTTPD-ACCELERATOR OPTIONS
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: httpd_accel_surrogate_id
# Surrogates (http://www.esi.org/architecture_spec_1.0.html)
# need an identification token to allow control targeting. Because
# a farm of surrogates may all perform the same tasks, they may share
# an identification token.
#
# When the surrogate is a reverse-proxy, this ID is also
# used as cdn-id for CDN-Loop detection (RFC 8586).
#Default:
# visible_hostname is used if no specific ID is set.
# TAG: http_accel_surrogate_remote on|off
# Remote surrogates (such as those in a CDN) honour the header
# "Surrogate-Control: no-store-remote".
#
# Set this to on to have squid behave as a remote surrogate.
#Default:
# http_accel_surrogate_remote off
# TAG: esi_parser libxml2|expat
# Selects the XML parsing library to use when interpreting responses with
# Edge Side Includes.
#
# To disable ESI handling completely, ./configure Squid with --disable-esi.
#Default:
# Selects libxml2 if available at ./configure time or libexpat otherwise.
# DELAY POOL PARAMETERS
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: delay_pools
# This represents the number of delay pools to be used. For example,
# if you have one class 2 delay pool and one class 3 delays pool, you
# have a total of 2 delay pools.
#
# See also delay_parameters, delay_class, delay_access for pool
# configuration details.
#Default:
# delay_pools 0
# TAG: delay_class
# This defines the class of each delay pool. There must be exactly one
# delay_class line for each delay pool. For example, to define two
# delay pools, one of class 2 and one of class 3, the settings above
# and here would be:
#
# Example:
# delay_pools 4 # 4 delay pools
# delay_class 1 2 # pool 1 is a class 2 pool
# delay_class 2 3 # pool 2 is a class 3 pool
# delay_class 3 4 # pool 3 is a class 4 pool
# delay_class 4 5 # pool 4 is a class 5 pool
#
# The delay pool classes are:
#
# class 1 Everything is limited by a single aggregate
# bucket.
#
# class 2 Everything is limited by a single aggregate
# bucket as well as an "individual" bucket chosen
# from bits 25 through 32 of the IPv4 address.
#
# class 3 Everything is limited by a single aggregate
# bucket as well as a "network" bucket chosen
# from bits 17 through 24 of the IP address and a
# "individual" bucket chosen from bits 17 through
# 32 of the IPv4 address.
#
# class 4 Everything in a class 3 delay pool, with an
# additional limit on a per user basis. This
# only takes effect if the username is established
# in advance - by forcing authentication in your
# http_access rules.
#
# class 5 Requests are grouped according their tag (see
# external_acl's tag= reply).
#
#
# Each pool also requires a delay_parameters directive to configure the pool size
# and speed limits used whenever the pool is applied to a request. Along with
# a set of delay_access directives to determine when it is used.
#
# NOTE: If an IP address is a.b.c.d
# -> bits 25 through 32 are "d"
# -> bits 17 through 24 are "c"
# -> bits 17 through 32 are "c * 256 + d"
#
# NOTE-2: Due to the use of bitmasks in class 2,3,4 pools they only apply to
# IPv4 traffic. Class 1 and 5 pools may be used with IPv6 traffic.
#
# This clause only supports fast acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#
# See also delay_parameters and delay_access.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: delay_access
# This is used to determine which delay pool a request falls into.
#
# delay_access is sorted per pool and the matching starts with pool 1,
# then pool 2, ..., and finally pool N. The first delay pool where the
# request is allowed is selected for the request. If it does not allow
# the request to any pool then the request is not delayed (default).
#
# For example, if you want some_big_clients in delay
# pool 1 and lotsa_little_clients in delay pool 2:
#
# delay_access 1 allow some_big_clients
# delay_access 1 deny all
# delay_access 2 allow lotsa_little_clients
# delay_access 2 deny all
# delay_access 3 allow authenticated_clients
#
# See also delay_parameters and delay_class.
#
#Default:
# Deny using the pool, unless allow rules exist in squid.conf for the pool.
# TAG: delay_parameters
# This defines the parameters for a delay pool. Each delay pool has
# a number of "buckets" associated with it, as explained in the
# description of delay_class.
#
# For a class 1 delay pool, the syntax is:
# delay_class pool 1
# delay_parameters pool aggregate
#
# For a class 2 delay pool:
# delay_class pool 2
# delay_parameters pool aggregate individual
#
# For a class 3 delay pool:
# delay_class pool 3
# delay_parameters pool aggregate network individual
#
# For a class 4 delay pool:
# delay_class pool 4
# delay_parameters pool aggregate network individual user
#
# For a class 5 delay pool:
# delay_class pool 5
# delay_parameters pool tagrate
#
# The option variables are:
#
# pool a pool number - ie, a number between 1 and the
# number specified in delay_pools as used in
# delay_class lines.
#
# aggregate the speed limit parameters for the aggregate bucket
# (class 1, 2, 3).
#
# individual the speed limit parameters for the individual
# buckets (class 2, 3).
#
# network the speed limit parameters for the network buckets
# (class 3).
#
# user the speed limit parameters for the user buckets
# (class 4).
#
# tagrate the speed limit parameters for the tag buckets
# (class 5).
#
# A pair of delay parameters is written restore/maximum, where restore is
# the number of bytes (not bits - modem and network speeds are usually
# quoted in bits) per second placed into the bucket, and maximum is the
# maximum number of bytes which can be in the bucket at any time.
#
# There must be one delay_parameters line for each delay pool.
#
#
# For example, if delay pool number 1 is a class 2 delay pool as in the
# above example, and is being used to strictly limit each host to 64Kbit/sec
# (plus overheads), with no overall limit, the line is:
#
# delay_parameters 1 none 8000/8000
#
# Note that 8 x 8K Byte/sec -> 64K bit/sec.
#
# Note that the word 'none' is used to represent no limit.
#
#
# And, if delay pool number 2 is a class 3 delay pool as in the above
# example, and you want to limit it to a total of 256Kbit/sec (strict limit)
# with each 8-bit network permitted 64Kbit/sec (strict limit) and each
# individual host permitted 4800bit/sec with a bucket maximum size of 64Kbits
# to permit a decent web page to be downloaded at a decent speed
# (if the network is not being limited due to overuse) but slow down
# large downloads more significantly:
#
# delay_parameters 2 32000/32000 8000/8000 600/8000
#
# Note that 8 x 32K Byte/sec -> 256K bit/sec.
# 8 x 8K Byte/sec -> 64K bit/sec.
# 8 x 600 Byte/sec -> 4800 bit/sec.
#
#
# Finally, for a class 4 delay pool as in the example - each user will
# be limited to 128Kbits/sec no matter how many workstations they are logged into.:
#
# delay_parameters 4 32000/32000 8000/8000 600/64000 16000/16000
#
#
# See also delay_class and delay_access.
#
#Default:
# none
# TAG: delay_initial_bucket_level (percent, 0-100)
# The initial bucket percentage is used to determine how much is put
# in each bucket when squid starts, is reconfigured, or first notices
# a host accessing it (in class 2 and class 3, individual hosts and
# networks only have buckets associated with them once they have been
# "seen" by squid).
#Default:
# delay_initial_bucket_level 50
# CLIENT DELAY POOL PARAMETERS
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: client_delay_pools
# This option specifies the number of client delay pools used. It must
# preceed other client_delay_* options.
#
# Example:
# client_delay_pools 2
#
# See also client_delay_parameters and client_delay_access.
#Default:
# client_delay_pools 0
# TAG: client_delay_initial_bucket_level (percent, 0-no_limit)
# This option determines the initial bucket size as a percentage of
# max_bucket_size from client_delay_parameters. Buckets are created
# at the time of the "first" connection from the matching IP. Idle
# buckets are periodically deleted up.
#
# You can specify more than 100 percent but note that such "oversized"
# buckets are not refilled until their size goes down to max_bucket_size
# from client_delay_parameters.
#
# Example:
# client_delay_initial_bucket_level 50
#Default:
# client_delay_initial_bucket_level 50
# TAG: client_delay_parameters
#
# This option configures client-side bandwidth limits using the
# following format:
#
# client_delay_parameters pool speed_limit max_bucket_size
#
# pool is an integer ID used for client_delay_access matching.
#
# speed_limit is bytes added to the bucket per second.
#
# max_bucket_size is the maximum size of a bucket, enforced after any
# speed_limit additions.
#
# Please see the delay_parameters option for more information and
# examples.
#
# Example:
# client_delay_parameters 1 1024 2048
# client_delay_parameters 2 51200 16384
#
# See also client_delay_access.
#
#Default:
# none
# TAG: client_delay_access
# This option determines the client-side delay pool for the
# request:
#
# client_delay_access pool_ID allow|deny acl_name
#
# All client_delay_access options are checked in their pool ID
# order, starting with pool 1. The first checked pool with allowed
# request is selected for the request. If no ACL matches or there
# are no client_delay_access options, the request bandwidth is not
# limited.
#
# The ACL-selected pool is then used to find the
# client_delay_parameters for the request. Client-side pools are
# not used to aggregate clients. Clients are always aggregated
# based on their source IP addresses (one bucket per source IP).
#
# This clause only supports fast acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
# Additionally, only the client TCP connection details are available.
# ACLs testing HTTP properties will not work.
#
# Please see delay_access for more examples.
#
# Example:
# client_delay_access 1 allow low_rate_network
# client_delay_access 2 allow vips_network
#
#
# See also client_delay_parameters and client_delay_pools.
#Default:
# Deny use of the pool, unless allow rules exist in squid.conf for the pool.
# TAG: response_delay_pool
# This option configures client response bandwidth limits using the
# following format:
#
# response_delay_pool name [option=value] ...
#
# name the response delay pool name
#
# available options:
#
# individual-restore The speed limit of an individual
# bucket(bytes/s). To be used in conjunction
# with 'individual-maximum'.
#
# individual-maximum The maximum number of bytes which can
# be placed into the individual bucket. To be used
# in conjunction with 'individual-restore'.
#
# aggregate-restore The speed limit for the aggregate
# bucket(bytes/s). To be used in conjunction with
# 'aggregate-maximum'.
#
# aggregate-maximum The maximum number of bytes which can
# be placed into the aggregate bucket. To be used
# in conjunction with 'aggregate-restore'.
#
# initial-bucket-level The initial bucket size as a percentage
# of individual-maximum.
#
# Individual and(or) aggregate bucket options may not be specified,
# meaning no individual and(or) aggregate speed limitation.
# See also response_delay_pool_access and delay_parameters for
# terminology details.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: response_delay_pool_access
# Determines whether a specific named response delay pool is used
# for the transaction. The syntax for this directive is:
#
# response_delay_pool_access pool_name allow|deny acl_name
#
# All response_delay_pool_access options are checked in the order
# they appear in this configuration file. The first rule with a
# matching ACL wins. If (and only if) an "allow" rule won, Squid
# assigns the response to the corresponding named delay pool.
#Default:
# Deny use of the pool, unless allow rules exist in squid.conf for the pool.
# WCCPv1 AND WCCPv2 CONFIGURATION OPTIONS
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: wccp_router
# Use this option to define your WCCP ``home'' router for
# Squid.
#
# wccp_router supports a single WCCP(v1) router
#
# wccp2_router supports multiple WCCPv2 routers
#
# only one of the two may be used at the same time and defines
# which version of WCCP to use.
#Default:
# WCCP disabled.
# TAG: wccp2_router
# Use this option to define your WCCP ``home'' router for
# Squid.
#
# wccp_router supports a single WCCP(v1) router
#
# wccp2_router supports multiple WCCPv2 routers
#
# only one of the two may be used at the same time and defines
# which version of WCCP to use.
#Default:
# WCCPv2 disabled.
# TAG: wccp_version
# This directive is only relevant if you need to set up WCCP(v1)
# to some very old and end-of-life Cisco routers. In all other
# setups it must be left unset or at the default setting.
# It defines an internal version in the WCCP(v1) protocol,
# with version 4 being the officially documented protocol.
#
# According to some users, Cisco IOS 11.2 and earlier only
# support WCCP version 3. If you're using that or an earlier
# version of IOS, you may need to change this value to 3, otherwise
# do not specify this parameter.
#Default:
# wccp_version 4
# TAG: wccp2_rebuild_wait
# If this is enabled Squid will wait for the cache dir rebuild to finish
# before sending the first wccp2 HereIAm packet
#Default:
# wccp2_rebuild_wait on
# TAG: wccp2_forwarding_method
# WCCP2 allows the setting of forwarding methods between the
# router/switch and the cache. Valid values are as follows:
#
# gre - GRE encapsulation (forward the packet in a GRE/WCCP tunnel)
# l2 - L2 redirect (forward the packet using Layer 2/MAC rewriting)
#
# Currently (as of IOS 12.4) cisco routers only support GRE.
# Cisco switches only support the L2 redirect assignment method.
#Default:
# wccp2_forwarding_method gre
# TAG: wccp2_return_method
# WCCP2 allows the setting of return methods between the
# router/switch and the cache for packets that the cache
# decides not to handle. Valid values are as follows:
#
# gre - GRE encapsulation (forward the packet in a GRE/WCCP tunnel)
# l2 - L2 redirect (forward the packet using Layer 2/MAC rewriting)
#
# Currently (as of IOS 12.4) cisco routers only support GRE.
# Cisco switches only support the L2 redirect assignment.
#
# If the "ip wccp redirect exclude in" command has been
# enabled on the cache interface, then it is still safe for
# the proxy server to use a l2 redirect method even if this
# option is set to GRE.
#Default:
# wccp2_return_method gre
# TAG: wccp2_assignment_method
# WCCP2 allows the setting of methods to assign the WCCP hash
# Valid values are as follows:
#
# hash - Hash assignment
# mask - Mask assignment
#
# As a general rule, cisco routers support the hash assignment method
# and cisco switches support the mask assignment method.
#Default:
# wccp2_assignment_method hash
# TAG: wccp2_service
# WCCP2 allows for multiple traffic services. There are two
# types: "standard" and "dynamic". The standard type defines
# one service id - http (id 0). The dynamic service ids can be from
# 51 to 255 inclusive. In order to use a dynamic service id
# one must define the type of traffic to be redirected; this is done
# using the wccp2_service_info option.
#
# The "standard" type does not require a wccp2_service_info option,
# just specifying the service id will suffice.
#
# MD5 service authentication can be enabled by adding
# "password=<password>" to the end of this service declaration.
#
# Examples:
#
# wccp2_service standard 0 # for the 'web-cache' standard service
# wccp2_service dynamic 80 # a dynamic service type which will be
# # fleshed out with subsequent options.
# wccp2_service standard 0 password=foo
#Default:
# Use the 'web-cache' standard service.
# TAG: wccp2_service_info
# Dynamic WCCPv2 services require further information to define the
# traffic you wish to have diverted.
#
# The format is:
#
# wccp2_service_info <id> protocol=<protocol> flags=<flag>,<flag>..
# priority=<priority> ports=<port>,<port>..
#
# The relevant WCCPv2 flags:
# + src_ip_hash, dst_ip_hash
# + source_port_hash, dst_port_hash
# + src_ip_alt_hash, dst_ip_alt_hash
# + src_port_alt_hash, dst_port_alt_hash
# + ports_source
#
# The port list can be one to eight entries.
#
# Example:
#
# wccp2_service_info 80 protocol=tcp flags=src_ip_hash,ports_source
# priority=240 ports=80
#
# Note: the service id must have been defined by a previous
# 'wccp2_service dynamic <id>' entry.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: wccp2_weight
# Each cache server gets assigned a set of the destination
# hash proportional to their weight.
#Default:
# wccp2_weight 10000
# TAG: wccp_address
# Use this option if you require WCCP(v1) to use a specific
# interface address.
#
# The default behavior is to not bind to any specific address.
#Default:
# Address selected by the operating system.
# TAG: wccp2_address
# Use this option if you require WCCPv2 to use a specific
# interface address.
#
# The default behavior is to not bind to any specific address.
#Default:
# Address selected by the operating system.
# PERSISTENT CONNECTION HANDLING
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
#
# Also see "pconn_timeout" in the TIMEOUTS section
# TAG: client_persistent_connections
# Persistent connection support for clients.
# Squid uses persistent connections (when allowed). You can use
# this option to disable persistent connections with clients.
#Default:
# client_persistent_connections on
# TAG: server_persistent_connections
# Persistent connection support for servers.
# Squid uses persistent connections (when allowed). You can use
# this option to disable persistent connections with servers.
#Default:
# server_persistent_connections on
# TAG: persistent_connection_after_error
# With this directive the use of persistent connections after
# HTTP errors can be disabled. Useful if you have clients
# who fail to handle errors on persistent connections proper.
#Default:
# persistent_connection_after_error on
# TAG: detect_broken_pconn
# Some servers have been found to incorrectly signal the use
# of HTTP/1.0 persistent connections even on replies not
# compatible, causing significant delays. This server problem
# has mostly been seen on redirects.
#
# By enabling this directive Squid attempts to detect such
# broken replies and automatically assume the reply is finished
# after 10 seconds timeout.
#Default:
# detect_broken_pconn off
# CACHE DIGEST OPTIONS
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: digest_generation
# This controls whether the server will generate a Cache Digest
# of its contents. By default, Cache Digest generation is
# enabled if Squid is compiled with --enable-cache-digests defined.
#Default:
# digest_generation on
# TAG: digest_bits_per_entry
# This is the number of bits of the server's Cache Digest which
# will be associated with the Digest entry for a given HTTP
# Method and URL (public key) combination. The default is 5.
#Default:
# digest_bits_per_entry 5
# TAG: digest_rebuild_period (seconds)
# This is the wait time between Cache Digest rebuilds.
#Default:
# digest_rebuild_period 1 hour
# TAG: digest_rewrite_period (seconds)
# This is the wait time between Cache Digest writes to
# disk.
#Default:
# digest_rewrite_period 1 hour
# TAG: digest_swapout_chunk_size (bytes)
# This is the number of bytes of the Cache Digest to write to
# disk at a time. It defaults to 4096 bytes (4KB), the Squid
# default swap page.
#Default:
# digest_swapout_chunk_size 4096 bytes
# TAG: digest_rebuild_chunk_percentage (percent, 0-100)
# This is the percentage of the Cache Digest to be scanned at a
# time. By default it is set to 10% of the Cache Digest.
#Default:
# digest_rebuild_chunk_percentage 10
# SNMP OPTIONS
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: snmp_port
# The port number where Squid listens for SNMP requests. To enable
# SNMP support set this to a suitable port number. Port number
# 3401 is often used for the Squid SNMP agent. By default it's
# set to "0" (disabled)
#
# Example:
# snmp_port 3401
#Default:
# SNMP disabled.
# TAG: snmp_access
# Allowing or denying access to the SNMP port.
#
# All access to the agent is denied by default.
# usage:
#
# snmp_access allow|deny [!]aclname ...
#
# This clause only supports fast acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#
#Example:
# snmp_access allow snmppublic localhost
# snmp_access deny all
#Default:
# Deny, unless rules exist in squid.conf.
# TAG: snmp_incoming_address
# Just like 'udp_incoming_address', but for the SNMP port.
#
# snmp_incoming_address is used for the SNMP socket receiving
# messages from SNMP agents.
#
# The default snmp_incoming_address is to listen on all
# available network interfaces.
#Default:
# Accept SNMP packets from all machine interfaces.
# TAG: snmp_outgoing_address
# Just like 'udp_outgoing_address', but for the SNMP port.
#
# snmp_outgoing_address is used for SNMP packets returned to SNMP
# agents.
#
# If snmp_outgoing_address is not set it will use the same socket
# as snmp_incoming_address. Only change this if you want to have
# SNMP replies sent using another address than where this Squid
# listens for SNMP queries.
#
# NOTE, snmp_incoming_address and snmp_outgoing_address can not have
# the same value since they both use the same port.
#Default:
# Use snmp_incoming_address or an address selected by the operating system.
# ICP OPTIONS
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: icp_port
# The port number where Squid sends and receives ICP queries to
# and from neighbor caches. The standard UDP port for ICP is 3130.
#
# Example:
# icp_port 3130
#Default:
# ICP disabled.
# TAG: htcp_port
# The port number where Squid sends and receives HTCP queries to
# and from neighbor caches. To turn it on you want to set it to
# 4827.
#
# Example:
# htcp_port 4827
#Default:
# HTCP disabled.
# TAG: log_icp_queries on|off
# If set, ICP queries are logged to access.log. You may wish
# do disable this if your ICP load is VERY high to speed things
# up or to simplify log analysis.
#Default:
# log_icp_queries on
# TAG: udp_incoming_address
# udp_incoming_address is used for UDP packets received from other
# caches.
#
# The default behavior is to not bind to any specific address.
#
# Only change this if you want to have all UDP queries received on
# a specific interface/address.
#
# NOTE: udp_incoming_address is used by the ICP, HTCP, and DNS
# modules. Altering it will affect all of them in the same manner.
#
# see also; udp_outgoing_address
#
# NOTE, udp_incoming_address and udp_outgoing_address can not
# have the same value since they both use the same port.
#Default:
# Accept packets from all machine interfaces.
# TAG: udp_outgoing_address
# udp_outgoing_address is used for UDP packets sent out to other
# caches.
#
# The default behavior is to not bind to any specific address.
#
# Instead it will use the same socket as udp_incoming_address.
# Only change this if you want to have UDP queries sent using another
# address than where this Squid listens for UDP queries from other
# caches.
#
# NOTE: udp_outgoing_address is used by the ICP, HTCP, and DNS
# modules. Altering it will affect all of them in the same manner.
#
# see also; udp_incoming_address
#
# NOTE, udp_incoming_address and udp_outgoing_address can not
# have the same value since they both use the same port.
#Default:
# Use udp_incoming_address or an address selected by the operating system.
# TAG: icp_hit_stale on|off
# If you want to return ICP_HIT for stale cache objects, set this
# option to 'on'. If you have sibling relationships with caches
# in other administrative domains, this should be 'off'. If you only
# have sibling relationships with caches under your control,
# it is probably okay to set this to 'on'.
# If set to 'on', your siblings should use the option "allow-miss"
# on their cache_peer lines for connecting to you.
#Default:
# icp_hit_stale off
# TAG: minimum_direct_hops
# If using the ICMP pinging stuff, do direct fetches for sites
# which are no more than this many hops away.
#Default:
# minimum_direct_hops 4
# TAG: minimum_direct_rtt (msec)
# If using the ICMP pinging stuff, do direct fetches for sites
# which are no more than this many rtt milliseconds away.
#Default:
# minimum_direct_rtt 400
# TAG: netdb_low
# The low water mark for the ICMP measurement database.
#
# Note: high watermark controlled by netdb_high directive.
#
# These watermarks are counts, not percents. The defaults are
# (low) 900 and (high) 1000. When the high water mark is
# reached, database entries will be deleted until the low
# mark is reached.
#Default:
# netdb_low 900
# TAG: netdb_high
# The high water mark for the ICMP measurement database.
#
# Note: low watermark controlled by netdb_low directive.
#
# These watermarks are counts, not percents. The defaults are
# (low) 900 and (high) 1000. When the high water mark is
# reached, database entries will be deleted until the low
# mark is reached.
#Default:
# netdb_high 1000
# TAG: netdb_ping_period
# The minimum period for measuring a site. There will be at
# least this much delay between successive pings to the same
# network. The default is five minutes.
#Default:
# netdb_ping_period 5 minutes
# TAG: query_icmp on|off
# If you want to ask your peers to include ICMP data in their ICP
# replies, enable this option.
#
# If your peer has configured Squid (during compilation) with
# '--enable-icmp' that peer will send ICMP pings to origin server
# sites of the URLs it receives. If you enable this option the
# ICP replies from that peer will include the ICMP data (if available).
# Then, when choosing a parent cache, Squid will choose the parent with
# the minimal RTT to the origin server. When this happens, the
# hierarchy field of the access.log will be
# "CLOSEST_PARENT_MISS". This option is off by default.
#Default:
# query_icmp off
# TAG: test_reachability on|off
# When this is 'on', ICP MISS replies will be ICP_MISS_NOFETCH
# instead of ICP_MISS if the target host is NOT in the ICMP
# database, or has a zero RTT.
#Default:
# test_reachability off
# TAG: icp_query_timeout (msec)
# Normally Squid will automatically determine an optimal ICP
# query timeout value based on the round-trip-time of recent ICP
# queries. If you want to override the value determined by
# Squid, set this 'icp_query_timeout' to a non-zero value. This
# value is specified in MILLISECONDS, so, to use a 2-second
# timeout (the old default), you would write:
#
# icp_query_timeout 2000
#Default:
# Dynamic detection.
# TAG: maximum_icp_query_timeout (msec)
# Normally the ICP query timeout is determined dynamically. But
# sometimes it can lead to very large values (say 5 seconds).
# Use this option to put an upper limit on the dynamic timeout
# value. Do NOT use this option to always use a fixed (instead
# of a dynamic) timeout value. To set a fixed timeout see the
# 'icp_query_timeout' directive.
#Default:
# maximum_icp_query_timeout 2000
# TAG: minimum_icp_query_timeout (msec)
# Normally the ICP query timeout is determined dynamically. But
# sometimes it can lead to very small timeouts, even lower than
# the normal latency variance on your link due to traffic.
# Use this option to put an lower limit on the dynamic timeout
# value. Do NOT use this option to always use a fixed (instead
# of a dynamic) timeout value. To set a fixed timeout see the
# 'icp_query_timeout' directive.
#Default:
# minimum_icp_query_timeout 5
# TAG: background_ping_rate time-units
# Controls how often the ICP pings are sent to siblings that
# have background-ping set.
#Default:
# background_ping_rate 10 seconds
# MULTICAST ICP OPTIONS
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: mcast_groups
# This tag specifies a list of multicast groups which your server
# should join to receive multicasted ICP queries.
#
# NOTE! Be very careful what you put here! Be sure you
# understand the difference between an ICP _query_ and an ICP
# _reply_. This option is to be set only if you want to RECEIVE
# multicast queries. Do NOT set this option to SEND multicast
# ICP (use cache_peer for that). ICP replies are always sent via
# unicast, so this option does not affect whether or not you will
# receive replies from multicast group members.
#
# You must be very careful to NOT use a multicast address which
# is already in use by another group of caches.
#
# If you are unsure about multicast, please read the Multicast
# chapter in the Squid FAQ (http://www.squid-cache.org/FAQ/).
#
# Usage: mcast_groups 239.128.16.128 224.0.1.20
#
# By default, Squid doesn't listen on any multicast groups.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: mcast_miss_addr
# Note: This option is only available if Squid is rebuilt with the
# -DMULTICAST_MISS_STREAM define
#
# If you enable this option, every "cache miss" URL will
# be sent out on the specified multicast address.
#
# Do not enable this option unless you are are absolutely
# certain you understand what you are doing.
#Default:
# disabled.
# TAG: mcast_miss_ttl
# Note: This option is only available if Squid is rebuilt with the
# -DMULTICAST_MISS_STREAM define
#
# This is the time-to-live value for packets multicasted
# when multicasting off cache miss URLs is enabled. By
# default this is set to 'site scope', i.e. 16.
#Default:
# mcast_miss_ttl 16
# TAG: mcast_miss_port
# Note: This option is only available if Squid is rebuilt with the
# -DMULTICAST_MISS_STREAM define
#
# This is the port number to be used in conjunction with
# 'mcast_miss_addr'.
#Default:
# mcast_miss_port 3135
# TAG: mcast_miss_encode_key
# Note: This option is only available if Squid is rebuilt with the
# -DMULTICAST_MISS_STREAM define
#
# The URLs that are sent in the multicast miss stream are
# encrypted. This is the encryption key.
#Default:
# mcast_miss_encode_key XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
# TAG: mcast_icp_query_timeout (msec)
# For multicast peers, Squid regularly sends out ICP "probes" to
# count how many other peers are listening on the given multicast
# address. This value specifies how long Squid should wait to
# count all the replies. The default is 2000 msec, or 2
# seconds.
#Default:
# mcast_icp_query_timeout 2000
# INTERNAL ICON OPTIONS
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: icon_directory
# Where the icons are stored. These are normally kept in
# /usr/share/squid/icons
#Default:
# icon_directory /usr/share/squid/icons
# TAG: global_internal_static
# This directive controls is Squid should intercept all requests for
# /squid-internal-static/ no matter which host the URL is requesting
# (default on setting), or if nothing special should be done for
# such URLs (off setting). The purpose of this directive is to make
# icons etc work better in complex cache hierarchies where it may
# not always be possible for all corners in the cache mesh to reach
# the server generating a directory listing.
#Default:
# global_internal_static on
# TAG: short_icon_urls
# If this is enabled Squid will use short URLs for icons.
# If disabled it will revert to the old behavior of including
# it's own name and port in the URL.
#
# If you run a complex cache hierarchy with a mix of Squid and
# other proxies you may need to disable this directive.
#Default:
# short_icon_urls on
# ERROR PAGE OPTIONS
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: error_directory
# If you wish to create your own versions of the default
# error files to customize them to suit your company copy
# the error/template files to another directory and point
# this tag at them.
#
# WARNING: This option will disable multi-language support
# on error pages if used.
#
# The squid developers are interested in making squid available in
# a wide variety of languages. If you are making translations for a
# language that Squid does not currently provide please consider
# contributing your translation back to the project.
# http://wiki.squid-cache.org/Translations
#
# The squid developers working on translations are happy to supply drop-in
# translated error files in exchange for any new language contributions.
#Default:
# Send error pages in the clients preferred language
# TAG: error_default_language
# Set the default language which squid will send error pages in
# if no existing translation matches the clients language
# preferences.
#
# If unset (default) generic English will be used.
#
# The squid developers are interested in making squid available in
# a wide variety of languages. If you are interested in making
# translations for any language see the squid wiki for details.
# http://wiki.squid-cache.org/Translations
#Default:
# Generate English language pages.
# TAG: error_log_languages
# Log to cache.log what languages users are attempting to
# auto-negotiate for translations.
#
# Successful negotiations are not logged. Only failures
# have meaning to indicate that Squid may need an upgrade
# of its error page translations.
#Default:
# error_log_languages on
# TAG: err_page_stylesheet
# CSS Stylesheet to pattern the display of Squid default error pages.
#
# For information on CSS see http://www.w3.org/Style/CSS/
#Default:
# err_page_stylesheet /etc/squid/errorpage.css
# TAG: err_html_text
# HTML text to include in error messages. Make this a "mailto"
# URL to your admin address, or maybe just a link to your
# organizations Web page.
#
# To include this in your error messages, you must rewrite
# the error template files (found in the "errors" directory).
# Wherever you want the 'err_html_text' line to appear,
# insert a %L tag in the error template file.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: email_err_data on|off
# If enabled, information about the occurred error will be
# included in the mailto links of the ERR pages (if %W is set)
# so that the email body contains the data.
# Syntax is <A HREF="mailto:%w%W">%w</A>
#Default:
# email_err_data on
# TAG: deny_info
# Usage: deny_info err_page_name acl
# or deny_info http://... acl
# or deny_info TCP_RESET acl
#
# This can be used to return a ERR_ page for requests which
# do not pass the 'http_access' rules. Squid remembers the last
# acl it evaluated in http_access, and if a 'deny_info' line exists
# for that ACL Squid returns a corresponding error page.
#
# The acl is typically the last acl on the http_access deny line which
# denied access. The exceptions to this rule are:
# - When Squid needs to request authentication credentials. It's then
# the first authentication related acl encountered
# - When none of the http_access lines matches. It's then the last
# acl processed on the last http_access line.
# - When the decision to deny access was made by an adaptation service,
# the acl name is the corresponding eCAP or ICAP service_name.
#
# NP: If providing your own custom error pages with error_directory
# you may also specify them by your custom file name:
# Example: deny_info ERR_CUSTOM_ACCESS_DENIED bad_guys
#
# By defaut Squid will send "403 Forbidden". A different 4xx or 5xx
# may be specified by prefixing the file name with the code and a colon.
# e.g. 404:ERR_CUSTOM_ACCESS_DENIED
#
# Alternatively you can tell Squid to reset the TCP connection
# by specifying TCP_RESET.
#
# Or you can specify an error URL or URL pattern. The browsers will
# get redirected to the specified URL after formatting tags have
# been replaced. Redirect will be done with 302 or 307 according to
# HTTP/1.1 specs. A different 3xx code may be specified by prefixing
# the URL. e.g. 303:http://example.com/
#
# URL FORMAT TAGS:
# %a - username (if available. Password NOT included)
# %A - Local listening IP address the client connection was connected to
# %B - FTP path URL
# %e - Error number
# %E - Error description
# %h - Squid hostname
# %H - Request domain name
# %i - Client IP Address
# %M - Request Method
# %O - Unescaped message result from external ACL helper
# %o - Message result from external ACL helper
# %p - Request Port number
# %P - Request Protocol name
# %R - Request URL path
# %T - Timestamp in RFC 1123 format
# %U - Full canonical URL from client
# (HTTPS URLs terminate with *)
# %u - Full canonical URL from client
# %w - Admin email from squid.conf
# %x - Error name
# %% - Literal percent (%) code
#
#Default:
# none
# OPTIONS INFLUENCING REQUEST FORWARDING
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: nonhierarchical_direct
# By default, Squid will send any non-hierarchical requests
# (not cacheable request type) direct to origin servers.
#
# When this is set to "off", Squid will prefer to send these
# requests to parents.
#
# Note that in most configurations, by turning this off you will only
# add latency to these request without any improvement in global hit
# ratio.
#
# This option only sets a preference. If the parent is unavailable a
# direct connection to the origin server may still be attempted. To
# completely prevent direct connections use never_direct.
#Default:
# nonhierarchical_direct on
# TAG: prefer_direct
# Normally Squid tries to use parents for most requests. If you for some
# reason like it to first try going direct and only use a parent if
# going direct fails set this to on.
#
# By combining nonhierarchical_direct off and prefer_direct on you
# can set up Squid to use a parent as a backup path if going direct
# fails.
#
# Note: If you want Squid to use parents for all requests see
# the never_direct directive. prefer_direct only modifies how Squid
# acts on cacheable requests.
#Default:
# prefer_direct off
# TAG: cache_miss_revalidate on|off
# RFC 7232 defines a conditional request mechanism to prevent
# response objects being unnecessarily transferred over the network.
# If that mechanism is used by the client and a cache MISS occurs
# it can prevent new cache entries being created.
#
# This option determines whether Squid on cache MISS will pass the
# client revalidation request to the server or tries to fetch new
# content for caching. It can be useful while the cache is mostly
# empty to more quickly have the cache populated by generating
# non-conditional GETs.
#
# When set to 'on' (default), Squid will pass all client If-* headers
# to the server. This permits server responses without a cacheable
# payload to be delivered and on MISS no new cache entry is created.
#
# When set to 'off' and if the request is cacheable, Squid will
# remove the clients If-Modified-Since and If-None-Match headers from
# the request sent to the server. This requests a 200 status response
# from the server to create a new cache entry with.
#Default:
# cache_miss_revalidate on
# TAG: always_direct
# Usage: always_direct allow|deny [!]aclname ...
#
# Here you can use ACL elements to specify requests which should
# ALWAYS be forwarded by Squid to the origin servers without using
# any peers. For example, to always directly forward requests for
# local servers ignoring any parents or siblings you may have use
# something like:
#
# acl local-servers dstdomain my.domain.net
# always_direct allow local-servers
#
# To always forward FTP requests directly, use
#
# acl FTP proto FTP
# always_direct allow FTP
#
# NOTE: There is a similar, but opposite option named
# 'never_direct'. You need to be aware that "always_direct deny
# foo" is NOT the same thing as "never_direct allow foo". You
# may need to use a deny rule to exclude a more-specific case of
# some other rule. Example:
#
# acl local-external dstdomain external.foo.net
# acl local-servers dstdomain .foo.net
# always_direct deny local-external
# always_direct allow local-servers
#
# NOTE: If your goal is to make the client forward the request
# directly to the origin server bypassing Squid then this needs
# to be done in the client configuration. Squid configuration
# can only tell Squid how Squid should fetch the object.
#
# NOTE: This directive is not related to caching. The replies
# is cached as usual even if you use always_direct. To not cache
# the replies see the 'cache' directive.
#
# This clause supports both fast and slow acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#Default:
# Prevent any cache_peer being used for this request.
# TAG: never_direct
# Usage: never_direct allow|deny [!]aclname ...
#
# never_direct is the opposite of always_direct. Please read
# the description for always_direct if you have not already.
#
# With 'never_direct' you can use ACL elements to specify
# requests which should NEVER be forwarded directly to origin
# servers. For example, to force the use of a proxy for all
# requests, except those in your local domain use something like:
#
# acl local-servers dstdomain .foo.net
# never_direct deny local-servers
# never_direct allow all
#
# or if Squid is inside a firewall and there are local intranet
# servers inside the firewall use something like:
#
# acl local-intranet dstdomain .foo.net
# acl local-external dstdomain external.foo.net
# always_direct deny local-external
# always_direct allow local-intranet
# never_direct allow all
#
# This clause supports both fast and slow acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#Default:
# Allow DNS results to be used for this request.
# ADVANCED NETWORKING OPTIONS
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: incoming_udp_average
# Heavy voodoo here. I can't even believe you are reading this.
# Are you crazy? Don't even think about adjusting these unless
# you understand the algorithms in comm_select.c first!
#Default:
# incoming_udp_average 6
# TAG: incoming_tcp_average
# Heavy voodoo here. I can't even believe you are reading this.
# Are you crazy? Don't even think about adjusting these unless
# you understand the algorithms in comm_select.c first!
#Default:
# incoming_tcp_average 4
# TAG: incoming_dns_average
# Heavy voodoo here. I can't even believe you are reading this.
# Are you crazy? Don't even think about adjusting these unless
# you understand the algorithms in comm_select.c first!
#Default:
# incoming_dns_average 4
# TAG: min_udp_poll_cnt
# Heavy voodoo here. I can't even believe you are reading this.
# Are you crazy? Don't even think about adjusting these unless
# you understand the algorithms in comm_select.c first!
#Default:
# min_udp_poll_cnt 8
# TAG: min_dns_poll_cnt
# Heavy voodoo here. I can't even believe you are reading this.
# Are you crazy? Don't even think about adjusting these unless
# you understand the algorithms in comm_select.c first!
#Default:
# min_dns_poll_cnt 8
# TAG: min_tcp_poll_cnt
# Heavy voodoo here. I can't even believe you are reading this.
# Are you crazy? Don't even think about adjusting these unless
# you understand the algorithms in comm_select.c first!
#Default:
# min_tcp_poll_cnt 8
# TAG: accept_filter
# FreeBSD:
#
# The name of an accept(2) filter to install on Squid's
# listen socket(s). This feature is perhaps specific to
# FreeBSD and requires support in the kernel.
#
# The 'httpready' filter delays delivering new connections
# to Squid until a full HTTP request has been received.
# See the accf_http(9) man page for details.
#
# The 'dataready' filter delays delivering new connections
# to Squid until there is some data to process.
# See the accf_dataready(9) man page for details.
#
# Linux:
#
# The 'data' filter delays delivering of new connections
# to Squid until there is some data to process by TCP_ACCEPT_DEFER.
# You may optionally specify a number of seconds to wait by
# 'data=N' where N is the number of seconds. Defaults to 30
# if not specified. See the tcp(7) man page for details.
#EXAMPLE:
## FreeBSD
#accept_filter httpready
## Linux
#accept_filter data
#Default:
# none
# TAG: client_ip_max_connections
# Set an absolute limit on the number of connections a single
# client IP can use. Any more than this and Squid will begin to drop
# new connections from the client until it closes some links.
#
# Note that this is a global limit. It affects all HTTP, HTCP, Gopher and FTP
# connections from the client. For finer control use the ACL access controls.
#
# Requires client_db to be enabled (the default).
#
# WARNING: This may noticably slow down traffic received via external proxies
# or NAT devices and cause them to rebound error messages back to their clients.
#Default:
# No limit.
# TAG: tcp_recv_bufsize (bytes)
# Size of receive buffer to set for TCP sockets. Probably just
# as easy to change your kernel's default.
# Omit from squid.conf to use the default buffer size.
#Default:
# Use operating system TCP defaults.
# ICAP OPTIONS
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: icap_enable on|off
# If you want to enable the ICAP module support, set this to on.
#Default:
# icap_enable off
# TAG: icap_connect_timeout
# This parameter specifies how long to wait for the TCP connect to
# the requested ICAP server to complete before giving up and either
# terminating the HTTP transaction or bypassing the failure.
#
# The default for optional services is peer_connect_timeout.
# The default for essential services is connect_timeout.
# If this option is explicitly set, its value applies to all services.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: icap_io_timeout time-units
# This parameter specifies how long to wait for an I/O activity on
# an established, active ICAP connection before giving up and
# either terminating the HTTP transaction or bypassing the
# failure.
#Default:
# Use read_timeout.
# TAG: icap_service_failure_limit limit [in memory-depth time-units]
# The limit specifies the number of failures that Squid tolerates
# when establishing a new TCP connection with an ICAP service. If
# the number of failures exceeds the limit, the ICAP service is
# not used for new ICAP requests until it is time to refresh its
# OPTIONS.
#
# A negative value disables the limit. Without the limit, an ICAP
# service will not be considered down due to connectivity failures
# between ICAP OPTIONS requests.
#
# Squid forgets ICAP service failures older than the specified
# value of memory-depth. The memory fading algorithm
# is approximate because Squid does not remember individual
# errors but groups them instead, splitting the option
# value into ten time slots of equal length.
#
# When memory-depth is 0 and by default this option has no
# effect on service failure expiration.
#
# Squid always forgets failures when updating service settings
# using an ICAP OPTIONS transaction, regardless of this option
# setting.
#
# For example,
# # suspend service usage after 10 failures in 5 seconds:
# icap_service_failure_limit 10 in 5 seconds
#Default:
# icap_service_failure_limit 10
# TAG: icap_service_revival_delay
# The delay specifies the number of seconds to wait after an ICAP
# OPTIONS request failure before requesting the options again. The
# failed ICAP service is considered "down" until fresh OPTIONS are
# fetched.
#
# The actual delay cannot be smaller than the hardcoded minimum
# delay of 30 seconds.
#Default:
# icap_service_revival_delay 180
# TAG: icap_preview_enable on|off
# The ICAP Preview feature allows the ICAP server to handle the
# HTTP message by looking only at the beginning of the message body
# or even without receiving the body at all. In some environments,
# previews greatly speedup ICAP processing.
#
# During an ICAP OPTIONS transaction, the server may tell Squid what
# HTTP messages should be previewed and how big the preview should be.
# Squid will not use Preview if the server did not request one.
#
# To disable ICAP Preview for all ICAP services, regardless of
# individual ICAP server OPTIONS responses, set this option to "off".
#Example:
#icap_preview_enable off
#Default:
# icap_preview_enable on
# TAG: icap_preview_size
# The default size of preview data to be sent to the ICAP server.
# This value might be overwritten on a per server basis by OPTIONS requests.
#Default:
# No preview sent.
# TAG: icap_206_enable on|off
# 206 (Partial Content) responses is an ICAP extension that allows the
# ICAP agents to optionally combine adapted and original HTTP message
# content. The decision to combine is postponed until the end of the
# ICAP response. Squid supports Partial Content extension by default.
#
# Activation of the Partial Content extension is negotiated with each
# ICAP service during OPTIONS exchange. Most ICAP servers should handle
# negotation correctly even if they do not support the extension, but
# some might fail. To disable Partial Content support for all ICAP
# services and to avoid any negotiation, set this option to "off".
#
# Example:
# icap_206_enable off
#Default:
# icap_206_enable on
# TAG: icap_default_options_ttl
# The default TTL value for ICAP OPTIONS responses that don't have
# an Options-TTL header.
#Default:
# icap_default_options_ttl 60
# TAG: icap_persistent_connections on|off
# Whether or not Squid should use persistent connections to
# an ICAP server.
#Default:
# icap_persistent_connections on
# TAG: adaptation_send_client_ip on|off
# If enabled, Squid shares HTTP client IP information with adaptation
# services. For ICAP, Squid adds the X-Client-IP header to ICAP requests.
# For eCAP, Squid sets the libecap::metaClientIp transaction option.
#
# See also: adaptation_uses_indirect_client
#Default:
# adaptation_send_client_ip off
# TAG: adaptation_send_username on|off
# This sends authenticated HTTP client username (if available) to
# the adaptation service.
#
# For ICAP, the username value is encoded based on the
# icap_client_username_encode option and is sent using the header
# specified by the icap_client_username_header option.
#Default:
# adaptation_send_username off
# TAG: icap_client_username_header
# ICAP request header name to use for adaptation_send_username.
#Default:
# icap_client_username_header X-Client-Username
# TAG: icap_client_username_encode on|off
# Whether to base64 encode the authenticated client username.
#Default:
# icap_client_username_encode off
# TAG: icap_service
# Defines a single ICAP service using the following format:
#
# icap_service id vectoring_point uri [option ...]
#
# id: ID
# an opaque identifier or name which is used to direct traffic to
# this specific service. Must be unique among all adaptation
# services in squid.conf.
#
# vectoring_point: reqmod_precache|reqmod_postcache|respmod_precache|respmod_postcache
# This specifies at which point of transaction processing the
# ICAP service should be activated. *_postcache vectoring points
# are not yet supported.
#
# uri: icap://servername:port/servicepath
# ICAP server and service location.
# icaps://servername:port/servicepath
# The "icap:" URI scheme is used for traditional ICAP server and
# service location (default port is 1344, connections are not
# encrypted). The "icaps:" URI scheme is for Secure ICAP
# services that use SSL/TLS-encrypted ICAP connections (by
# default, on port 11344).
#
# ICAP does not allow a single service to handle both REQMOD and RESPMOD
# transactions. Squid does not enforce that requirement. You can specify
# services with the same service_url and different vectoring_points. You
# can even specify multiple identical services as long as their
# service_names differ.
#
# To activate a service, use the adaptation_access directive. To group
# services, use adaptation_service_chain and adaptation_service_set.
#
# Service options are separated by white space. ICAP services support
# the following name=value options:
#
# bypass=on|off|1|0
# If set to 'on' or '1', the ICAP service is treated as
# optional. If the service cannot be reached or malfunctions,
# Squid will try to ignore any errors and process the message as
# if the service was not enabled. No all ICAP errors can be
# bypassed. If set to 0, the ICAP service is treated as
# essential and all ICAP errors will result in an error page
# returned to the HTTP client.
#
# Bypass is off by default: services are treated as essential.
#
# routing=on|off|1|0
# If set to 'on' or '1', the ICAP service is allowed to
# dynamically change the current message adaptation plan by
# returning a chain of services to be used next. The services
# are specified using the X-Next-Services ICAP response header
# value, formatted as a comma-separated list of service names.
# Each named service should be configured in squid.conf. Other
# services are ignored. An empty X-Next-Services value results
# in an empty plan which ends the current adaptation.
#
# Dynamic adaptation plan may cross or cover multiple supported
# vectoring points in their natural processing order.
#
# Routing is not allowed by default: the ICAP X-Next-Services
# response header is ignored.
#
# ipv6=on|off
# Only has effect on split-stack systems. The default on those systems
# is to use IPv4-only connections. When set to 'on' this option will
# make Squid use IPv6-only connections to contact this ICAP service.
#
# on-overload=block|bypass|wait|force
# If the service Max-Connections limit has been reached, do
# one of the following for each new ICAP transaction:
# * block: send an HTTP error response to the client
# * bypass: ignore the "over-connected" ICAP service
# * wait: wait (in a FIFO queue) for an ICAP connection slot
# * force: proceed, ignoring the Max-Connections limit
#
# In SMP mode with N workers, each worker assumes the service
# connection limit is Max-Connections/N, even though not all
# workers may use a given service.
#
# The default value is "bypass" if service is bypassable,
# otherwise it is set to "wait".
#
#
# max-conn=number
# Use the given number as the Max-Connections limit, regardless
# of the Max-Connections value given by the service, if any.
#
# connection-encryption=on|off
# Determines the ICAP service effect on the connections_encrypted
# ACL.
#
# The default is "on" for Secure ICAP services (i.e., those
# with the icaps:// service URIs scheme) and "off" for plain ICAP
# services.
#
# Does not affect ICAP connections (e.g., does not turn Secure
# ICAP on or off).
#
# ==== ICAPS / TLS OPTIONS ====
#
# These options are used for Secure ICAP (icaps://....) services only.
#
# tls-cert=/path/to/ssl/certificate
# A client X.509 certificate to use when connecting to
# this ICAP server.
#
# tls-key=/path/to/ssl/key
# The private key corresponding to the previous
# tls-cert= option.
#
# If tls-key= is not specified tls-cert= is assumed to
# reference a PEM file containing both the certificate
# and private key.
#
# tls-cipher=... The list of valid TLS/SSL ciphers to use when connecting
# to this icap server.
#
# tls-min-version=1.N
# The minimum TLS protocol version to permit. To control
# SSLv3 use the tls-options= parameter.
# Supported Values: 1.0 (default), 1.1, 1.2
#
# tls-options=... Specify various OpenSSL library options:
#
# NO_SSLv3 Disallow the use of SSLv3
#
# SINGLE_DH_USE
# Always create a new key when using
# temporary/ephemeral DH key exchanges
#
# ALL Enable various bug workarounds
# suggested as "harmless" by OpenSSL
# Be warned that this reduces SSL/TLS
# strength to some attacks.
#
# See the OpenSSL SSL_CTX_set_options documentation for a
# more complete list. Options relevant only to SSLv2 are
# not supported.
#
# tls-cafile= PEM file containing CA certificates to use when verifying
# the icap server certificate.
# Use to specify intermediate CA certificate(s) if not sent
# by the server. Or the full CA chain for the server when
# using the tls-default-ca=off flag.
# May be repeated to load multiple files.
#
# tls-capath=... A directory containing additional CA certificates to
# use when verifying the icap server certificate.
# Requires OpenSSL or LibreSSL.
#
# tls-crlfile=... A certificate revocation list file to use when
# verifying the icap server certificate.
#
# tls-flags=... Specify various flags modifying the Squid TLS implementation:
#
# DONT_VERIFY_PEER
# Accept certificates even if they fail to
# verify.
# DONT_VERIFY_DOMAIN
# Don't verify the icap server certificate
# matches the server name
#
# tls-default-ca[=off]
# Whether to use the system Trusted CAs. Default is ON.
#
# tls-domain= The icap server name as advertised in it's certificate.
# Used for verifying the correctness of the received icap
# server certificate. If not specified the icap server
# hostname extracted from ICAP URI will be used.
#
# Older icap_service format without optional named parameters is
# deprecated but supported for backward compatibility.
#
#Example:
#icap_service svcBlocker reqmod_precache icap://icap1.mydomain.net:1344/reqmod bypass=0
#icap_service svcLogger reqmod_precache icaps://icap2.mydomain.net:11344/reqmod routing=on
#Default:
# none
# TAG: icap_class
# This deprecated option was documented to define an ICAP service
# chain, even though it actually defined a set of similar, redundant
# services, and the chains were not supported.
#
# To define a set of redundant services, please use the
# adaptation_service_set directive. For service chains, use
# adaptation_service_chain.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: icap_access
# This option is deprecated. Please use adaptation_access, which
# has the same ICAP functionality, but comes with better
# documentation, and eCAP support.
#Default:
# none
# eCAP OPTIONS
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: ecap_enable on|off
# Controls whether eCAP support is enabled.
#Default:
# ecap_enable off
# TAG: ecap_service
# Defines a single eCAP service
#
# ecap_service id vectoring_point uri [option ...]
#
# id: ID
# an opaque identifier or name which is used to direct traffic to
# this specific service. Must be unique among all adaptation
# services in squid.conf.
#
# vectoring_point: reqmod_precache|reqmod_postcache|respmod_precache|respmod_postcache
# This specifies at which point of transaction processing the
# eCAP service should be activated. *_postcache vectoring points
# are not yet supported.
#
# uri: ecap://vendor/service_name?custom&cgi=style¶meters=optional
# Squid uses the eCAP service URI to match this configuration
# line with one of the dynamically loaded services. Each loaded
# eCAP service must have a unique URI. Obtain the right URI from
# the service provider.
#
# To activate a service, use the adaptation_access directive. To group
# services, use adaptation_service_chain and adaptation_service_set.
#
# Service options are separated by white space. eCAP services support
# the following name=value options:
#
# bypass=on|off|1|0
# If set to 'on' or '1', the eCAP service is treated as optional.
# If the service cannot be reached or malfunctions, Squid will try
# to ignore any errors and process the message as if the service
# was not enabled. No all eCAP errors can be bypassed.
# If set to 'off' or '0', the eCAP service is treated as essential
# and all eCAP errors will result in an error page returned to the
# HTTP client.
#
# Bypass is off by default: services are treated as essential.
#
# routing=on|off|1|0
# If set to 'on' or '1', the eCAP service is allowed to
# dynamically change the current message adaptation plan by
# returning a chain of services to be used next.
#
# Dynamic adaptation plan may cross or cover multiple supported
# vectoring points in their natural processing order.
#
# Routing is not allowed by default.
#
# connection-encryption=on|off
# Determines the eCAP service effect on the connections_encrypted
# ACL.
#
# Defaults to "on", which does not taint the master transaction
# w.r.t. that ACL.
#
# Does not affect eCAP API calls.
#
# Older ecap_service format without optional named parameters is
# deprecated but supported for backward compatibility.
#
#
#Example:
#ecap_service s1 reqmod_precache ecap://filters.R.us/leakDetector?on_error=block bypass=off
#ecap_service s2 respmod_precache ecap://filters.R.us/virusFilter config=/etc/vf.cfg bypass=on
#Default:
# none
# TAG: loadable_modules
# Instructs Squid to load the specified dynamic module(s) or activate
# preloaded module(s).
#Example:
#loadable_modules /usr/lib/MinimalAdapter.so
#Default:
# none
# MESSAGE ADAPTATION OPTIONS
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: adaptation_service_set
#
# Configures an ordered set of similar, redundant services. This is
# useful when hot standby or backup adaptation servers are available.
#
# adaptation_service_set set_name service_name1 service_name2 ...
#
# The named services are used in the set declaration order. The first
# applicable adaptation service from the set is used first. The next
# applicable service is tried if and only if the transaction with the
# previous service fails and the message waiting to be adapted is still
# intact.
#
# When adaptation starts, broken services are ignored as if they were
# not a part of the set. A broken service is a down optional service.
#
# The services in a set must be attached to the same vectoring point
# (e.g., pre-cache) and use the same adaptation method (e.g., REQMOD).
#
# If all services in a set are optional then adaptation failures are
# bypassable. If all services in the set are essential, then a
# transaction failure with one service may still be retried using
# another service from the set, but when all services fail, the master
# transaction fails as well.
#
# A set may contain a mix of optional and essential services, but that
# is likely to lead to surprising results because broken services become
# ignored (see above), making previously bypassable failures fatal.
# Technically, it is the bypassability of the last failed service that
# matters.
#
# See also: adaptation_access adaptation_service_chain
#
#Example:
#adaptation_service_set svcBlocker urlFilterPrimary urlFilterBackup
#adaptation service_set svcLogger loggerLocal loggerRemote
#Default:
# none
# TAG: adaptation_service_chain
#
# Configures a list of complementary services that will be applied
# one-by-one, forming an adaptation chain or pipeline. This is useful
# when Squid must perform different adaptations on the same message.
#
# adaptation_service_chain chain_name service_name1 svc_name2 ...
#
# The named services are used in the chain declaration order. The first
# applicable adaptation service from the chain is used first. The next
# applicable service is applied to the successful adaptation results of
# the previous service in the chain.
#
# When adaptation starts, broken services are ignored as if they were
# not a part of the chain. A broken service is a down optional service.
#
# Request satisfaction terminates the adaptation chain because Squid
# does not currently allow declaration of RESPMOD services at the
# "reqmod_precache" vectoring point (see icap_service or ecap_service).
#
# The services in a chain must be attached to the same vectoring point
# (e.g., pre-cache) and use the same adaptation method (e.g., REQMOD).
#
# A chain may contain a mix of optional and essential services. If an
# essential adaptation fails (or the failure cannot be bypassed for
# other reasons), the master transaction fails. Otherwise, the failure
# is bypassed as if the failed adaptation service was not in the chain.
#
# See also: adaptation_access adaptation_service_set
#
#Example:
#adaptation_service_chain svcRequest requestLogger urlFilter leakDetector
#Default:
# none
# TAG: adaptation_access
# Sends an HTTP transaction to an ICAP or eCAP adaptation service.
#
# adaptation_access service_name allow|deny [!]aclname...
# adaptation_access set_name allow|deny [!]aclname...
#
# At each supported vectoring point, the adaptation_access
# statements are processed in the order they appear in this
# configuration file. Statements pointing to the following services
# are ignored (i.e., skipped without checking their ACL):
#
# - services serving different vectoring points
# - "broken-but-bypassable" services
# - "up" services configured to ignore such transactions
# (e.g., based on the ICAP Transfer-Ignore header).
#
# When a set_name is used, all services in the set are checked
# using the same rules, to find the first applicable one. See
# adaptation_service_set for details.
#
# If an access list is checked and there is a match, the
# processing stops: For an "allow" rule, the corresponding
# adaptation service is used for the transaction. For a "deny"
# rule, no adaptation service is activated.
#
# It is currently not possible to apply more than one adaptation
# service at the same vectoring point to the same HTTP transaction.
#
# See also: icap_service and ecap_service
#
#Example:
#adaptation_access service_1 allow all
#Default:
# Allow, unless rules exist in squid.conf.
# TAG: adaptation_service_iteration_limit
# Limits the number of iterations allowed when applying adaptation
# services to a message. If your longest adaptation set or chain
# may have more than 16 services, increase the limit beyond its
# default value of 16. If detecting infinite iteration loops sooner
# is critical, make the iteration limit match the actual number
# of services in your longest adaptation set or chain.
#
# Infinite adaptation loops are most likely with routing services.
#
# See also: icap_service routing=1
#Default:
# adaptation_service_iteration_limit 16
# TAG: adaptation_masterx_shared_names
# For each master transaction (i.e., the HTTP request and response
# sequence, including all related ICAP and eCAP exchanges), Squid
# maintains a table of metadata. The table entries are (name, value)
# pairs shared among eCAP and ICAP exchanges. The table is destroyed
# with the master transaction.
#
# This option specifies the table entry names that Squid must accept
# from and forward to the adaptation transactions.
#
# An ICAP REQMOD or RESPMOD transaction may set an entry in the
# shared table by returning an ICAP header field with a name
# specified in adaptation_masterx_shared_names.
#
# An eCAP REQMOD or RESPMOD transaction may set an entry in the
# shared table by implementing the libecap::visitEachOption() API
# to provide an option with a name specified in
# adaptation_masterx_shared_names.
#
# Squid will store and forward the set entry to subsequent adaptation
# transactions within the same master transaction scope.
#
# Only one shared entry name is supported at this time.
#
#Example:
## share authentication information among ICAP services
#adaptation_masterx_shared_names X-Subscriber-ID
#Default:
# none
# TAG: adaptation_meta
# This option allows Squid administrator to add custom ICAP request
# headers or eCAP options to Squid ICAP requests or eCAP transactions.
# Use it to pass custom authentication tokens and other
# transaction-state related meta information to an ICAP/eCAP service.
#
# The addition of a meta header is ACL-driven:
# adaptation_meta name value [!]aclname ...
#
# Processing for a given header name stops after the first ACL list match.
# Thus, it is impossible to add two headers with the same name. If no ACL
# lists match for a given header name, no such header is added. For
# example:
#
# # do not debug transactions except for those that need debugging
# adaptation_meta X-Debug 1 needs_debugging
#
# # log all transactions except for those that must remain secret
# adaptation_meta X-Log 1 !keep_secret
#
# # mark transactions from users in the "G 1" group
# adaptation_meta X-Authenticated-Groups "G 1" authed_as_G1
#
# The "value" parameter may be a regular squid.conf token or a "double
# quoted string". Within the quoted string, use backslash (\) to escape
# any character, which is currently only useful for escaping backslashes
# and double quotes. For example,
# "this string has one backslash (\\) and two \"quotes\""
#
# Used adaptation_meta header values may be logged via %note
# logformat code. If multiple adaptation_meta headers with the same name
# are used during master transaction lifetime, the header values are
# logged in the order they were used and duplicate values are ignored
# (only the first repeated value will be logged).
#Default:
# none
# TAG: icap_retry
# This ACL determines which retriable ICAP transactions are
# retried. Transactions that received a complete ICAP response
# and did not have to consume or produce HTTP bodies to receive
# that response are usually retriable.
#
# icap_retry allow|deny [!]aclname ...
#
# Squid automatically retries some ICAP I/O timeouts and errors
# due to persistent connection race conditions.
#
# See also: icap_retry_limit
#Default:
# icap_retry deny all
# TAG: icap_retry_limit
# Limits the number of retries allowed.
#
# Communication errors due to persistent connection race
# conditions are unavoidable, automatically retried, and do not
# count against this limit.
#
# See also: icap_retry
#Default:
# No retries are allowed.
# DNS OPTIONS
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: check_hostnames
# For security and stability reasons Squid can check
# hostnames for Internet standard RFC compliance. If you want
# Squid to perform these checks turn this directive on.
#Default:
# check_hostnames off
# TAG: allow_underscore
# Underscore characters is not strictly allowed in Internet hostnames
# but nevertheless used by many sites. Set this to off if you want
# Squid to be strict about the standard.
# This check is performed only when check_hostnames is set to on.
#Default:
# allow_underscore on
# TAG: dns_retransmit_interval
# Initial retransmit interval for DNS queries. The interval is
# doubled each time all configured DNS servers have been tried.
#Default:
# dns_retransmit_interval 5 seconds
# TAG: dns_timeout
# DNS Query timeout. If no response is received to a DNS query
# within this time all DNS servers for the queried domain
# are assumed to be unavailable.
#Default:
# dns_timeout 30 seconds
# TAG: dns_packet_max
# Maximum number of bytes packet size to advertise via EDNS.
# Set to "none" to disable EDNS large packet support.
#
# For legacy reasons DNS UDP replies will default to 512 bytes which
# is too small for many responses. EDNS provides a means for Squid to
# negotiate receiving larger responses back immediately without having
# to failover with repeat requests. Responses larger than this limit
# will retain the old behaviour of failover to TCP DNS.
#
# Squid has no real fixed limit internally, but allowing packet sizes
# over 1500 bytes requires network jumbogram support and is usually not
# necessary.
#
# WARNING: The RFC also indicates that some older resolvers will reply
# with failure of the whole request if the extension is added. Some
# resolvers have already been identified which will reply with mangled
# EDNS response on occasion. Usually in response to many-KB jumbogram
# sizes being advertised by Squid.
# Squid will currently treat these both as an unable-to-resolve domain
# even if it would be resolvable without EDNS.
#Default:
# EDNS disabled
# TAG: dns_defnames on|off
# Normally the RES_DEFNAMES resolver option is disabled
# (see res_init(3)). This prevents caches in a hierarchy
# from interpreting single-component hostnames locally. To allow
# Squid to handle single-component names, enable this option.
#Default:
# Search for single-label domain names is disabled.
# TAG: dns_multicast_local on|off
# When set to on, Squid sends multicast DNS lookups on the local
# network for domains ending in .local and .arpa.
# This enables local servers and devices to be contacted in an
# ad-hoc or zero-configuration network environment.
#Default:
# Search for .local and .arpa names is disabled.
# TAG: dns_nameservers
# Use this if you want to specify a list of DNS name servers
# (IP addresses) to use instead of those given in your
# /etc/resolv.conf file.
#
# On Windows platforms, if no value is specified here or in
# the /etc/resolv.conf file, the list of DNS name servers are
# taken from the Windows registry, both static and dynamic DHCP
# configurations are supported.
#
# Example: dns_nameservers 10.0.0.1 192.172.0.4
#Default:
# Use operating system definitions
# TAG: hosts_file
# Location of the host-local IP name-address associations
# database. Most Operating Systems have such a file on different
# default locations:
# - Un*X & Linux: /etc/hosts
# - Windows NT/2000: %SystemRoot%\system32\drivers\etc\hosts
# (%SystemRoot% value install default is c:\winnt)
# - Windows XP/2003: %SystemRoot%\system32\drivers\etc\hosts
# (%SystemRoot% value install default is c:\windows)
# - Windows 9x/Me: %windir%\hosts
# (%windir% value is usually c:\windows)
# - Cygwin: /etc/hosts
#
# The file contains newline-separated definitions, in the
# form ip_address_in_dotted_form name [name ...] names are
# whitespace-separated. Lines beginning with an hash (#)
# character are comments.
#
# The file is checked at startup and upon configuration.
# If set to 'none', it won't be checked.
# If append_domain is used, that domain will be added to
# domain-local (i.e. not containing any dot character) host
# definitions.
#Default:
# hosts_file /etc/hosts
# TAG: append_domain
# Appends local domain name to hostnames without any dots in
# them. append_domain must begin with a period.
#
# Be warned there are now Internet names with no dots in
# them using only top-domain names, so setting this may
# cause some Internet sites to become unavailable.
#
#Example:
# append_domain .yourdomain.com
#Default:
# Use operating system definitions
# TAG: ignore_unknown_nameservers
# By default Squid checks that DNS responses are received
# from the same IP addresses they are sent to. If they
# don't match, Squid ignores the response and writes a warning
# message to cache.log. You can allow responses from unknown
# nameservers by setting this option to 'off'.
#Default:
# ignore_unknown_nameservers on
# TAG: ipcache_size (number of entries)
# Maximum number of DNS IP cache entries.
#Default:
# ipcache_size 1024
# TAG: ipcache_low (percent)
#Default:
# ipcache_low 90
# TAG: ipcache_high (percent)
# The size, low-, and high-water marks for the IP cache.
#Default:
# ipcache_high 95
# TAG: fqdncache_size (number of entries)
# Maximum number of FQDN cache entries.
#Default:
# fqdncache_size 1024
# MISCELLANEOUS
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# TAG: configuration_includes_quoted_values on|off
# If set, Squid will recognize each "quoted string" after a configuration
# directive as a single parameter. The quotes are stripped before the
# parameter value is interpreted or used.
# See "Values with spaces, quotes, and other special characters"
# section for more details.
#Default:
# configuration_includes_quoted_values off
# TAG: memory_pools on|off
# If set, Squid will keep pools of allocated (but unused) memory
# available for future use. If memory is a premium on your
# system and you believe your malloc library outperforms Squid
# routines, disable this.
#Default:
# memory_pools on
# TAG: memory_pools_limit (bytes)
# Used only with memory_pools on:
# memory_pools_limit 50 MB
#
# If set to a non-zero value, Squid will keep at most the specified
# limit of allocated (but unused) memory in memory pools. All free()
# requests that exceed this limit will be handled by your malloc
# library. Squid does not pre-allocate any memory, just safe-keeps
# objects that otherwise would be free()d. Thus, it is safe to set
# memory_pools_limit to a reasonably high value even if your
# configuration will use less memory.
#
# If set to none, Squid will keep all memory it can. That is, there
# will be no limit on the total amount of memory used for safe-keeping.
#
# To disable memory allocation optimization, do not set
# memory_pools_limit to 0 or none. Set memory_pools to "off" instead.
#
# An overhead for maintaining memory pools is not taken into account
# when the limit is checked. This overhead is close to four bytes per
# object kept. However, pools may actually _save_ memory because of
# reduced memory thrashing in your malloc library.
#Default:
# memory_pools_limit 5 MB
# TAG: forwarded_for on|off|transparent|truncate|delete
# If set to "on", Squid will append your client's IP address
# in the HTTP requests it forwards. By default it looks like:
#
# X-Forwarded-For: 192.1.2.3
#
# If set to "off", it will appear as
#
# X-Forwarded-For: unknown
#
# If set to "transparent", Squid will not alter the
# X-Forwarded-For header in any way.
#
# If set to "delete", Squid will delete the entire
# X-Forwarded-For header.
#
# If set to "truncate", Squid will remove all existing
# X-Forwarded-For entries, and place the client IP as the sole entry.
#Default:
# forwarded_for on
# TAG: cachemgr_passwd
# Specify passwords for cachemgr operations.
#
# Usage: cachemgr_passwd password action action ...
#
# Some valid actions are (see cache manager menu for a full list):
# 5min
# 60min
# asndb
# authenticator
# cbdata
# client_list
# comm_incoming
# config *
# counters
# delay
# digest_stats
# dns
# events
# filedescriptors
# fqdncache
# histograms
# http_headers
# info
# io
# ipcache
# mem
# menu
# netdb
# non_peers
# objects
# offline_toggle *
# pconn
# peer_select
# reconfigure *
# redirector
# refresh
# server_list
# shutdown *
# store_digest
# storedir
# utilization
# via_headers
# vm_objects
#
# * Indicates actions which will not be performed without a
# valid password, others can be performed if not listed here.
#
# To disable an action, set the password to "disable".
# To allow performing an action without a password, set the
# password to "none".
#
# Use the keyword "all" to set the same password for all actions.
#
#Example:
# cachemgr_passwd secret shutdown
# cachemgr_passwd lesssssssecret info stats/objects
# cachemgr_passwd disable all
#Default:
# No password. Actions which require password are denied.
# TAG: client_db on|off
# If you want to disable collecting per-client statistics,
# turn off client_db here.
#Default:
# client_db on
# TAG: refresh_all_ims on|off
# When you enable this option, squid will always check
# the origin server for an update when a client sends an
# If-Modified-Since request. Many browsers use IMS
# requests when the user requests a reload, and this
# ensures those clients receive the latest version.
#
# By default (off), squid may return a Not Modified response
# based on the age of the cached version.
#Default:
# refresh_all_ims off
# TAG: reload_into_ims on|off
# When you enable this option, client no-cache or ``reload''
# requests will be changed to If-Modified-Since requests.
# Doing this VIOLATES the HTTP standard. Enabling this
# feature could make you liable for problems which it
# causes.
#
# see also refresh_pattern for a more selective approach.
#Default:
# reload_into_ims off
# TAG: connect_retries
# Limits the number of reopening attempts when establishing a single
# TCP connection. All these attempts must still complete before the
# applicable connection opening timeout expires.
#
# By default and when connect_retries is set to zero, Squid does not
# retry failed connection opening attempts.
#
# The (not recommended) maximum is 10 tries. An attempt to configure a
# higher value results in the value of 10 being used (with a warning).
#
# Squid may open connections to retry various high-level forwarding
# failures. For an outside observer, that activity may look like a
# low-level connection reopening attempt, but those high-level retries
# are governed by forward_max_tries instead.
#
# See also: connect_timeout, forward_timeout, icap_connect_timeout,
# ident_timeout, and forward_max_tries.
#Default:
# Do not retry failed connections.
# TAG: retry_on_error
# If set to ON Squid will automatically retry requests when
# receiving an error response with status 403 (Forbidden),
# 500 (Internal Error), 501 or 503 (Service not available).
# Status 502 and 504 (Gateway errors) are always retried.
#
# This is mainly useful if you are in a complex cache hierarchy to
# work around access control errors.
#
# NOTE: This retry will attempt to find another working destination.
# Which is different from the server which just failed.
#Default:
# retry_on_error off
# TAG: as_whois_server
# WHOIS server to query for AS numbers. NOTE: AS numbers are
# queried only when Squid starts up, not for every request.
#Default:
# as_whois_server whois.ra.net
# TAG: offline_mode
# Enable this option and Squid will never try to validate cached
# objects.
#Default:
# offline_mode off
# TAG: uri_whitespace
# What to do with requests that have whitespace characters in the
# URI. Options:
#
# strip: The whitespace characters are stripped out of the URL.
# This is the behavior recommended by RFC2396 and RFC3986
# for tolerant handling of generic URI.
# NOTE: This is one difference between generic URI and HTTP URLs.
#
# deny: The request is denied. The user receives an "Invalid
# Request" message.
# This is the behaviour recommended by RFC2616 for safe
# handling of HTTP request URL.
#
# allow: The request is allowed and the URI is not changed. The
# whitespace characters remain in the URI. Note the
# whitespace is passed to redirector processes if they
# are in use.
# Note this may be considered a violation of RFC2616
# request parsing where whitespace is prohibited in the
# URL field.
#
# encode: The request is allowed and the whitespace characters are
# encoded according to RFC1738.
#
# chop: The request is allowed and the URI is chopped at the
# first whitespace.
#
#
# NOTE the current Squid implementation of encode and chop violates
# RFC2616 by not using a 301 redirect after altering the URL.
#Default:
# uri_whitespace strip
# TAG: chroot
# Specifies a directory where Squid should do a chroot() while
# initializing. This also causes Squid to fully drop root
# privileges after initializing. This means, for example, if you
# use a HTTP port less than 1024 and try to reconfigure, you may
# get an error saying that Squid can not open the port.
#Default:
# none
# TAG: pipeline_prefetch
# HTTP clients may send a pipeline of 1+N requests to Squid using a
# single connection, without waiting for Squid to respond to the first
# of those requests. This option limits the number of concurrent
# requests Squid will try to handle in parallel. If set to N, Squid
# will try to receive and process up to 1+N requests on the same
# connection concurrently.
#
# Defaults to 0 (off) for bandwidth management and access logging
# reasons.
#
# NOTE: pipelining requires persistent connections to clients.
#
# WARNING: pipelining breaks NTLM and Negotiate/Kerberos authentication.
#Default:
# Do not pre-parse pipelined requests.
# TAG: high_response_time_warning (msec)
# If the one-minute median response time exceeds this value,
# Squid prints a WARNING with debug level 0 to get the
# administrators attention. The value is in milliseconds.
#Default:
# disabled.
# TAG: high_page_fault_warning
# If the one-minute average page fault rate exceeds this
# value, Squid prints a WARNING with debug level 0 to get
# the administrators attention. The value is in page faults
# per second.
#Default:
# disabled.
# TAG: high_memory_warning
# Note: This option is only available if Squid is rebuilt with the
# GNU Malloc with mstats()
#
# If the memory usage (as determined by gnumalloc, if available and used)
# exceeds this amount, Squid prints a WARNING with debug level 0 to get
# the administrators attention.
#Default:
# disabled.
# TAG: sleep_after_fork (microseconds)
# When this is set to a non-zero value, the main Squid process
# sleeps the specified number of microseconds after a fork()
# system call. This sleep may help the situation where your
# system reports fork() failures due to lack of (virtual)
# memory. Note, however, if you have a lot of child
# processes, these sleep delays will add up and your
# Squid will not service requests for some amount of time
# until all the child processes have been started.
# On Windows value less then 1000 (1 milliseconds) are
# rounded to 1000.
#Default:
# sleep_after_fork 0
# TAG: windows_ipaddrchangemonitor on|off
# Note: This option is only available if Squid is rebuilt with the
# MS Windows
#
# On Windows Squid by default will monitor IP address changes and will
# reconfigure itself after any detected event. This is very useful for
# proxies connected to internet with dial-up interfaces.
# In some cases (a Proxy server acting as VPN gateway is one) it could be
# desiderable to disable this behaviour setting this to 'off'.
# Note: after changing this, Squid service must be restarted.
#Default:
# windows_ipaddrchangemonitor on
# TAG: eui_lookup
# Whether to lookup the EUI or MAC address of a connected client.
#Default:
# eui_lookup on
# TAG: max_filedescriptors
# Set the maximum number of filedescriptors, either below the
# operating system default or up to the hard limit.
#
# Remove from squid.conf to inherit the current ulimit soft
# limit setting.
#
# Note: Changing this requires a restart of Squid. Also
# not all I/O types supports large values (eg on Windows).
#Default:
# Use operating system soft limit set by ulimit.
# TAG: force_request_body_continuation
# This option controls how Squid handles data upload requests from HTTP
# and FTP agents that require a "Please Continue" control message response
# to actually send the request body to Squid. It is mostly useful in
# adaptation environments.
#
# When Squid receives an HTTP request with an "Expect: 100-continue"
# header or an FTP upload command (e.g., STOR), Squid normally sends the
# request headers or FTP command information to an adaptation service (or
# peer) and waits for a response. Most adaptation services (and some
# broken peers) may not respond to Squid at that stage because they may
# decide to wait for the HTTP request body or FTP data transfer. However,
# that request body or data transfer may never come because Squid has not
# responded with the HTTP 100 or FTP 150 (Please Continue) control message
# to the request sender yet!
#
# An allow match tells Squid to respond with the HTTP 100 or FTP 150
# (Please Continue) control message on its own, before forwarding the
# request to an adaptation service or peer. Such a response usually forces
# the request sender to proceed with sending the body. A deny match tells
# Squid to delay that control response until the origin server confirms
# that the request body is needed. Delaying is the default behavior.
#Default:
# Deny, unless rules exist in squid.conf.
# TAG: http_upgrade_request_protocols
# Controls client-initiated and server-confirmed switching from HTTP to
# another protocol (or to several protocols) using HTTP Upgrade mechanism
# defined in RFC 7230 Section 6.7. Squid itself does not understand the
# protocols being upgraded to and participates in the upgraded
# communication only as a dumb TCP proxy. Admins should not allow
# upgrading to protocols that require a more meaningful proxy
# participation.
#
# Usage: http_upgrade_request_protocols <protocol> allow|deny [!]acl ...
#
# The required "protocol" parameter is either an all-caps word OTHER or an
# explicit protocol name (e.g. "WebSocket") optionally followed by a slash
# and a version token (e.g. "HTTP/3"). Explicit protocol names and
# versions are case sensitive.
#
# When an HTTP client sends an Upgrade request header, Squid iterates over
# the client-offered protocols and, for each protocol P (with an optional
# version V), evaluates the first non-empty set of
# http_upgrade_request_protocols rules (if any) from the following list:
#
# * All rules with an explicit protocol name equal to P.
# * All rules that use OTHER instead of a protocol name.
#
# In other words, rules using OTHER are considered for protocol P if and
# only if there are no rules mentioning P by name.
#
# If both of the above sets are empty, then Squid removes protocol P from
# the Upgrade offer.
#
# If the client sent a versioned protocol offer P/X, then explicit rules
# referring to the same-name but different-version protocol P/Y are
# declared inapplicable. Inapplicable rules are not evaluated (i.e. are
# ignored). However, inapplicable rules still belong to the first set of
# rules for P.
#
# Within the applicable rule subset, individual rules are evaluated in
# their configuration order. If all ACLs of an applicable "allow" rule
# match, then the protocol offered by the client is forwarded to the next
# hop as is. If all ACLs of an applicable "deny" rule match, then the
# offer is dropped. If no applicable rules have matching ACLs, then the
# offer is also dropped. The first matching rule also ends rules
# evaluation for the offered protocol.
#
# If all client-offered protocols are removed, then Squid forwards the
# client request without the Upgrade header. Squid never sends an empty
# Upgrade request header.
#
# An Upgrade request header with a value violating HTTP syntax is dropped
# and ignored without an attempt to use extractable individual protocol
# offers.
#
# Upon receiving an HTTP 101 (Switching Protocols) control message, Squid
# checks that the server listed at least one protocol name and sent a
# Connection:upgrade response header. Squid does not understand individual
# protocol naming and versioning concepts enough to implement stricter
# checks, but an admin can restrict HTTP 101 (Switching Protocols)
# responses further using http_reply_access. Responses denied by
# http_reply_access rules and responses flagged by the internal Upgrade
# checks result in HTTP 502 (Bad Gateway) ERR_INVALID_RESP errors and
# Squid-to-server connection closures.
#
# If Squid sends an Upgrade request header, and the next hop (e.g., the
# origin server) responds with an acceptable HTTP 101 (Switching
# Protocols), then Squid forwards that message to the client and becomes
# a TCP tunnel.
#
# The presence of an Upgrade request header alone does not preclude cache
# lookups. In other words, an Upgrade request might be satisfied from the
# cache, using regular HTTP caching rules.
#
# This clause only supports fast acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#
# Each of the following groups of configuration lines represents a
# separate configuration example:
#
# # never upgrade to protocol Foo; all others are OK
# http_upgrade_request_protocols Foo deny all
# http_upgrade_request_protocols OTHER allow all
#
# # only allow upgrades to protocol Bar (except for its first version)
# http_upgrade_request_protocols Bar/1 deny all
# http_upgrade_request_protocols Bar allow all
# http_upgrade_request_protocols OTHER deny all # this rule is optional
#
# # only allow upgrades to protocol Baz, and only if Baz is the only offer
# acl UpgradeHeaderHasMultipleOffers ...
# http_upgrade_request_protocols Baz deny UpgradeHeaderHasMultipleOffers
# http_upgrade_request_protocols Baz allow all
#Default:
# Upgrade header dropped, effectively blocking an upgrade attempt.
# TAG: server_pconn_for_nonretriable
# This option provides fine-grained control over persistent connection
# reuse when forwarding HTTP requests that Squid cannot retry. It is useful
# in environments where opening new connections is very expensive
# (e.g., all connections are secured with TLS with complex client and server
# certificate validation) and race conditions associated with persistent
# connections are very rare and/or only cause minor problems.
#
# HTTP prohibits retrying unsafe and non-idempotent requests (e.g., POST).
# Squid limitations also prohibit retrying all requests with bodies (e.g., PUT).
# By default, when forwarding such "risky" requests, Squid opens a new
# connection to the server or cache_peer, even if there is an idle persistent
# connection available. When Squid is configured to risk sending a non-retriable
# request on a previously used persistent connection, and the server closes
# the connection before seeing that risky request, the user gets an error response
# from Squid. In most cases, that error response will be HTTP 502 (Bad Gateway)
# with ERR_ZERO_SIZE_OBJECT or ERR_WRITE_ERROR (peer connection reset) error detail.
#
# If an allow rule matches, Squid reuses an available idle persistent connection
# (if any) for the request that Squid cannot retry. If a deny rule matches, then
# Squid opens a new connection for the request that Squid cannot retry.
#
# This option does not affect requests that Squid can retry. They will reuse idle
# persistent connections (if any).
#
# This clause only supports fast acl types.
# See http://wiki.squid-cache.org/SquidFaq/SquidAcl for details.
#
# Example:
# acl SpeedIsWorthTheRisk method POST
# server_pconn_for_nonretriable allow SpeedIsWorthTheRisk
#Default:
# Open new connections for forwarding requests Squid cannot retry safely.
# TAG: happy_eyeballs_connect_timeout (msec)
# This Happy Eyeballs (RFC 8305) tuning directive specifies the minimum
# delay between opening a primary to-server connection and opening a
# spare to-server connection for the same master transaction. This delay
# is similar to the Connection Attempt Delay in RFC 8305, but it is only
# applied to the first spare connection attempt. Subsequent spare
# connection attempts use happy_eyeballs_connect_gap, and primary
# connection attempts are not artificially delayed at all.
#
# Terminology: The "primary" and "spare" designations are determined by
# the order of DNS answers received by Squid: If Squid DNS AAAA query
# was answered first, then primary connections are connections to IPv6
# peer addresses (while spare connections use IPv4 addresses).
# Similarly, if Squid DNS A query was answered first, then primary
# connections are connections to IPv4 peer addresses (while spare
# connections use IPv6 addresses).
#
# Shorter happy_eyeballs_connect_timeout values reduce master
# transaction response time, potentially improving user-perceived
# response times (i.e., making user eyeballs happier). Longer delays
# reduce both concurrent connection level and server bombardment with
# connection requests, potentially improving overall Squid performance
# and reducing the chance of being blocked by servers for opening too
# many unused connections.
#
# RFC 8305 prohibits happy_eyeballs_connect_timeout values smaller than
# 10 (milliseconds) to "avoid congestion collapse in the presence of
# high packet-loss rates".
#
# The following Happy Eyeballs directives place additional connection
# opening restrictions: happy_eyeballs_connect_gap and
# happy_eyeballs_connect_limit.
#Default:
# happy_eyeballs_connect_timeout 250
# TAG: happy_eyeballs_connect_gap (msec)
# This Happy Eyeballs (RFC 8305) tuning directive specifies the
# minimum delay between opening spare to-server connections (to any
# server; i.e. across all concurrent master transactions in a Squid
# instance). Each SMP worker currently multiplies the configured gap
# by the total number of workers so that the combined spare connection
# opening rate of a Squid instance obeys the configured limit. The
# workers do not coordinate connection openings yet; a micro burst
# of spare connection openings may violate the configured gap.
#
# This directive has similar trade-offs as
# happy_eyeballs_connect_timeout, but its focus is on limiting traffic
# amplification effects for Squid as a whole, while
# happy_eyeballs_connect_timeout works on an individual master
# transaction level.
#
# The following Happy Eyeballs directives place additional connection
# opening restrictions: happy_eyeballs_connect_timeout and
# happy_eyeballs_connect_limit. See the former for related terminology.
#Default:
# no artificial delays between spare attempts
# TAG: happy_eyeballs_connect_limit
# This Happy Eyeballs (RFC 8305) tuning directive specifies the
# maximum number of spare to-server connections (to any server; i.e.
# across all concurrent master transactions in a Squid instance).
# Each SMP worker gets an equal share of the total limit. However,
# the workers do not share the actual connection counts yet, so one
# (busier) worker cannot "borrow" spare connection slots from another
# (less loaded) worker.
#
# Setting this limit to zero disables concurrent use of primary and
# spare TCP connections: Spare connection attempts are made only after
# all primary attempts fail. However, Squid would still use the
# DNS-related optimizations of the Happy Eyeballs approach.
#
# This directive has similar trade-offs as happy_eyeballs_connect_gap,
# but its focus is on limiting Squid overheads, while
# happy_eyeballs_connect_gap focuses on the origin server and peer
# overheads.
#
# The following Happy Eyeballs directives place additional connection
# opening restrictions: happy_eyeballs_connect_timeout and
# happy_eyeballs_connect_gap. See the former for related terminology.
#Default:
# no artificial limit on the number of concurrent spare attemptssystemctl squid startWebmin 설치
Webmin은 Squid를 관리하기 위한 웹 기반 인터페이스입니다. Webmin을 설치하기 위해 아래 명령을 실행합니다.
sudo vim /etc/apt/sources.list편집기에서 sources.list 파일을 열고 다음 줄을 파일의 맨 아래에 추가합니다
deb http://download.webmin.com/download/repository sarge contrib저장하고 에디터를 닫은 후 아래 명령을 실행하여 Webmin의 GPG 키를 추가합니다
wget http://www.webmin.com/jcameron-key.ascsudo apt-key add jcameron-key.asc패키지 목록을 업데이트하고 Webmin을 설치합니다
sudo apt-get updatesudo apt-get install -y webmin728x90
Webmin 액세스
- 계정 패스워드 정보
- 계정 : root
- 패스워드 : root 패스워드
https://your_server_ip:10000
Dashboard
Squid Proxy Server
squid 구성 파일 설정
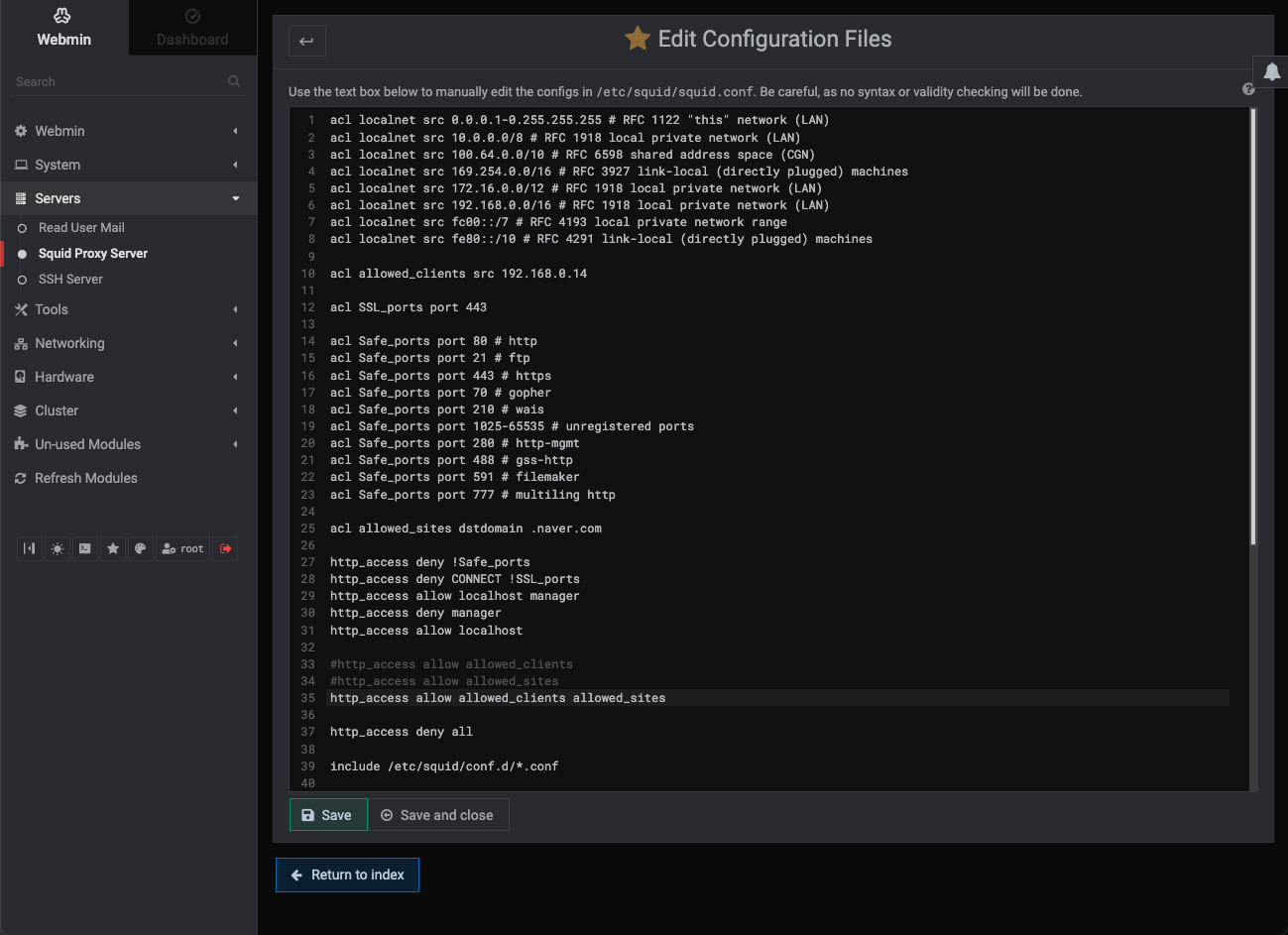
acl localnet src 0.0.0.1-0.255.255.255 # RFC 1122 "this" network (LAN)
acl localnet src 10.0.0.0/8 # RFC 1918 local private network (LAN)
acl localnet src 100.64.0.0/10 # RFC 6598 shared address space (CGN)
acl localnet src 169.254.0.0/16 # RFC 3927 link-local (directly plugged) machines
acl localnet src 172.16.0.0/12 # RFC 1918 local private network (LAN)
acl localnet src 192.168.0.0/16 # RFC 1918 local private network (LAN)
acl localnet src fc00::/7 # RFC 4193 local private network range
acl localnet src fe80::/10 # RFC 4291 link-local (directly plugged) machines
acl allowed_clients src 192.168.0.14
acl SSL_ports port 443
acl Safe_ports port 80 # http
acl Safe_ports port 21 # ftp
acl Safe_ports port 443 # https
acl Safe_ports port 70 # gopher
acl Safe_ports port 210 # wais
acl Safe_ports port 1025-65535 # unregistered ports
acl Safe_ports port 280 # http-mgmt
acl Safe_ports port 488 # gss-http
acl Safe_ports port 591 # filemaker
acl Safe_ports port 777 # multiling http
acl allowed_sites dstdomain .naver.com
http_access deny !Safe_ports
http_access deny CONNECT !SSL_ports
http_access allow localhost manager
http_access deny manager
http_access allow localhost
#http_access allow allowed_clients
#http_access allow allowed_sites
http_access allow allowed_clients allowed_sites
http_access deny all
include /etc/squid/conf.d/*.conf
http_port 3128
cache_dir ufs /var/spool/squid 100 16 256
access_log daemon:/var/log/squid/access.log squid
logfile_rotate 7
coredump_dir /var/spool/squid
refresh_pattern ^ftp: 1440 20% 10080
refresh_pattern ^gopher: 1440 0% 1440
refresh_pattern -i (/cgi-bin/|\?) 0 0% 0
refresh_pattern \/(Packages|Sources)(|\.bz2|\.gz|\.xz)$ 0 0% 0 refresh-ims
refresh_pattern \/Release(|\.gpg)$ 0 0% 0 refresh-ims
refresh_pattern \/InRelease$ 0 0% 0 refresh-ims
refresh_pattern \/(Translation-.*)(|\.bz2|\.gz|\.xz)$ 0 0% 0 refresh-ims
refresh_pattern . 0 20% 4320
cache_effective_user proxy
cache_effective_group proxy
squid 구성 파일 검사
- /etc/squid/squid.conf
sudo squid -k parse
728x90
'리눅스' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 리눅스에 프록시를 지정하는 방법 (0) | 2023.05.12 |
|---|---|
| Squid를 Docker 컨테이너로 실행하는 방법 (0) | 2023.05.12 |
| docker proxy 설정하는 방법(환경 변수 구성) (0) | 2023.05.11 |
| nginx와 php-fpm을 사용하는 경우 *.html 파일에서도 PHP 코드를 실행하도록 설정하는 방법 (0) | 2023.05.09 |
| 우분투에서 최신 버전의 ansible을 설치하는 방법 (0) | 2023.05.08 |



